Dermatopathology Flashcards
What are the functions of skin?
- Enveloping barrier
- Protection from environment
- Motion and form
- Appendages
- Regulation of temperature
- Storage unit
- Indicator
- Immune regulation
- Pigmentation
- Defense against microorganisms
- Sensory function
- Secretion and excretion
- Metabolism (Vit. D3 synthesis)
- Blood pressure
What are the layers of the epidermis?
- Stratum corneum- keratinized cell layer
- Stratum lucidum- translucent cell layer
- Stratum granulosum- granular cell layer
- Stratum spinosum- prickle cell layer
- Stratum basale- basal cell layer
What are the cell types of the epidermis?
- Keratinocytes
- Melanocytes
- Langerhans cells
- Merkel cells
- Mast cells
What are intercellular adhesions between keratinocytes?
Desmosomes (“adherens junctions”)
What are adhesions from keratinocytes to the basement membrane?
- Hemidesmosomes
- Focal adhesions
What comprises the dermo-epidermal junction?
- Lamina lucida (bullous pemphigoid antigen, laminin, proteoglycan)
- Lamina densa (type IV collagen)
- Sub-lamina densa zone (type I, III, VII collagen)

What makes up the dermis?
- Collagen fibers
- Fibroblasts
- Dermal dendrocytes
- Melanocytes
- Mast cells
What makes up the subcutis/hypodermis/panniculus?
- Adipocytes
- Skeletal muscle cells
- Endotheliocytes
- Smooth muscle cells
- Nerves/ganglia
What makes up the adnexa of skin?
- Hair follicles
- Arrector pili muscles
- Sebaceous glands
- Apocrine sweat glands
- Eccrine sweat glands
What are the phases of the hair cycle?
- Telogen
- Eary anagen
- Anagen
- Anagen
- Early catagen
- Catagen

What are the blood and lymph plexuses of the skin?
- Superficial (subpapillary)
- Middle (mid-dermal)
- Deep (subcutaneous)
What are some challenges associated with skin diseases?
- Diverse problems with similar clinical presentation
- Conditions producing multiple patterns
- Stereotypical response of chronic skin conditions
- Pruritic conditions with secondary (self-inflicted) lesions
- Misunderstanding (representing) control for cure
- Frustrated owners
- Need for a bigger team (owner, practitioner, pathologist, microbiologist)
Describe this lesion.

Fluid-filled vesicle/cyst over the level of the surface of the skin
Describe this lesion.

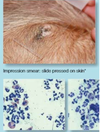
Pustules, raised over the surface of the skin
Describe this lesion.

Solid, raised growth; papule (notice the hairs)
Describe this lesion.

Nodule; histiocytoma
Describe this lesion.

Hyperpigmentation within the level of the skin
Describe this lesion from a horse.

Indentation; ulcer
Describe this lesion.

Crust
Describe this lesion.

Dry; fissures
Describe this lesion.

Loss of hair, hyperpigmentation
Describe this lesion.

Sharp demarcation, hemorrhage, scab, ulcer
What is the difference between a primary lesion and a secondary lesion?
- Primary lesion- direct result of injury
- Secondary lesion- develop from primary lesions over time due to healing, traumatization, secondary infection, treatment…
This primary lesions is flat, has (dis) coloration, and is
Macule (color change within skin)