Dermatology Flashcards
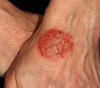
What is this rash?
Erythema multiforme
What is Erythema Multiforme?
hypersensitivity reaction which is most commonly triggered by infections. It may be divided into minor and major forms.
Features of Erythema Multiforme
- target lesions
- initially seen on the back of the hands / feet before spreading to the torso
- upper limbs are more commonly affected than the lower limbs
- pruritus is occasionally seen and is usually mild
causes of Erythema Multiforme
- viruses: herpes simplex virus (the most common cause), Orf*
- idiopathic
- bacteria: Mycoplasma, Streptococcus
- drugs: penicillin, sulphonamides, carbamazepine, allopurinol, NSAIDs, oral contraceptive pill, nevirapine
- connective tissue disease e.g. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- sarcoidosis
- malignancy
*Orf is a skin disease of sheep and goats caused by a parapox virus
What is this rash?

Dermatitis herpetiformis
What is dermatitis herpetiformis?
Dermatitis herpetiformis is an autoimmune blistering skin disorder associated with coeliac disease.
blistering disease with granular IgA deposition in dermis
dermatitis herpetiformis
What is dapsone?
Dermatitis herpetiformis management
- gluten-free diet
- dapsone
- rash on hands and feet
- nickel allergy
- small blisters intensely itchy
Pompholyx is a type of eczema which affects both the hands (cheiropompholyx) and the feet (pedopompholyx). It is also known as dyshidrotic eczema.
Pompholyx features
Pompholyx management
- cool compresses
- emollients
- topical steroids
A 23-year-old woman who is 10 weeks pregnant presents with a rapidly growing lesion on her finger. This has grown from the size of a ‘pin-prick’ when it first appeared 4 weeks ago.
Pyogenic granuloma
what are pyogenic granulomas?
relatively common benign skin lesion. The name is confusing as they are neither true granulomas nor pyogenic in nature. There are multiple alternative names but perhaps ‘eruptive haemangioma’ is the most useful.
pyogenic granulomas cause
- trauma
- pregnancy
- more common in women and young adults
pyogenic granulomas features
- most common sites are head/neck, upper trunk and hands. Lesions in the oral mucosa are common in pregnancy
- initially small red/brown spot
- rapidly progress within days to weeks forming raised, red/brown lesions which are often spherical in shape
- the lesions may bleed profusely or ulcerate
pyogenic granuloma management
- lesions associated with pregnancy often resolve spontaneously post-partum
- other lesions usually persist. Removal methods include curettage and cauterisation, cryotherapy, excision
Dandruff, itchy scalp
Psoriasis
Chronic plaque psoriasis general management
- regular emollients may help to reduce scale loss and reduce pruritus
- first-line: NICE recommend:
- a potent corticosteroid applied once daily plus vitamin D analogue applied once daily
- should be applied separately, one in the morning and the other in the evening)
- for up to 4 weeks as initial treatment
- second-line: if no improvement after 8 weeks then offer:
- a vitamin D analogue twice daily
- third-line: if no improvement after 8-12 weeks then offer either:
- a potent corticosteroid applied twice daily for up to 4 weeks, or
- a coal tar preparation applied once or twice daily
- short-acting dithranol can also be used
scalp psoriasis management
potent topical corticosteroids used once daily for 4 weeks
if no improvement after 4 weeks then either use a different formulation of the potent corticosteroid (for example, a shampoo or mousse) and/or a topical agents to remove adherent scale (for example, agents containing salicylic acid, emollients and oils) before application of the potent corticosteroid
Face, flexural and genital psoriasis management
NICE recommend offering a mild or moderate potency corticosteroid applied once or twice daily for a maximum of 2 weeks
how do vitamin D analogues work in psoriasis?
- examples of vitamin D analogues include calcipotriol (Dovonex), calcitriol and tacalcitol
- they work by ↓ cell division and differentiation → ↓ epidermal proliferation
- adverse effects are uncommon
- unlike corticosteroids they may be used long-term
- unlike coal tar and dithranol they do not smell or stain
- they tend to reduce the scale and thickness of plaques but not the erythema
- they should be avoided in pregnancy
- the maximum weekly amount for adults is 100g
how does Dithranol work?
- inhibits DNA synthesis
- wash off after 30 mins
- adverse effects include burning, staining
lesion that dimples on pinch test
Dermatofibroma
what is a dermatofibroma?
(also known as histiocytomas) are common benign fibrous skin lesions. They are caused by the abnormal growth of dermal dendritic histiocyte cells, often following a precipitating injury. Common areas include the arms and legs.
prognostic markers in eczema
- onset at age 3-6 months
- severe disease in childhood
- associated asthma or hay fever
- small family size
- high IgE serum levels
eczema management
- emollients
- topical steroids
- UV radiation
- immunosuppressants: e.g. ciclosporin, antihistamines and azathioprine