Dermatology Flashcards
How do you describe a skin lesion?
Start with whether it is raised (papule, plaque, nodule, vesicle, pustule), flat (macule, patch), or lowered (erosion, ulcer).
Then describe the size, shape, color, texture, configuration and distribution.
What is the diagnosis?

Moderate comedonal acne without evidence of scarring
What is the diagnosis?

Severe nodulocystic acne
What are 4 causative factors for acne?
Androgens, bacteria in the follicle, follicular plugging, sebum secretion
What is the first-line treatment for moderate nodular acne without scarring?
Topical benzoyl peroxide OR topical retinoid + tetracycline / doxycycline or minocycline
What is appropriate treatment for severe nodular acne or acne with scarring and keloids?
Referral to dermatologist for isotretinoin
What are common side effects of isotretinoin?
Xerosis, cheilitis, elevated liver enzymes, hypertriglyceridemia.
Monitor for mood changes and depression in individuals with severe acne
How would you treat hormonal acne?
Spironolactone / OCP
Describe the lesion. What is the diagnosis?

Facial erythema with papules and pustules on the nose and cheeks; scattered papules and pustules on forehead and chin.
Rosacea
What should you always ask patients with rosacea?
If they have ocular symptoms ; refer to opthalmology
What is the diagnosis?

Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea
What is the diagnosis?

Phymatous rosacea
How do you treat rosacea?
Avoid triggers (things that make you flush)
Use sunscreen
Add oral antibiotic if there are papules or pustules
Offer laser or bromidine for telangiectasias and erythema
Counsel the patient that it is not curable.
What is the diagnosis?

SCC
What must you do to diagnose SCC?
Shave biopsy
What are risk factors for SCC?
Fair skin, sun exposure, if in non-sun exposed area consider HPV, arsenic or smoking.
How do you manage SCC?
Excision, can use radiation or 5-FU cream if in situ or poor surgical candidate.
What is the diagnosis?

Actinic Keratosis. Can occur on lips; it’s a thick scaly plaque that feels like sandpaper.
What is the diagnosis?

BCC
Do you treat AK?
Yes, because it is precancerous. Use liquid nitrogen cryotherapy or 5-FU cream
What is the diagnosis?

Nodular BCC
What are the differences in etiology between BCC and SCC/AK
BCC -> keratinocyte in basal layer of epidermis.
Is the diagnosis and management of SCC and BCC the same?
Yes.
What is the diagnosis?

Ulcerated BCC
What is the diagnosis?

Superficial BCC
What is the diagnosis?

Pigmented BCC
What is the diagnosis?

Morpheaform BCC
What is the diagnosis?

Sebhorreic Keratosis
What is the diagnosis?

Acrochordon
What is the diagnosis?

Cherry angioma
What is the diagnosis?

Dermatofibroma
What is the lesion?

Sebaceous hyperplasia
How do you treat keloids?
Intralesional cortisoid injection q4weeks
What is the diagnosis?

Epidermal inclusion cyst
What is the diagnosis?

Milia
What is the diagnosis?

lipoma
Should you use cryotherapy for benign lesions in darker skin?
No, electrodessication is preferred because melanocytes are very sensative to cold.
What is the atopic triad?
Asthma, atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis
What is the classic symptom of atopic dermatitis?
Rash that itches. Often accompanied by xerosis.
How does the distribution of atopic dermatitis change with age?
Infants -> cheeks, forhead, scalp and extensor surfaces
Older children, teens -> lichenified eczematous plaques, flexural areas
Adults: similar to older adults, may involve hands, wrists, ankles feet and face.
How do you treat atopic dermatitis?
Gentle skin care
Lots of moisturizers
Topical anti inflammatory
Anti-pruritius (antihistamine)
Antibiotic if existing skin infection
What is the diagnosis?

Pityriasis alba
How do you estimate body surface area.
1 patient’s palm = 1% body surface area
How do you calculate how many grams to give?
1 fingertip unit, 500mg = 2% BSA.
So multiply by BSA, frequency, days.
How many grams do you give to cover an adult (1 application)
30g
What is the diagnosis?

Tinea pedis
Name the 4 types of tinea pedis
Moccasin (may also be 1 hand, 2 feet)
Vesicobullus
Interdigital
Vesicular
How do you diagnose tinea?
KOH; parallel walls, septated and branching hyphae
How would you treat tinea?
Terbinafine cream BID, 4 weeks
What is the diagnosis?

tinea corporis — typcal would be a “ringworm” with central clearing
What is tinea cruris?
Jock itch, tinea in groin.
When would topical antifungals be required?
Poor response to topical agensts, animal is the suspected source of infection, large surface area. Give terbinafine 7-14 days once daily.
What is the diagnosis? What is the next step?

onychomycosis; get a fungal culture of subungual debris.
How do you treat onychomycosis?
Oral terbinafine (but must confirm susceptibility of organism first) for 12 weeks.
Must monitor liver function, may have taste disturbance, skin reactions, drug interactions.
What is the diagnosis?

Melanoma.
What are the risk factors for melanoma?
Age, fair skin, blue eyes, blond hair, freckles
Lots of nevi, atypical nevi
Immunosuppression
Personal or family history of melanoma
UV exposure (esp before puberity, tanning booths)
Genetic syndroms
What is the diagnosis?

Superficial spreading melanoma
What is the diagnosis?

Nodular melanoma
What is the diagnosis?

Lentigo maligna melanoma
What is the diagnosis?

Acral lentiginous melanoma
What is the diagnosis?

amelanoic melanoma
What is the next step if you suspect melanoma?
Biopsy the lesion and do a total body skin exam
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma?
Asymmetry
Border
Colour
Diameter (>pencil eraser)
Evolving
What are some sun safety tips for patients?
Use SPF30 or more to all exposed skin with broad spectrum protection
Cover up or seek shade
Watch out near snow, water and sand
Don’t tan for vitamin D
Avoid tanning beds
Check your skin regularly (every month).
What is the prevalence of psoriasis? What is the typical age of onset?
2$
Camel distribution (20-30 / 50-60)
What is the diagnosis? What often precedes flares?

guttate psoriasis; strep pharyngitis
What is the diagnosis?

Flexural (inverse) psoriasis
What is the diagnosis? What must you do if this is generalized?

Pustular psoriasis; hospitalization and derm consult.
What is the diagnosis?

palmoplantar psoriasis
What is the diagnosis?

plaque psoriasis
What are 4 key relevant questions for the psoriasis history?
Any family history? (1/3 of patients have positive FHx)
Medication history (esp. corticosteroid withdrawal, beta blockers, lithium, anti-malarias, interferon)
PMH (also ask about arthritis, cardiac disease, infections)
Social Hx (smoking, alcohol and obesity are risk factors)
What are key areas for plaque psoriasis?
scalp, ears, elbows/knees (extensor surfaces), umbilicus, gluteal cleft, nail, recent injury/trauma
What is the first line treatment for localized psoriasis?
High-potency topical steroid
What is the diagnosis?

Psoriatic onychodystrophy (nail psoriasis)
What is the diagnosis?

Psoriatic arthritis
What are some alternatives to steroids for topical treatment of psoriasis?
calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolismus), calcipotriene, salicylic acid, tar
For systemic treatment of psoriasis what is the appropriate agent?
Phototherapy
Immunosuppression w Methotrexate / cyclosporine
Biologics e.g. TNF-alpha inhibitors (infliximab, etanercept, adalumimab) or an IL 12/23 blocker (ustekinumab)
Should you use a systemic steroid to treat psoriasis?
No, because while it may be effective in the short term, steroid withdrawal often causes worsening flare-up of the psoriasis.
What is the diagnosis and the most likely causative organism?
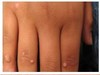
Verruca vulgaris; human papillomavirus.
What is the first line treatment for warts?
Cryotherapy or salicylic acid
What is the preferred treatment for warts on the face?
topical tretinoin
What is the diagnosis? What is the most likely infection?

genital warts; HPV-6 or HPV-11 (but may also be accompanied by HPV 16/18 which leads to cervical cancer)
What treatment options are available for genital warts?
Cryotherapy
Topical imiquimod
Topical podophyllin


