Dermatology Flashcards
What specific Lipid are Xanthomas associated with?
TGL Note: NOT associated with familial hyperlipidemia
What is the most likely dx and how do you confirm?
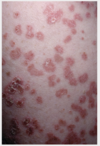
Tinea
Dx: KOH preparation
What is calcipotriene?
vitamin D analog used to treat psoriasis because it inhibits keratinocyte proliferation
What is the treatment for extensive psoriasis?
Narrowband ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy has become the standard form of phototherapy used in the initial treatment of psoriasis. T
This wavelength of light is not absorbed by DNA. The theory is that if the light is not absorbed by DNA, less skin damage will occur, and there will be far fewer skin cancers as a side effect of the therapy.
What is the treatment for severe poison ivy?
Severe allergic contact eruptions such as those from poison ivy may necessitate a 2- to 3-week taper of systemic glucocorticoids; because of the risk of rebound dermatitis, shorter courses are not recommended.
What is considered severe psoriasis? What is the tx?
severe psoriasis:
- 30% or more body surface area involvement
- Or 10% with psoriatic arthritis, recalcitrant palmoplantar psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, or psoriasis in challenging anatomic areas (groin, scalp)
Tx: Systemic therapy
- TNF-a inhibitors
- MTX
- IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors
- Phototherapy
What is this?

INVERSE Psoriasis
NOT Tinea
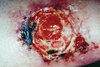
44F is evaluated for painful nodules, ulcers, and skin changes on the lower legs of 2 years’ duration. She takes no medications.
VSS. Tender subcutaneous nodules, stellate ulcerations, and livido reticularis are evenly distributed bilaterally over her lower legs. The dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are normal. There are no varicosities present on the legs. The remainder of the examination is normal.
ESR is high
Skin biopsy shows vasculitis of a mid-sized arteriole in the subcutis.
ANCA negative
ANA 1:40
C3 and C4 are wnl
RF negative
Stool is negative for occult blood, and urinalysis is unremarkable.
What is this?
Polyarteritis Nodosum, cutaneous only
- medium-vessel vasculitis
- ANCA negative
- The skin may be the only organ involved (cutaneous-only PAN)
Note: Patients with cutaneous-only polyarteritis nodosa experience tender subcutaneous nodules from vascular inflammation, stellate erosions, or ulcerations from ischemia in the watershed of the affected vessels, and may develop livedo reticularis or livedoid purpura.
When do you do a skin biopsy for urticaria?
When you are concerned about urticarial vasculitis, when lesions last >24h
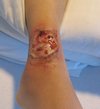
What is this?
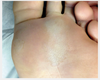
Pitted keratolysis is a superficial bacterial infection characterized by small pits and punctate erosions primarily on the plantar aspects of the feet; risk factors include increased perspiration (hyperhidrosis) and prolonged occlusion of the feet.
When do you use topical retinoids v topical antibiotics in the treatment of acne?
Topical Retinoids: Comedomes
Topical abx: When there is evidence of inflammation with pustules and inflammatory papule
What is this?

Melanonychia is a longitudinal brown pigmentation of the nail plate; it can be a normal variant in persons with darker skin types, but it may also occur as a result of systemic disease, medication, infection, or an underlying melanocytic lesion.
23F with a cold sore on her lip 4d ago. Now has this. VSS. The arms and face have lesions similar to those on the palm. There is no sloughing of the skin when shearing force is applied. The lesions affect about 7% body surface area. There is no corneal injection or tearing and no genital erosion or ulceration.
What is this?

Erythema multiforme (EM) features the development of characteristic tricolored targetoid plaques, as this patient demonstrates on the extremities and face. In EM major, these targetoid plaques are accompanied by mucous membrane involvement. The most common cause of EM is infection, and herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 are the most commonly recognized, followed by Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Note: SJS and TEN don’t have the exact tricolor lesions
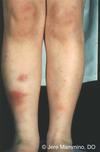
What are these “bruises” on an elderly patient?

Actinic Purpura
Note: It is caused by age-related capillary fragility and bleeding under atrophic skin; minor trauma can cause impressive purpuric macules and patches, most commonly on the forearm.
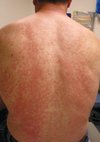
52F presents with this rash with increasing redness, scaling, and itchiness of the skin. Over the last 2 days, it has expanded to cover most of her body. She complains of being cold and shivering. Her skin is flaking so badly she is embarrassed to go out in public. Medical history is significant for psoriasis since childhood and COPD for 5 years. She was treated for a COPD exacerbation last week with 5 days of 40-mg prednisone therapy.
What is this? What is the cause?

Erythroderma (redness over >80% of body surface area)
Prednisone-induced flare of her underlying psoriasis
What are achrocordons?
Skin tags