Dermatology Flashcards
6 functions of skin
protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, regulation, sensation
6 morphological things to describe
- palpability (indicated by shadow)
- Color
- Shape
- Texture
- Size
- Location
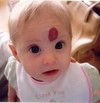
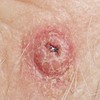
circumscribed; non-palpable discoloration of the skin; less than 1 cm

Macule
Primary lesion
ex: freckles and rubella
non palpable discoloration; irregular border; greater than 1 cm

Patch
Primary lesion
ex: vitiligo
well-circumscribed; solid lesion; flat topped, plateau-like; greater than 1 cm
In Epidermis

Plaque
Primary lesion
ex: psoriasis, discoid lupus, erythematosus
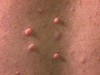
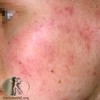
solid elevation; less than 1 cm

Papule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, warts, insect bites
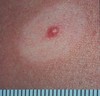
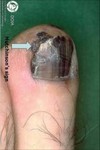
solid, palpable; circumscribed lesion; larger than a papule (> 1 cm)
smaller than a tumor; originates in dermal or subcutaneous tissue

Nodule
Primary lesion
ex: erythema nodosum, gouty tophi
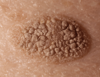
solid, palpable, circumscribed lesion
> 2 cm
can be above, level or beneath skin surface
Tumor
Primary lesion
ex: lipoma
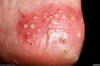
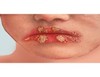
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid-filled lesion
contains serous fluid
less than 0.5 cm

Vesicle
Primary lesion
ex: herpes simplex, varicella (chickenpox)
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid filled lesion
> 0.5 cm
Epidermis
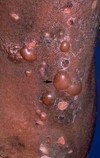
Bulla (blister)
Primary lesion
ex: bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis
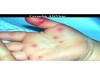
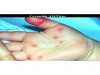
a vesicle filled with PURULENT fluid small, circumscribed

Pustule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, impetigo
slightly raised, red, irregular, transient lesions,
secondary to edema of the skin
erythematous borders with pale centers epidermis

Wheal
Primary lesion
ex: urticarial (hives), allergic rxn to injections or insect bites
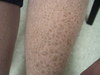
flat, non-blanching, red-purple lesions; caused by a hemorrhage to the skin
2 non-palpable types

Purpura
Primary lesion
- Petechia: less than 5 mm
- Ecchymosis (bruise): greater than 5 mm
SECONDARY LESION
visible shedding of stratum corneum
epidermal origin

Scale
ex: often seen with psoriasis
SECONDARY LESION
slightly raised; irregular border; variable color
resulting from dried blood, serum or other exudate
epidermis origin
Crust
ex: scab
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion; resulting from loss of epidermis due to rupture of vesicles or bullae; often caused by friction or pressure
heals WITHOUT scar confined to epidermis

Erosion
ex: rupture of herpes simplex blister
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion resulting from loss epidermis and part of dermis
HEALS WITH SCAR irregular size and shape

Ulcer
ex: decubitus ulcers, primary lesion of syphilis
SECONDARY LESION
deep linear lesion into the dermis; wedge-shaped in epidermis with abrupt walls
can extend into dermis

Fissure
ex: cracks in athlete’s foot
SECONDARY LESION
linear superficial lesion, may be covered with dried blood due to scratching of skin
*specific to itching

Excoriation
SECONDARY LESION
Thickening of epidermis, resulting in accentuation of skin lines results from chronic irritation and rubbing

Lichenification
ex: atopic dermatitis
SECONDARY LESION
replacement of normal skin with fibrous tissue; often resulting from injury involved in deeper dermis
Scar
SECONDARY LESION
thinning or depression of the skin surface due to reduction of underlying tissue depression in epidermis

Atrophy
ex: aging, stretch marks
SECONDARY LESION
hardening of the skin caused by an increase in collagen, mucin, edema or cellular infiltration

Sclerosis
SECONDARY LESION
tissue death
Necrosis
Hypertrophic scar

heals above layer of epidermis; confined to edges of wound
Keloidal scar
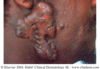
scar tissue goes beyond the edges of original wound
darkened plug of sebum and keratin that occludes the pilosebaceous follicle
some open; some closed

Comedone
ex: blackhead (open)
NODULE; encapsulated containing fluid or semi-fluid substance; fluctuant

Cyst
linear or serpinginous tunnels within the epidermis

Burrow
ex: scabies
small, superficial blood vessels that become visible because they are dilated;
disappear with pressure (blanch)

Telangiectasia
Poikiloderma

combination of: cutaneous pigmentation (hyper- & hypo-), atrophy, and telangiectasia
Distribution
location on the body
Configuration
the lesions are arranged or relate to each other
each lesion is easily separated from others

discrete configuration
edges of the lesions blend into one another
Confluent configuration
Isolated/solitary configuration

one lesion in an area
lesions are discrete; multiple and distributed in no pattern
scattered configuration
lesions are close together WITH normal skin between groups
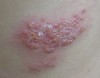
grouped configuration
configuration

linear configuration
configuration

dermatomal
distributed in one spinal nerve or equivalent branch
shape

annular
ring-like shape
shape

polycyclic
shape made up of tangential rings
shape

arcuate
arc/crescent-shaped
shape

serpinginous
shaped like a snake
shape
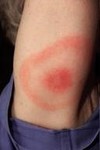
iris/targetoid
shaped like a bulls-eye
net-like pattern

reticulate
shape

glaborous
shiny and smooth surface; bald
Atopic triad
asthma
allergies
atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Instruments for Elliptical excision
Anesthesia, 15 blade, forceps and suture
Instruments for shave/biopsy excision
anesthesia, 11-blade/curved razor, forceps and scissors
Instruments for punch biopsy
Anesthsia, punch, forceps, scissors/scalpel
Instruments for KOH preparation
15-blade, glass slide, 10-20% KOH, +/- petri dish test for fungal infections
Instruments for tzanck smear
11 blade-, glass slide OR herpes culture swab, collecting fluid to see if multinucleated giant cells ; confirms HSV/VZV
Wood’s light: Coral/pink
Erythrasma (corynebacterium)
Wood’s light: Pale blue
Pseudomonas
Wood’s light: Yellow
Microsporum (tinea capitis)
*Fungal infection of scalp
Wood’s light: Green/gold
tinea versicolor
*Fungal infection causing HYPOpigmentation
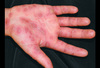
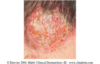
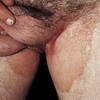
describe this!
Macule
Primary lesion
ex: freckles and rubella
circumscribed; non-palpable discoloration of the skin; less than 1 cm

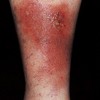
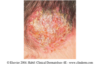
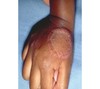
describe this!
Patch
Primary lesion
ex: vitiligo
non palpable discoloration; irregular border; greater than 1 cm
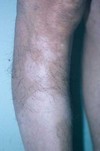
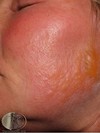
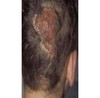
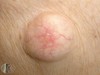
describe this!
Plaque
Primary lesion
ex: psoriasis, discoid lupus, erythematosus
well-circumscribed; solid lesion; flat topped, plateau-like; greater than 1 cm
In Epidermis

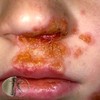
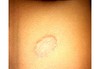
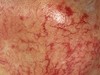
describe this!
Papule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, warts, insect bites
solid elevation; less than 1 cm
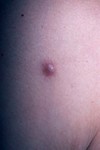
describe this!
Nodule
Primary lesion
ex: erythema nodosum, gouty tophi
solid, palpable; circumscribed lesion; larger than a papule (> 1 cm)
smaller than a tumor; originates in dermal or subcutaneous tissue

describe this!
Tumor
Primary lesion
ex: lipoma
solid, palpable, circumscribed lesion
> 2 cm
can be above, level or beneath skin surface
describe this!
Vesicle
Primary lesion
ex: herpes simplex, varicella (chickenpox)
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid-filled lesion
contains serous fluid
less than 0.5 cm
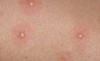
describe this!
Bulla (blister)
Primary lesion
ex: bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid filled lesion
> 0.5 cm
Epidermis

describe this!
Pustule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, impetigo
a vesicle filled with PURULENT fluid small, circumscribed

describe this!
Wheal
Primary lesion
ex: urticarial (hives), allergic rxn to injections or insect bites
slightly raised, red, irregular, transient lesions,
secondary to edema of the skin
erythematous borders with pale centers epidermis

describe this!
Purpura
Primary lesion
- Petechia: less than 5 mm
- Ecchymosis (bruise): greater than 5 mm
flat, non-blanching, red-purple lesions; caused by a hemorrhage to the skin
2 non-palpable types

describe this!
Scale
ex: often seen with psoriasis
SECONDARY LESION
visible shedding of stratum corneum
epidermal origin

describe this!
Crust
ex: scab
SECONDARY LESION
slightly raised; irregular border; variable color
resulting from dried blood, serum or other exudate
epidermis origin
describe this!
Erosion
ex: rupture of herpes simplex blister
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion; resulting from loss of epidermis due to rupture of vesicles or bullae; often caused by friction or pressure
heals WITHOUT scar confined to epidermis
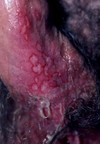
describe this!
Ulcer
ex: decubitus ulcers, primary lesion of syphilis
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion resulting from loss epidermis and part of dermis
HEALS WITH SCAR irregular size and shape

describe this!
Fissure
ex: cracks in athlete’s foot
SECONDARY LESION
deep linear lesion into the dermis; wedge-shaped in epidermis with abrupt walls
can extend into dermis
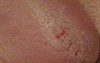
describe this!
Excoriation
SECONDARY LESION
linear superficial lesion, may be covered with dried blood due to scratching of skin
*specific to itching
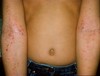
describe this!
Lichenification
ex: atopic dermatitis
SECONDARY LESION
Thickening of epidermis, resulting in accentuation of skin lines results from chronic irritation and rubbing
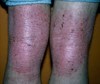
describe this!
Scar
SECONDARY LESION
replacement of normal skin with fibrous tissue; often resulting from injury involved in deeper dermis
describe this!
Atrophy
ex: aging, stretch marks
SECONDARY LESION
thinning or depression of the skin surface due to reduction of underlying tissue depression in epidermis

describe this!
Sclerosis
SECONDARY LESION
hardening of the skin caused by an increase in collagen, mucin, edema or cellular infiltration
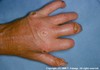
describe this!
Necrosis
SECONDARY LESION
tissue death
describe this!
heals above layer of epidermis; confined to edges of wound
Hypertrophic scar

describe this!
scar tissue goes beyond the edges of original wound
Keloidal scar

describe this!
Comedone
ex: blackhead (open)
darkened plug of sebum and keratin that occludes the pilosebaceous follicle
some open; some closed
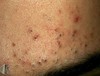
describe this!
Cyst
NODULE; encapsulated containing fluid or semi-fluid substance; fluctuant

describe this!
Burrow
ex: scabies
linear or serpinginous tunnels within the epidermis
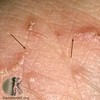
describe this!
Telangiectasia
small, superficial blood vessels that become visible because they are dilated;
disappear with pressure (blanch)

Location, incidence, treatment, Ddx
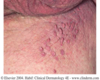
Acrochordon (skin tag)
Commonly found in skin folds
Females > males
Treated: snip excision & reassurance; few need biopsy
Ddx: wart & nevus
Location, incidence, treatment

Cafe au’Lait Spot
Usually inherited
6+ may indicate neurofibromatosis type 1
No treatment required
Description, location, treatment, Ddx
MOST COMMON VASCULAR GROWTH ON SKIN

Cherry Angioma
Round-dome shape, slightly raised, red/purple
Mostly on trunk
Treatment: reassurance or cosmetic removal via cauterization
Description, incidence,location, treatment, Ddx

Cutaneous horm
Skin colored, horny growth
Can arise from benign, pre-CA, malignant lesions
mostly on face/scalp
Treatment: excisional biopsy; MUST INCLUDE BASE