Dermatological Manifestations of GI Disease Flashcards
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?

- Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum
- plucked chicken appearance
- neck, axilla, groin
- Autosomal recessive
- mutation ATP-binding cassette transporter C6 (ABCC6)
- Affects elastic fibers
- skin, blood vessels, heart valves
- degenerate & calcify & accumulate
- fragmentation of medium sized vessels
- vascular occlusion or bleeding
- in GI tract or myocardium
- Angioid Streaks
- linear & branching streaks radiating from optic disk
- plucked chicken appearance

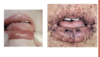
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?

- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telagiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber Syndrome)
- autosomal dominant
- see it in mouth & palms
- Multisystem vascular dysplasia
- Dialated blood vessels
- vascular malformations of the GI tract, pulmonary, and nervous system
- symptomatic & asymptomatic bleeds
- liver A-V malformations
- Epistaxis (bloody nose) is most comon presenting symptom in childhood
- autosomal dominant

How can you tell if a red papule is vascular?
Where are they most common in patients with HHT?
- Telangiectasias (red blanchable macules) present on oral mucosa & lips
- Take a slide & if blanches (pushing the blood out) then it is vascular

What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- autosomal recessive – mutaiton in intestinal zinc transporter
- usually seen in infants
- can also be acquired
- Pink erythymous scaly lesions
- neck, perioral & perirectal surfaces
- Resolves with zinc supplementation

What disease is shown in the image provided?

Metastatic Chron’s Disease
- Cutaneous granulomas
- beefy red
- not common, need a biopsy & to see several times
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?

- Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- neither infectious or gangreous
- uncommon, chronic, recurrent, ulcerative neutrophilic disease
- Ulcer with grey, gunky, irregular border surrounded by erythema & necrosis on the inside
- initial lesion is papulopustule w/ surrounding erythem
- Frequently associated with systemic disease
- Heals w/ atrophic cribiform pigmented scars
- Lesions at trauma sites (pathergy) – important not to debris
-
Associated with inflammatory bowel disease
- associated with ulcerative & Chron’s

Disgnosis, Histology & Treatment of Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
- Diagnosis of exclusion, rule out factitial disease
- Histology
- massive dermal edema
- epidermal neutrophilic abscesses at the violaceous undermined border
- Treatment
- agressiveness of treament based on severity of disease

What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Recurrent Apthous Stomatitis
- painful lesions
- “kanker sores”
- Can be associated with inflammaory bowel disease
- Behcets
- HIV
- malabsorption
- neutropenia
- ulcerative Colitis, Crohn’s disease
- connective tissue disorder
- Treatment
- usually controlled through topical corticosteroids
- symptomatic, elixir of benadryl adn maalox with lidocaine
- dapsone or colchicine and avoiding triggers
- 20% patients with low B12
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

Necrolytic Migratory Erythema
- annulat & arcuate, erythematous papules, coalesce to form large plaques with necrosis & slough of the superficial dermis
- erosin, crusting,
- periorficial, flexural intertriginous, acral areas
- strong associatin with islet cell tumor of the pancreas (glucacon secretign tumor of pancreas)
- weight loss, diabetes mellitus, constitutional symptoms
- elevated serum glucagon
- Treatment
- removal of tumor
- responds poorly to topical corticosteoid/antifungals

What disease is shown in the image provided?
Symptoms?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?

- Hepatic Disease and CIrrhosis
- Symptoms
- vascular lesions
- telangiectasias
- palmar erythema
- nail changes
- Terry’s nails- proximal white nail and distal pink
- clubbing
- Thinning of hair
- Pruritus
- vascular lesions

What disease is shown in the image provided? (the person on the right)– White person living in Alaska
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Hemochromatosis
- “Bronze diabetes”
- deposition of iron in tissues including skin, liver, heart, pancreas, and endocrine lesions
- metallic grey or brown generalized hyperpigmentation
- accentuated in flexual folds
- presents in 4th to 6th decade
- Treatment
- phlebotomy
What sign of disease is depicted in provided image?
What disease?
Symptoms?

- Wilson’s Disease
- “Kayser Fleischer ring”
- excess copper builds up in the body.
- Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and itchiness
What are the two type of cutaneous lesions that can result from pancreatic disease?
- Purpura
- Panniculitis
- inflammation of adipose tissue
- direct effect of pancreatic enzymes

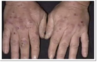
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrom (Upper GI)
- Autosomal dominant
- symptoms
- perioral melanotic freckles (often appearing during infancy)
- also gingiva, buccal, and genital mucosa
- GI polyps (sepecially jejunum/small intestine)
- 10-18x cancer risk (1/2 develop by 40)
- colon, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, breat, thyroid, lung
- abdominla
- pain, bleeding, intussusception
- Treatmetn
- regular, frequent, gastrointestina screening

What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Gardner Syndrome (Lower GI)
- epidermal inclusion cysts, osteomas, lipomas, fibromas
- associated with intestinal polyposis (colon & rectum)
- high malignatn potential by age 40
- half with carcinoma by age 30, most die before 50
- Treatment
- total colectomy
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Dermatitis Herpetiformis (Duhring Disease)
- cutaneous manifestation of gluten sensitivity
- Symptoms
- severely pruritic grouped vesicles
- symmetrically on extensor surfaces (elbows & knees), scalp, muchal areas, buttocks (distribution is key)
- usually exoriated at time of presentation (scratched & busted pustules)
- pigmented spots over lumbarsacral area
- rare mucosal involvement
- oral
- dryness, ulceration, tooth enamel defects
- Intesnse itching & burning
- Chronic relapsing w/ spontaneous improvement
- 70-100% of DH have abnormal jejunal mucosa
- 25% celiac patients have DH
- 2-5th decade

Describe the pathogenesis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis
- Exposed to wheat
- gliadin
- in GI junction form antibody response
- these IgA don’t just stay in the intestine– they spread throughout the body creating inflammation – along w/neutrophils
- can also spread to the skin & depositing at the dermal/epidermal junction causing a blister to form
- causing the skin rash
- Associations
- Thyroid disease
- Lymphoma (T-cell)
- gluten-free diet

Diagnosis of Dermatitis Herpetiformis?
Treatment?
- Diagnosis
- Clinical
- Biopsy
- Intact lesion for histology
- skin adjacent to lesion for DIF
- IgA deposits
-
Antiendomysial antibodies
- sensitive & specific
- reflect severity of enteropathy and compliance of diet
-
Antigliadin antibodies
- also found in pemphingus & pemphigoid
- Treatment
- Dapsone
- control not clear
- can cause hemolysis (anemia)
- need to screen for G6P dehydrogenase deficiency
- Gluten-free diet
- barley rye, oats (contaminated) & wheat
- corn, rice & oats are okay
- Dapsone

The quick development of the shown skin condition is indicative of what larger problem?
What is the name of this sign?

- Sign of Leser-Trelat
- rare
- rare cutaneous marker of internal malignancy (in particular gastric or colonic adecarcinoma, breast carcinoma, lymphoma)
- abrupt quick onset of many seborrheic keratoses (age spots – forom 0 to 100s all at once)
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?
Treatment?

- Necrobiosis Lipoidica Diabeticorum
- 20% have diabetes or glucose intolerance
- F>M
- single or multiple, well-demarcated red-brown papules that progress to yellow-brown atrophic, telangiectatic plaques with violaceous irregular border
- skins, ankles, calves, thighs adn feet
- cutaneous anesthesia, hypohidrisis and partial alopecia
- palisading granulomas containing degernerating collagen, inflammatory infiltrate w/ plasma cells and MNGC, no increase in mucin
- Treatment
- prevent ulcers
- ILS, topical steroids, ASA, dipyrdamole, pentoxyfyline
- cyclosporin, PUVA
- controlling diabetes has not effect on lesions
- prevent ulcers
What disease is shown in the image provided?
Type of disease?
How can this indicated problems in the GI?

- Diabetic Dermopathy
- shin spots
- MC cutaneous lesion in diabetics
- dull-red papules that profess to well-circumscribed, small, round, atrophic, hyperpigmented lesions on shins
- If 4 or more are present, specificity is hight for microvascular disease in other tissues
The skin conditions showed the provided images are indicative of waht larger problem?

- Diabetic skin manifestations
- recurrent candidiasis (candidal intertrigo)
- erythematous, well demarcated
- tendency to fissure
- concomitant infections
- Tx
- drying agents & topical agents
- Eruptive xanthomas
- also manifestations of lipid abnormalities
- Diabetic Bullae
- rapid onset of painless, tense blisters on hands and feet
- intraepidermal/subepidermal split w/o acantholysis
- recurrent candidiasis (candidal intertrigo)
The skin conditions showed the provided images are indicative of waht larger problem?

- Diabetic Skin Manifestations
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- velvety, grayish-brown thickenign of the neck, axillae, and groin
- sign of insulin resistance or other endocrinopathies
- may also precede, accompany or follow adenocarcinoma of the GI
- Treatment: treating underlying disorder
- Acanthosis Nigricans
What is Cushing’s Syndrome?
Symptoms?
- Chronic excess of glucocorticoids
- Symptoms
- central obesity (face, neck, upper back and abdomen)
- Striae (stretch marks)
- Hypertrichosis- face/body
- thin hair
- dryness, skin fragility, facial acne, dermatophyte infections
- moon face
- buffalo hump
- Systemic
- HTN, weakness, decreased bone density, DM, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, decreased libido