Derm/Pictures Flashcards

PYOGENIC GRANULOMA
- Common benign vascular tumors that resemble small hemangiomas
- Usually face or extremity
- Solitary bright red, soft nodules, often peduncultaed
- Surface is friable and bleeds easily
- Onset well after newborn period (vs. hemangioma)
- Tx: shave excision and electrodessication of “feeder” blood vessels at the base.

NUMMULAR ECZEMA
- Acute papulovesicular eruption
- Coin-shaped configuration
- Red scaly patches
- Usually on extensor thighs or abdomen of children with atopic dermatitis
- Lack of central clearing to distinguish from ringworm

ECZEMA HERPETICUM
- Particularly severe form of primary HSV infection in pts with atopic eczema and/or chronic dermatitis
- Onset of high fever, irritability, and discomfort
- Lesions in crops on areas of recently affected skin
- Evolve to form pustules that rupture and form crusts
- Can become hemorrhagic (to distinguish from chicken pox)
- Tx: acyclovir

ERYTHEMA CHRONICUM MIGRANS
- Distinctive exanthem of Lyme disease
- Appears in 50% of cases of LYme
- Begins as red papule or macule at site of tick bit that enlarges (up to 15cm) forming large plaque
- Tends to clear centrally
- Multiple secondary smaller lesions can develop in 25% of patients
- Accompanied by flu-like symptoms

ERYTHEMA MARGINATUM
- Evanescent, nonpruritic, sharp serpiginous margins
- Found on inner aspects of upper arms and thighs and on trunk
- Not specific to acute rheumatic fever

KLIPPEL-TRENAUNEY-WEBER SYNDROME
- Port-wine stain that usually located over lateral aspect of one leg
- Surface lesion is associated with underlying vascular malformation (rich blood supply) that leads to soft tissue and bone hypertrophy (hemihypertrophy)
- Progressive enlargement during the first few years
- MRI/MRV to evaluate extent of venous/lymphatic malformation
- Complications: DVT, PE, GI bleed, vascular blebs within capillary malformation
- (This picture is atypical b/c bilateral)

SPRENGEL DEFORMITY
- Congenital malformation with abnormally small, high-riding scapula
- Usually unilateral
- Associated with Klippel-Feil syndrome
- Scoliosis and torticollis
- Shoulder motion severely limited, especially abduction

KLIPPEL-FEIL SYNDROME
- Congenital malformation of the neck that results from failure of segmentation in the developing cervical spine
- Leads to fused vertebrae
- Short, broad neck with webbing
- Low hairline
- Gross restriction of motion
- Associated with Sprengel deformity, rib deformities, scoliosis, CNS defects, and cardiopulmonary and renal anomalies

IMPERFORATE HYMEN WITH HEMATOCOLPOS
- Thick imperforate membrane located inside the hymenal ring
- May become evident by 8 to 12 weeks of age
- Can also develop in late puberty (think well-developed secondary sex characteristics but no menstrual periods)
- Tx: incision of membrane to allow drainage then excision of redundant tissue

VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
- Regular, wide-complex tachycardia with AV dissociation if p waves visible
- Usually children with open-heart surgical repair for TOF or other complex anomalies, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, or congenital ion channel abnormality (long QT, Brugada) or myocardial tumor
- Prolonged QTc can lead to Vtach

PERIRECTAL STREP
- Can dx with rapid testing for strep from perineal tissues
- Perineal burning and dysuria
- Sharply circumscribed area of intense erythema
- Involved skin may weep serous fluid
- Desquamation occurs with recorvery
- Tx: penicillin (or amox)

HURLER SYNDROME
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS I) = lysosomal storage disease
- Onset 6-24 months
- Growth retardation, coarse facial features, hepatosplenomegaly, dysostosis multiplex, cardiac valve disease
- Tx: BMT
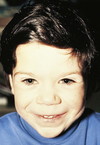
WILLIAMS SYNDROME
- 7q microdeletion (autosomal dominant)
- Characteristic “elfin” facies: broad maxilla, small mandible with full mouth and large upper lip (philtrum)
- Upturned nose
- Full forehead
- Associated with hypercalcemia
- Strikingly affabe personality
- Varying degrees of developmental delay
- Supravalvular aortic stenosis and pulmonary artery branch stenosis

TRANSIENT NEONATAL PUSTULAR MELANOSIS
- Self-limited dermatosis
- Presents at birth with 1- to 2-mm vesiculopustules or ruptured pustules that disappear in 24-48 hours, leaving pigmented macules with a collarete of scale
- Usually neck, forehead, lower back, and legs
- Wright stain: numerous neutrophils
- NO THERAPY
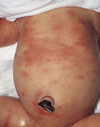
ERYTHEMA TOXICUM
- Benign, self limited
- Occurs in 50% of full-term infants
- Appears within 24-48 hours of birth
- Intense erythema with central papule or pustule that resembles flea bite
- Pustules contain eosinophils
- NO TREATMENT

HENOCH-SCHONLEIN PURPURA
- Small-vessel leukocytoclastic vasculutis
- IgA immune complex mediated
- Rash with “waist-down” distribution
- Petechiae or papules that coalesce; non-blanching
- Younger child more likely to demonstrate facial involvement.

MENINGOCOCCEMIA
- Involves trunk and extremities
- Tender pink macules; petechiae, which may be palpably raised; and purpura, which when present is most prominent on the extremities and may progress to form areas of frank necrosis

STAPHYLOCOCCAL SCALDED SKIN SYNDROME
- Begins as impetigo or nasopharyngitis/conjunctivitis
- Tender, sunburn-like rash –> scarlatiniform –> widespread blistering/peeling of skin (flexural, perioral) locations

EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
- Group of inherited mechanobullous disorders
- Development of blisters after the skin is subjected to mild friction or trauma
*

IMPETIGO
- Superficial infection of the epidermis
- Caused by strep, staph, or both
- Usually exposed portions of the body (face, extremities, hands, and neck)
- Potential source of transmission to others
- Papule (strep) or macule (staph) that evolved to vesicle with erythematous halo –> honey-colored crust

STEVENS JOHNSON SYNDROME
- Full-thickness sloughing
- Involves 10-30% of BSA
- Severe vesiculobullous disease of skin, mouth, eyes, and genitals (**mucous membrane involvement**)
- Etiologies: drugs (AEDs, sulfa, NSAIDs) and infections (mycoplasma)

ALOPECIA AREATA
- Round or oval patches of alopecia
- Immunologic disease
- “Exclamation mark hairs”
- Associated with nail pitting

KAWASAKI DISEASE
- SMall and medium-sized blood vessels
- Rash (variable - can be morbilliform or scarlatiniform)
- Non-exudative conjunctivitis with limbal sparing
- Red or cracked lips, diffuse erythema, strawberry tongue
- Lymphadenopathy >1.5cm
- Hand and/or foot edema, erythema or desquamation

TOXIC SHOCK SYNDROME
- Fevers, chills, myalgias, generalized malaise
- Diffuse erythroderma mimicking sunburn
- Conjunctivitis with photophobia
- Oropharyngeal erythema, strawbery tongue
- Severe watery diarrhea, hypotension, oliguria
- Usually starts with tampon, skin lesion, abscess, or purulent conjunctivitis

KOEBNER PHENOMENON
- Lesions are often induced at sites of local injury such as scratches, surgical scars, or sunburn
- Seen in psoriasis, lichen planus, JIA rash, Gianotti-Crosti syndrome

LUMBOSACRAL HEMANGIOMA
- Should do MRI to evaluate for occult spinal dysraphism

MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM
- Sharply circumscribed dome-shaped papules with waxy surfaces
- Can occur singly or multiply and be pruritic
- Usually umbilicated centrally
- Trunk, face, axillae, and genital area
- Spread through scratching
- Many undergo spontaneous remission within 2-3 years

INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI
- X-linked dominant
- Typically lethal in males prenatally. 97% of affected infants are female.
- Newborns have linear papules/vesicles –> progress to verrucous streaks that resolve. At 3-6 months, hyperpigmented whorls and swirls appear. By 2nd or 3rd decade, whorls become hypopigmented.
- Associated with alopecia, dystrophic nails, adontia.
- 1/3 have mental retardation, seizures, and spastic paralysis

HYPOMELANOSIS OF ITO
- Marbleized or mottled areas of hypopigmented whorls of skin along the Blaschko lines
- Can have multiple congenital anomalies, dysmorphic features, variable mental retardation, and other neurologic findings
- Karyotype of skin lesions shows mosaicism

THYROGLOSSAL DUCT CYST
- Failure of regression of the thyroglossal duct may lead to cyst formation.
- Prone to infectious complications
- Require surgical excision of midportion of hyoid bone and ligation of the tract leading to the foramen cecum to prevent future recurrence

LANGERHANS CELL HISTIOCYTOSIS
- Chronic, hemorrhagic and erosive, often “punched out” eruption with petechiae
- Histiocytic infiltrate on skin biopsy
- +staining for S-100 and CD1a
- Associated with systemic disease (bone marrow, pulm, hepatic, GI)
- Tx: Chemotherapy
- (formerly known as Letterer-Siwe disease, Hand-Schüller-Christian disease, and eosinophilic granuloma)

CONGENITAL RUBELLA
- Due to maternal rubella infection during first 20 weeks of pregnancy
- Triad: (1) congenital cataracts, (2) deafness, and (3) congenital heart malformations
- 2- to 8-mm bluish red macules (“blueberry muffin rash”) from dermal erythropoiesis
- Noted within first day of life
- Differential for blueberry muffin rash: (1) rubella, (2) toxo, (3) CMV

CONGENITAL SYPHILIS
- Cutaneous lesions involve reddish-brown macules, papules, and bullae in the groin area and palms/soles
- Condylomata lata
- Oral mucous patches
- Frontal bossing
- Saber shins
- Hutchinson’s triad = interstitial keratitis, Hutchinson’s incisors, and CNVIII deafness
- Diffuse periosteal reaction

PITYRIASIS ALBA
- Postinflammatory hypopigmentation
- Usually after sun exposure in children with darker skin types
- Associated with atopic dermatitis
- Resolves in months to years
- Tx: moisturizers, photoprotection, low potency topical steroids
Infection associated with pityriasis rosea
Secondary syphilis (check RPR if sexually active)
Infection associated with erythema multiforme
HSV
Infection associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Mycoplasma pneumoniae

CONGENITAL GLAUCOMA
- Cornea has a hazy or cloudy appearance
- Associated with unilateral tearing
- Can be seen in: Sturge-Weber syndrome, neurofibromatosis, Lowe syndrome, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, and congenital rubella syndrome

CORNELIA DE LANGE
- IUGR, persistent postnatal failure to thrive, moderate to severe cognitive impairment, and microcephaly with a flat occiput and low hairline
- Facial features seen in an infant and an older child include finely arched heavy eyebrows, long eyelashes, small upturned nose, long smooth philtrum, and cupid’s-bow mouth
- Small hands, hypoplastic proximally placed thumb, and short fifth finger with mild clinodactyly are examples of commonly associated extremity anomalies.

RADIAL EPIPHYSITIS
- Widening of epiphysis (more pronounced volarly and radially)
- Common in gymnasts
- Pain in dorsal wrists


