Derm Pics- Common Dermatoses I and II, Skin Cancers Flashcards
Describe

= multiple scattered macuoles on the chest, red and pink in color
Diagnose:

Vitiligo
-depigmented patch
Describe:

- multiple monomorphic flesh colored papules (elevated < 1 cm)
- umbilicated
Diagnose and describe:

Psoriasis
- large salmon colored plques w/ well defined border in a geographic distribution on the lower back and buttocks
- lots of silvery scale (secondary lesion)
Describe

Monomorphic pustules
Describe:

Erosion with a bit of crust (stuff dried on top)
- erosion loss of some or all of the epidermis
- often from vesicles or bullae
Describe:

Fissures on the edges/sides of the mouth
- different from erosions and ulcers
- fissures = linear or wedge shape tears in the epidermis
Differentiate the clinical picture of atrophy of the
(a) epidermis
(b) dermis

Atropy of the (a) epidermis = thin, wrinked skin
- attached to answer card
ex: sun exposure, aging
Atrophy of the (b) dermis => clinically detectable depression in the skin (attached to question card)

Describe the process:
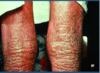
= Lichenification
- thickening of the skin (hyperkeratosis) due to chronic scratching or rubbing
- noted by the increased lines and skin markings
- associated w/ eczema
Describe and diagnose:

-small flat monomorphic papules, skin colored
= Flat warts

Describe and diagnose

= Warts
-periuncal (around the fingers) papules (raised < 1 cm)
Describe:

-filiform (thread like) warts on nose
Diagnose

Plantars wart
Describe and diagnose:

Salmon colored plque w/ sharply defined borders and silvery white plaque = psoriasis
Describe and diagnose:

Small, salmon-pink droplets on skin
= Guttate psoriasis
-typically on upper trunk or extremities, in young adults, classically after bacterial infection (ex: strep throat)
Describe and diagnose:

Salmon pink plaque with well defined borders in intertrigenous area (where two skin areas touch)
= Inverse psoriasis = very red lesions in body folds
What is the white arrow pointing to?
(a) Diagnose
(b) Other nail findings of this disorder

White arrow pointing to a yellow oil spot
(a) Psoriatic nails
(b) Other nail findings in psoriasis = pitting, onycholysis (loosening or separation of nail from the nail beds), subungal debris (crap under the nail)
Describe and diagnose:

Hyperpigmented macules (small patches) scattered
= Tinea versicolor
-versicolor b/c color varies- can be either hyper or hypopigmneted compared to background skin

Describe and diagnose:

-yellow scale on erethematous border in nasolabial fold
= Seborrheic dermatitis
Describe how these three factors play into the pathogenesis of acne
(a) Bacterial
(b) Hormonal
(c) Epidermial
Acne:
(a) Propionibacterium acne releases lipase that hydrolyzes the sebum TGs into FFAs
(b) Hormonal: androgens increase sebaceous gland activity
(c) Epidermial: hyperkeratinization of the hair follicle lining clogs the pore
- get proliferation of the bacteria, regression of the sebaceous lobule, and inflammation

Describe and diagnose:

-warty brown papule, well demarcated, verrucous (wart-like), appears ‘stuck on’
= Seborrheic Keratosis

Descirbe and diagnose:
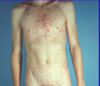
Many small oval erethematous macules w/ a collarette of scale (circulation lesion w/ circular rim of scale or peeling edge) in a Christmas tree distribution on the chest and upper extremities
Describe and diagnose:

Erethematous macules (flat < 1 cm) w/ honey colored crusts (crap dried on top) = impetigo
Describe and diagnose:

-pearly papule with central crater and telangectasia = Basal cell carcinoma














