DERM: Nodules & Papules I & II Flashcards
verrucae / condyloma acuminatum - pathogenesis
- HPV infects underdifferentiated epithelial cells in the stratum basal then -> ascends thru upper layers -> infects terminally differentiated squamous cells = koilocytes
- HPV 6, 11 (m/c - low malignant risk)
- HPV 16, 18 (high malignant risk)
verruca vulgaris - presentation
d/t HPV
-
= common wart: papules that are
- keratotic
- velvet textured / rough
- tend to occur on the hands
condyloma acuninatum - presentation
d/t HPV
-
= anogenital wart
- cauliflower-surfaced
- pedunculated
- on genitalia / urethra / perianal / tissue OR lips
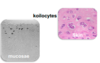
verrucae vulgaris / condyloma acuminatum - diagnosis
= presence of koilocytes:
- altered squamous epithelial cells with irregular nuclei:
- pyknotic, dense nucleus
- surrounded by clear perinuclear space (halo)
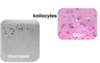
identify picture. what is its significance?

koilocytes: HPV infected squamous epithelial cells with abnormal nuclei: pyknotic & surrounded by clear pernuclear space
diagnostic of verrucae / condyloma accunimanatum
identify each picture

- verruca vulgaris: keratotic, velvet textured common warts typically on hands
- condyloma accuminatum: cauliflower-surfaced, pendunculated, anogenital warts
verrucae / condyloma acuminatum
- prognosis
- therapy
- prevention
- prognosis: m/c dissapear w/in 2 years
- therapy: removal - cryosurgery / curretage OR topicals
- prevention: safe sex & HPV vaccine (Gardasil 9)
condyloma latum - pathogenesis
= genital secondary syphyllis
treponema pallidum (a highly infectious STI) creates chanrce at innoculation site
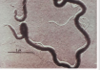
condyloma lata - presentation
= treponema pallidum
- skin: papules that are
- hypertrophic
- smooth & flat
- white
- moist
- systemic: general prodrome

condyloma latum
- diagnosis
- prognosis
- therapy
- prevention
= treponema pallidum
- diagnosis:
- RPR / VDLR then FTA-ABS - m/c
- spirochetes in darkfield microscopy, also
- prognosis - follows that of syphyllis
- therapy - benzanthine penicillin G
- prevention - safe sex

identify picture - why is it significant?

darkfield microscopy showing spirochetes (treponema pallidum) - dx of condyloma latum
kaposi sarcoma - pathogenesis
-
HHV-8 infection of endothelial cells (capillary lining) leading to -> angioproliferative diseases, the progression of which depends on the demographic infected
- IC (AIDS / transplant recipients): fulminant (rapid) progression
- genetic predisposition: indolent (slow) progression
kaposi sarcoma - presentation
HHV -8
- systemic:
- genetic (indolent): lymphedema (leg edema)
- fulminant lesions: joint, GI
- skin: reddish-purple vascularized macules -> progress into tumors / nodules
- genetic (indolent) lesions: on lowers limbs
- fulminant lesions:
- sun-exposed skin
- mucous membranes

kaposi sarcoma - diagnosis
-
spindled endothelial cells with
- extravasated RBCs
- hemosiderin laden macrophaeges
kaposi sarcoma
- prognosis
- therapy
- prevention
- prognosis: is a latent incurable infection (HHV-8) though asymptomatic (rarely, multi-organ failure in fulminant pts)
- therapy:
- removal
- radiation
- chemotherapy
- prevention: avoid contracting HIV









