DERM Flashcards
1
Q

A
Pyogenic Granuloma
2
Q
Psoriasis cytokines
A
- TNFa, IL23( and 12), IL17
3
Q
Epidermal Inclusion Cyst (EIC)
A
- Benign, mobile SubQ nodule, often with underlying punctum
- Arises from hair follicles
- May discharge foul smelling white material
- I&D only for ruptured EICs that create abscesses
- Can be surgically removed if complaints of pain, discomfort, or Hx of inflammation
4
Q
Epidermolytic Ichthyosis
A
- KRT 1/10 mutation
5
Q

A
Pyogenic Granuloma
6
Q
Contact dermatitis
A
- Irritant
- TNFa driven
- Allergic
- Cell-cell mediated immune response (requires prior sensitization) - delayed reaction
- Langerhans cells, lymphocytes, IgE production, IL-9 and IL-17
7
Q

A
Seborrheic Keratosis
8
Q
Bullous Pemphigold
A
- Autoantibodies against collagen 17 (hemidesmosome protein)
- Most common in older adults
9
Q

A
Solar Lentigo
10
Q
Cornified layer of epidermis
A
- Cell death but cross-linked keratin bundles are preserved
- Cornified envelope surround these corneocytes
- Protein cross-links via transglutaminases (like TGM1)
- Embedded in lamellar membrane of secreted, insoluble lipids
- “Brick and mortar”
11
Q
Merkel cells
A
- Mechanoreceptors in the epidermis
- Convey sense of light touch with nerve endings in basal layer
12
Q
Staph-mediated desmosome cleavage via toxin occurs in…
A
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (newborns)
- Bullous impetigo (children)
13
Q
Cherry angioma
A
- Benign, shiny bright red papule
- Common to have multiple spots
- Common on trunk, but can be anywhere like face/scalp
14
Q

A
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
15
Q
Acrochordons
A
- Aka skin tags
- Benign soft fleshy papules that are skin colored to brown
- Axilla, neck, groin, eyelids
- Often pedunculated - connected to skin via small stalk
16
Q
Hair follicle
A
- Anagen (growth) phase → Catagen (involution) phase → Telogen (rest) phase
- Of epithelial origin and associated with arrector pilorum muscles and sebaceous glands
- Hair follicle bulge important multipotent stem cell niche for not only producing hairs but also healing epidermal wounds
17
Q
Psoriasis treatment
A
- Widespread
- Biologics targeting TNFa, IL23(12), IL17
- Cyclosporine, MTX
- Local
- High potency topical steroids (Clobetasol, triamcinolone)
- Topical VitD analogs - Calcipotriene
- Narrowband UVB light
18
Q
Spinous layer of epidermis
A
- Keratinocytes begin process of terminal differentiation
- Keratin 1 and 10
- Desmosomes at cell-cell junctions = integrity
19
Q
Two layers of the dermis
A
- Papillary dermis
- Under epidermis, less dense CT
- Reticular dermis
- Between papillary dermis and SubQ fat
- More dense CT
20
Q
Foul smelling white discharge

A
Epidermal Inclusion Cyst (EIC)
21
Q
Alopecia areata associations
A
- Physiological/emotional distress
- Thryoid disease (check TSH), vitiligo, diabetes,
22
Q
Triggers of psoriasis
A
- Streptococci (Strep pharyngitis)
- Stress/trauma to skin
- Drugs - lithium and B-blockers
23
Q
Follows injury to skin like insect bite or inflammed hair follicle

A
Dermatofibroma
24
Q
Elastic fiber disorders
A
- Marfan syndrome
- Mutation in fibrillin 1 gene (FBN1)
- Elastolysis (Congenital cutis laxa)
- Mutations in elastin gene (ELN) and other genes that affect elastic fiber formation
- Skin slacks and hangs in folds
25
Collagen diseases disorders
* Scleroderma
* Chronic autoimmune disease with excess collagen deposition (fibrosis)
* Vascular and autoantibody abnormalities
* Keloids
* Excess collagen → fibrous scars
* More prevalent in pigmented individuals
26

Hemangioma
27
Solar Lentigo
* Benign flat light brown macules
* Due to sun damage - sun exposed regions
* Aka sun spots, liver spots, age spots
* No treatment required, but indicate patients at risk for skin cancer due to sun exposure
* Histology: Increased melanin, no increase in melanocytes
28
Langerhans cells
* Bone-marrowed derived, dendritic APCs
* Suprabasal layer of epidermis
* Regulate immune responsiveness in skin (alert and dampen)
29
Hemangioma
* Benign, raised soft, easily compressed vascular growths
* aka Strawberry hemangiomas
* Usually solitary
* Commonly head and neck, but can occur anywhere
* Most common benign tumor of childhood, present at birth or within first few weeks of life
* Slowly dissapears after first year of growth
30
Pyogenic granuloma
* Benign, eruptive, small solitary sessile or pedunculated vascular raised papule
* Bleeds easily with trauma
* Relatively quick onset
31

Acrochordon (Skin tag)
32
Pemphigus vulgaris/foliaceous
* Autoantibodies against proteins found in desmosomes
* Breaks connection between adjacent keratinocytes
33
Pityriases rosea
* Exanthema - salmon colored papules/macules
* Herald patch → development of other smaller macules
* Mostly trunk, Christman tree distribution
* Self-resolving (lasts 3-8 weeks), only treat with topical steroid if complaint of itch
* Possibly viral etiology - reactivation of HHV6/7
* _Cold/flu-like symptoms before rash_
* DDx: Secondary Syphilis
34
Types of psoriasis
* Guttate - smaller, coin-sized plaques
* Precedes sore throat, strep, viral infection
* Pustular
* Palmo-plantar
* Erythroderma - red, scaly involvement of entire body
35
Distribution of AD with age
* Infancy – Facial and scalp dermatitis
* Toddler – Extensor dermatitis (over elbows and knees)
* Older children/young adults – Flexural distribution (Antecubital and popliteal fossa; mentions anterior neck, wrist, ankles too)
* Adults – More head (also eyelids), neck, hand lesions
36
Follows injury to skin like insect bite or inflammed hair follicle

Dermatofibroma
37
Dupilumab
* IL-4/13 monoclonal antibody
* Main SFx: Conjunctivitis (allergic/non-allergic) and injection site reaction
38
Ichthyosis vulgaris
* Caused by filaggrin mutations
* Predisposes patients to eczema and other chronic inflammatory skin disorders
39
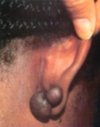
Keloid
* Benign firm plaque or nodule, often smooth.shiny surface
* Hyperpigmented, pink, or red
* Site of previous tissue trauma - burn, cut, acne, piercing
* Excess scar tissue out of control
* Can be tender, itchy
* Treatment: Interlesional steroid injection can help flatten and alleviate itch/pain
40
4 layers of epidermis (basement to surface)
* Basal layer
* Spinous layer
* Granular layer
* Cornified layer
41
Seborrheic Keratosis
* Benign superficial raised epidermal growths
* Sometimes fissures and cracks
* Tan/brown/black in color
* Anywhere on body EXCEPT palms and soles
* Common after 30yo
* Often multiple, can be extensive, doesn't go away
42
Lipoma
* Benign, soft ill-defined rubbery, painless subQ nodules
* Usually larger than cysts and without pain/discharge
43
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
* Benign cream-colored or yellowish, round elevated papule with central depression
* Usually face and multiple in number
* 40yo age of onset
44
Foul smelling white discharge

Epidermal Inclusion Cyst (EIC)
45
Psoriasis
* Chronic inflammatory skin disease that waxes and wanes, onset at any age, M=F
* Improper keratinocyte maturation and shedding
* Raised, well-defined scaly rash with silverly scale
* Pink/salmon colored underneath
* Redness - blood vessels closer to surface, proliferate, dilate
* Anywhere, but commonly elbows and knees
* Trunk, extremities, scalp, and genitals
* Nail bed pitting and onycholysis
46
Atopic dermatitis
* FLG (Filaggrin 1) gene mutation
* Inflammation driven by Th2 T cells releasing _IL-4 and IL-13_
* Also leads to IgE elevation
* Increased IL-31 expression → itch/pruiritis
*
47
Keloid
48
Sebaceous gland
* Acini cells that produce complex set of lipids
* Ductal epithelial cells → keratinocytes that move from sebaceous gland duct into hair follicle canal
* Holocrine secretion - dumping of contents from sebocytes into sebaceous gland
49
Melanocytes
* Neural crest-derived, pigment producing cells in epidermis
* Synthesize melanin-containing melanosomes which are secreted directly into keratinocytes
50
Basal layer of epidermis
* Anchors to BM/ECM of underlying dermis via hemidesmosomes
* Micture of proliferating and nonproliferating keratinocytes
* Stem cells
* Self-renewal
* Wound repair
* Keratin 5 and 14
51
Epidermis Bullosa Simplex
* KRT 5/14 mutation
* Relatively mild blisters in hands/feet, usually improves with age
52

Lipoma
53
AD treatment
* Mild AD
* Topical agents: steroids and calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus)
* Moderate/Severe AD
* Systemic agents: Steroids/Tacrolimus, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, MTX, Azathrioprine
* Light therapy and lasers
* Dupilumab
54
Seborrheic dermatitis
* Redness and waxy scaly patches on scalp, hairline, eyebrows, nasolabial/melolabial folds, beard distribution
* Etiology may be related to yeast (pityrosporum ovale)
* Treatment: antifungals and low potency topical steroids
55
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa
* Mutation in COL17A1 (hemidesmosome gene)
* Severe, often fatal subepidermal blistering
56

Cherry Angioma
57
AD associations
* Weather/climate/environmental exposure
* Obesity
* Type 2 diabetes
* HTN
* HLD
58
Granular layer of epidermis
* Keratinocytes produce granules containing filament aggregating proteins (like _profilaggrin_)
* Filaggrin bundles keratin filaments for barrier formation and prep for final stages of differentiation
* Keratin 1 and 10
* Tight junctions complement lipid barrier of cornified layer
* Semipermeable = limits water loss, prevents entry of noxious agents and pathogens
59
Sweat apparatus ducts
* Eccrine and apocrine glands - secretory coil and duct
* Eccrine - secretes products directly onto skin
* Reabsorb sodium from secretory coil making product more hypotonic
* Apocrine - secreted products in hair follicle canal
60
Dermatofibroma
* Benign solitary small round firm papule
* Pink/Reddish brown/Hyperpigmented (Variable)
* "Dimple sign"
* Follows injuries to skin like insect bites or inflammed hair follicles, scars
* Lower extremities


