Derm Flashcards
(118 cards)
explain the location of atopic dermatitis

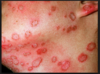
atopic dermatitis

what age group is this found it? what are the three characteristics in a patient that make them higher risk for this? what are three things you might see on this patient? what type of hypersensitivity is this? where is this most commonly found (2) places and 4 others? what must you differentiate from? what is the diagnosis made from?
chronic relapsing skin disoder that starts in children and goes through adulthood
ALLERGY, ALLERGIC RHINNITIS, ASTHMA, PERIORAL PALOR, DENNIE MORGAN LINES, ALLERGIC SHINERS
type 1 IgE mediated hypersensitivity
-dry skin, puritis with “itch scratch cycle” flexor creases (antecubital and popliteal) most common
neck, eyelids, forehead, face, and dorsum of hands and feet, dermatographism characteristic
can be either atopic or contact (touching something you’re allergic to)
*make sure to culture for S. aureus and make sure not secondary infection and HSV in crusted lesions*
DX: IgE serum levels

atopic dermatitis

what are 6 possible treatment options for this?
1. avoid irritants
- skin lubrication/emollients (moistureizers)
3. topical corticosteroids
4. antihistamines
- calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimbus + pimecrolmus)
- UVB phototherapy is effective
for atopic dermatitis….what can you do to figure out what is causing it?
PATCH TESTING!!!
contact dermatitis: allergic

what cells initiati this? what are 5 common causes? what is the difference between the acute and chronic skin presentations?
t-cell mediated, occurs in those that have become sensitized
- common causes: medication, jelwrey, rubber, disinfectants, cosmetics, plants*
acute: erythema, vesicles, eroisions, crusting
chronic: papules, plaques, crusts
**can do patch testing after dermatitis to figure out the cause**

contact dermatitis: non allergic
what is this caused by? (3)
what do the acute and chronic skin presentations look like?
comes from contact with an irritating substance
direct toxin on the skin
common causes: abrasive, cleaning agents, caustic agents
Acute: erythema, vesicles, erosions, crusting
chronic: papules, plaques, crusts
where is the rash for seborrheic dermatitis?

seborrheic dermatitis

what does this occur in? what are the four most common places? what is the most common agent? what does this cause in infants and what does this cause in adults? what do the infected areas look like? what are the 7 treatment options for this?
subacute/chronic inflammation of the areas with increased SEBACEOUS GLANDS
body folds, face, scalp, genitalia
caustitive agent: pityrosporum ovale (yeast)
“cradle cap” in infants, “dandruff” in adults
scattered yellow gray scaly macules and papules with GREASY LOOK!!!
sticky crusts with fissures found behind the ears!!!
Tx:
- OTC dandruff shampoo
- cold tar shampoo
- Ketoconazole
- cradle cap: olive oil compresses, shampoo with sulfur, or ketoconazole shampoo
- UV radiation
6. shampoos with selenium sulfide
7. topical steroids hydrocorisone

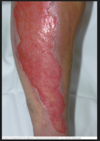
stasis dermatitis

what causes this? what two populations of people is it worse in? the incompetency leads to what 5 things? what does the pt complain of? what 3 things do you see before the skin changes? what are two ways to make the DX and what do you see?
chronic rash on lower legs secondary to venous insufficiency
worse in pregnancy and women
see papules, scales and crusts
valvular incompetency leads to edema, dermatitis, brown stippled hyperpigmentation, fibrosis, ulceration (30%)
pt complain of aching in legs that is worse with standing, relieved by walking
typically see caricose veins, superficial phlebitis, and venous thrombus before skin changes
DX:
- doppler studies, sonography or venography will confirm chronic insufficiency
- biospy-show dilated tortuous veins, edema, and fibrin deposition
dyshidrosis

what type of dermatitis is this and where does it occur? what age group? what is it commonly associated with? what is the funny food it is associated with looking like and what other characteristic is common? what are four triggers? what does it transform in to in late disease (5)? what two things are used to diagnose it?
acute/chronic puritic vesicular dermatitis on palms and soles
purititc, clusters of small vesicles in clusters “tapioca like appearence” on palms/soles
triggers: sweating, emotional stress, warm/humid weather, metals
Late disease: papules, scaling, lichenification, erosions ruptured from vesicles, painful fissures
DX: culture and KOH to rule out dermatophytosis

dyshridrosis

what are the 5 treatment options?
- burrows solution and antihistamines (control itch)
2. topical high steroids
- systemic steroids if severe
4. intralesional triamcinolone
- fissures treated with: collodoin

what are the treatment options for stasis dermatitis?
(6)
1. manage edema
2. topical corticosteroids
3. wet compress for oozing and crusting (caution with ulcers)
- compression stockings
- sclerosis of varicose veins to prevent dermatitis
- vascular bypass, endothelial thermal ablation or stenting (these are only mildy effective)
explain the locations that are common for…:
- acne vulgaris

acne vulgaris
what are the four causes?

1. increased sebum production seen with puberty and increased androgens
2. clogged sebaceous glands
3. propionibacterium acne overgrowth
- anaerobic bacteria that is part of normal flora in the PS unit
- digeste the sebum, but when large plug stimulates baterial for form lipase, this breaks down sebum in to fatty acids which spart inflammation process causing neutrophil attach to follcular wall
4. inflammatory response

Acne Vulgaris
what are the three general types?
- comedomes
2. inflammatory pustules/papules
3. nodular or cystic acne
acne vulgaris
comedomes
what are the two types? explain what causes each.
- open “blackheads”
- infundibulum: hyperkeratosis, comecyte cohesiveness
- androgen stimulations and sebum secretion
2. closed “whiteheads” - accumulation of shed keratin and sebum
- formation whorled lamellar concentrations
what are the ratings for acne severity? (3)
what are the meds associated with each?
mild: comedones +/- small amounts of pustules retinoids, azelaic acids, salicyclic acid
moderate: comedones larger amounts of pustules and papules topical trentoin, erythromycin, clindamycin
severe: nodular or cystic oral minocycline, tetracycline, doxy, Isotrentoin
erythmatotelangiectatic rosacea
what is it
facial flushing with telangiectasis, central face edema, SPARES PERIORBITAL AREAS

papulopustular rosacea (PPR)
central face erythema with papules and pustules, less often stinging
SPARES THE PERIORBITAL AREA

Phymatous rosacea
what is it and where does it occur?
follicular orficies thicken!!!! get nodularities that are disfiguring!
more common in men
get a rubery thickening of skin of the nose, chin, forehead, eyelids, or ears

what are the treatment options for acne vulgaris? (6) options
- benzyl peroxide
- topical antibiotics (clindamycin, erythromycin, dapsone)
- azeleic acid-unique plant derived compound that has anti-bacterial and anti-comedogenic properties
- salycyclic and glycolic acids gels and washes
- topical retenoids-adapalenes (differin), tretoin, and tazarotene
- oral antibiotics minocycline, tetracycline, doxy! these are different than the topical abx!!
- isotretinoin-drastically attentuates acivitt of sebaceous glands and rate of keratinization in epi ONLY DERM CAN DO THIS HIGHLY TETRAGENIC!!!!
*****notice there is a difference between oral and topical antibiotics*******
rosacea
what is this caused from? who is this most common in? what can be triggers for this? what are 4 unique presentations to this? what distinguishes this from acne? what are the 5 treatment options?
conrtoversy if cause is from inflammation or infectious
most common in fair skinned individuals
triggers: hot/cold,, HOT DRINKS, hot baths, spicy foods, ETOH, emotions
flushing and telangiectasis are key features of disease!!! causes phyma (enlargement of random area of the body), symmetrical presentation can have facial burning or stining, dry appearance, occular manifestifestations
***absense of comedones, distinguishes it from acne***
TX:
- topical metronidazole sodium, sulfacetamide, sulfur, erythromycin
- systemic abx: minocycline, doxy, metronidazole
- isotrentinoin
- ivermectin (anihelminthic)
- surgery for phyma
cellulitis

where does this infection occur? what are the 3 organisms most likely to cause this in adults? what are the 3 organisms likely in kids? what are the 5 symptoms the patient will experience? what is the strange animal you can get this from? what do you do to DX this?
acute, spreading inflammation of the dermis and subcuteous tissues, occurs from breaks in the skin
adults: s. aureus, group A strep can get it from cat bite pasturella mulicida
children: hae. influenzae (periorbital), strep pneumoniae, s. aureus
expanding, red, swollen and tender, FEVER!! HEAD!! LYMPAHDENOPHATHY!! EDEMA!! NOT sharply demarkated…pt feels ILL
DX: culturing and drainage of discharge by needle aspiration