Derm Flashcards
Papules and paulopustules. OPen and closed comedones.

Acne vulgaris
Acne pathogenesis
Microcomedone
Comedone
Inflammatory papule/pustule
Nodule
What must be present to Dx acne?
Comedones.
Facial flushing, telangiectases, central face edema, burning, stinging; spares periorbital areas
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR)
Central face erythema with papules/pustules; edema of skin; less often burning, stinging; flushing less severe; spares periorbital areas
Papulopustular rosacea (PPR)
Patulous follicular orifices, thickened skin, nodularities; and in men, phyma - rubbery thickening of skin nose, chin, forehead, eyelids, or ears
Phymatous rosacea
Initial presentation in ~20%; more often occur after an above type; most often blepharitis; also conjunctivitis, iritis, scleritis, hypopyon, keratitis
Ocular rosacea
Possible rosacea triggers
Hot or cold temperature, exercise, cosmetics
sunlight, spicy food, topical irritants
wind, alcohol, menopausal flushing
hot drinks, emotions, medications
Rosacea stage 1
Persistent erythema with telangiectases
Rosacea stage 2
Persistent erythema, telangiectases, papules, tiny pustules
Rosacea stage 3
Persistent deep erythema, dense telangiectases, papules, pustules, nodules, rarely persistent “solid” edema of central face
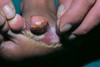
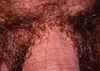
Chronic diseas of unknonw etiology. Very tender, red, inflamed nodules/abscesses. May contain double comedones.
Distributed to axilla, breast, groin.

Hidradenitis Suppurativa
May occur minutes afte exposure. lesions range from erythema to vesiculation to necrosis.

Irritant contact dermatitis
Delayed, cell-mediated hypersensitivity rxn

Allergic contact dermatitis
Poorly defined erythematous patches with or without scales. Found on flexor surfaces. Usually begins in infancy.

Atopic dermatitis
Solid plaque of lichenification, arising from a confluence of small papules. Excoriations are often present.
Lichen simplex chronicus
Sudden onset of many deep-seeded, pruritic, clear, tapioca-like vesicles

Dyshidrosis
Management for dyshidrosis
Burow wet dressings
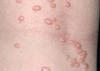
Chronic, pruritic, inflammatory dematitis in the form of coin-shpaed plaques composed of grouped small papules and vesicles on an erythematous base
Nummular eczema
Common, chronic dermatitis characterized by redness and scaling and occuring where sebaceous glands are active

Seborrheic dermatitis
T-cell mediated papulosquamous disease
Psoriasis
Common areas for psoriasis breakouts
Extensor surfaces
sacrogluteal region
scalp
palms/soles
*Often bilateral and symmetric
Three most common psoriasis subtypes
Chronic stable plaque psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis
Palmoplantar pustular psoriasis
What do you call psoriasis that presents on the groin or genitals?
Inverse psoriasis
What test should you perform if you suspect guttate psoriasis?
Throat culture (looking for strep)
Raindrop psoriasis

Guttate
Middle to older aged patient with history of mild chronic stable plaque psoriasis who gets a nasty URI and has sudden guttate flare.
Prognosis?
Good prognosis for return to baseline after treatment with antibiotics
Young adult without prior history of psoriasis gets nasty URI and has sudden guttate flare
Prognosis?
Guttate lesions often slow to improve with slow shift into chronic plaque psoriasis.
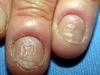
Velvity thickening anf hyperpigmentation related to heredity, obesity, endocrine disorders, drug administration, and maligancy

Acanthos Nigricans
Bullous automimmune disease usually seen in the elderly.
Bullous pemphigoid
Often the first location for bullous pemphigoid to appear
Lower legs
Oval, slightly raised plaques. Salmon-colored and often begins with a Heald patch

Pityriasis Rosea
This lesions is a:
purple
polygonal
pruritic
planar
papule

Lichen planus
Comon rxn pattern of blood vessels in the dermis with secondary epidermal changes. Most cases related to HSV infection.

Erythema multiforme
Necrotic epidermis and sloughing covering <10% BSA

Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Epidermal necrosis and sloughing >30% BSA

Toxic epidermal Necrolysis
Located in derma-epidermal junction
Macules or may be slightly raised

Junctional nevus
Located in papillary dermis
Raised lesions

Compound nevus
Epithelial lining of a hair follicle
Assymptomatic
May grow to max 3 cm
Central pore
Usually face, neck, upper trunk

Epidermoid cyst
Benign subcutaneous tumor- between skin and underlying muscle layer

Lipoma
Most common benign epithelial tumors.
Warty plaque with a “stuck on” appearance
Seborrheic keratosis