Defining The Pelvic Region Flashcards
(38 cards)
•The four bones that together* make the pelvis (os coxa/ hip bone):
1. Two innominate bones: ilium, ischium and pubis
The innominate bones, also known as the hip bones or os coxae, are the fused bones of the pelvis either side of the sacrum. The bone comprises the ischium, pubis and ilium which are fused to each other in the acetabulum and are part of the appendicular skeleton
2. Sacrum, formed by the fusion of the 5 sacral vertebrae
3. Coccyx, formed by the fusion of the 4 coccygeal vertebrae

The innominate bones

The primary joints of the pelvis are the
1. sacro-iliac joints ; The sacroiliac joint is a secondary cartilaginous joint
2. pubic symphysis; The pubic symphysis is a fibrocartilaginous disc

During standing, Weight is transferred from the axial skeleton to the
ilia via ligaments.

During the sitting, Weight is transferred from the axial skeleton to the
the ischial tuberosities (aka), the sitting bone

The pelvic brim
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet and its formed by the;
1. Promontory and ala (wing) of the sacrum (White/black line)
2. Right + Left linea terminalis:
a) Arcuate line (blue line) - Marks the transition between the wing and the body of the ilium and also form part of the border of the pelvic inlet.
b) Pectineal line (green line)
These are bonny landmarks associated with the ilium.

Ligaments of the pelvis
1. Sacroiliac
2. Sacrococcygeal
3. Sacrospinous
4. Sacrotuberous

Sacroiliac ligament
between the sacrum and the ilium, has an anterior and posterior components

Sacrococcygeal ligament
between the sacrum to the coccyx

Sacrospinous Ligament
between the ischial spine and the sacrum/coccyx

Sacrotuberous
posterior to the sacrospinous; between the lateral aspect of sacrum + coccyx onto medial margin of ischial tuberosity

The perineum
•Refers to the space located at the pelvic outlet and inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (ie muscles of the pelvic floor)
- It can be said to describe the narrow region between the thighs
- Diamond-shaped surface extending from the mons pubis (in females) to the medial surface of the thighs and posteriorly to the gluteal folds

• A transverse line joining the two ischial tuberosities splits the perineum into two triangles:
1. Urogenital
2. anal triangles
- The midpoint of this line defines the perineal body
- The perineal body sees the convergence of several sphincter and perineal pouch muscles

Male perineum

Perineal Spaces
The space bounded above by the perineal membrane and below by the superficial perineal fascia and containing the root structure of the penis or clitoris.
The arrangement of the fascial layers in the pelvis * create two potential spaces- the superficial and deep perineal spaces.
But- they are not empty spaces, they each contain certain structures. *details of which you do not need to know for 203.

Superficial perineal pouch
• Superficial perineal pouch is a space between the perineal fascia and the perineal membrane.
It contains:
•Males: Root (bulb and crura) of the penis and ischocavernosus and bulbospongiosus
•Females: Clitoris and ischocavernosus and bulb of vestibule (bulbospongiosus), greater vestibular gland
•Urethra
•Superficial Transverse perineal muscle
•Pudendal Vessels
Deep perineal pouch
• Deep perineal pouch is deep to the perineal membrane.
It contains:
- Males: Bulbourethral glands, dorsal neurovasculature of the penis
- Females: Dorsal neurovasculature of the clitoris
•Urethra and external urethra sphincter
•Ischioanal fat pads
•Deep Transverse perineal muscle- maybe more of a smooth mass in females- associated with the perineal body.

Borders of The pelvic cavity (true)
1. Posterior – sacrum/coccyx
2. Anterior – pubic symphysis
3. Inferior – pelvic floor
4. Superior – pelvic brim
5. Lateral – obturator internus muscle

Contents of the pelvic cavity (true)
1. Reproductive organs/tracts
2. Bladder
3. Rectum

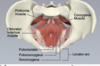
Muscles that line the wall of the pelvis
1. Piriformis
2. Obturator internus

-muscles that line the floor of the pelvis
- Coccygeus
- Levator ani (iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus and puborectalis)
Arteries of the Anterior division of internal iliac supply
1. Superior artery
2. vesical artery
3. inferior vesical artery
4. uterine artery
4. vaginal artery
5. obturator artery
6. internal pudendal artery
7. middle rectal, inferior gluteal) artery

Arteries of the posterior division of internal iliac supply
1. Iliolumbar artery
2. lateral sacral artery
3. superior gluteal artery

Gonadal artery
The gonadal arteries are paired vessels that usually originate from the abdominal aorta at the level of second lumbar vertebra. In 5-20% of cases, the gonadal artery has a high origin (superior to L2) and in 5-6% of cases it originates from the main or accessory renal artery.













