cytoskeleton II 2.4 Flashcards
(17 cards)
during mitosis, what role does kinesin and Dynein play compared to actin and myosin II
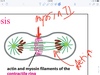
Kinesin and Dynein is involved in spingle assembly because they are associatd with microtubules. Myosin two and actin form the contractile ring
what role does actin play in morphogenesis?
to form the neural tube, actin filaments form an adhesion belt across the epithelial tissue. contrating of myosin two leads to invagination and the formation of the neural tube

what do all three cytoskeletal motors have in common?
they are all ATPases. this time ATP IS hydrolysed to aid the movement unlike in polymerization of actin and microtubules
what is the difference in directionality of vessicles as compared to motors?
vessicles can move in either direction but any specific motor is capable of moving only in one direction.
how are the myosins classified?
based on their variable tail region

explain the role myosin plays in cytokinesis
myosin forms the contractile ring in mitosis, thus it is in charge of physically separating the two cells.
where are you most likely to find Dynein doing work?
found in ciliary and flagellar arms necessary for beating. also functions as transport of mRNA, vesicles, organelles and viruses

which motor protein has a neck and stalk region and what are they there for?
neck- determins polarity
stalk- for dimerization
what is the disease associated with dynein associated diseases and what is the manifestation?

primary ciliary dyskinesia leading to dynein being in the wrong location. this leads to immotile cilia. if you look closely at the picture, you will see the dynein arms are missing

what are the steps of kinesin movement on the microtubule
When kinesin encounters a microtuble, it binds tightly. then it kicks off its ADP and replaces with ATP. the binding of ATP makies the kinesin to microtubule binding strong! to move, it must hydrolyse ATP and form ADP thus on one head at a time and moves one head at a time
what releases myosin from actin and causes the power stroke
the binding of ATP
what weakings the head binding in kinesin walking?
Pi dissociating from the trailing head weakings the head binding to microtubules
what determins what cargo can bind to a motor proteins
the variable tail region which is different in different isoforms

which proteins are involved in intracellular motility that requires polymerization vs. molecular motors
cell movement for the most part requires polymerization of microtubules. actin is involved in scafolding of microvilli but movement of organelles or contraction of muscles require motors like kinesin and myosin
what are the functions of myosin 1,2 and 5
- scafold for microvilli
- muscle contraction and contratile rings during cytokinesis
- carries cargo

how can vesicles be transported inside the cell both when motor proteins are used vs. when they are not used
if motor protiens are not used, the transport can happen on the plus end of a microtubule. if a motor protein is used, you can transport it both forwards and backwards using Kinesin and dynein. vesicles can travel on both microtubules and actin
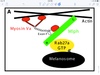
which protein mediates myosin 5 binding to melanin vesicle
Rab27aGTP