CVS Flashcards
describe the presentation of the condition seen in the image
- presentation = classic sudden death from arrhythmias (athlete that collapses and dies)
- exertional dyspnea
- diastolic dysfunction
- decreased LVEDV and decreased stroke volume → normal EF

describe symptoms of the acute vs. subacute form of the condition seen in the image

- acute:
- high fever
- splinter hemorrhages
- no splenomegaly
- no finger clubbing
- no anemia
- subacute
- low-grade fever
- splenomegaly
- finger clubbing

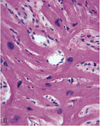
describe what is seen in the image


describe the presentation of the condition seen in the image

- presentation:
- becomes apparent 6 months after birth (once fetal Hb decreases, since fetal Hb binds O2 with higher affinity)
- tet spells (squatting)
- afterload increases to reverse the shunt (L → R) → cyanosis transiently improves
- single S2 → no sound from pulmonic valve
- large VSD → no murmur

describe the image

Wegener/GPA
lung from a patient with granulomatosis with polyangiitis, demonstrating large nodular cavitating lesions
describe what would be seen on x-ray in the condition seen in the image

x-ray: widening of mediastinum since the blood collects in the media

describe the complications of the condition seen in the image

- complications:
- arrhythmias → HF

describe the treatment for the condition seen in the image

treatment = large aneurysms → surgically replaced by prosthetic grafts

describe what is seen in the image


describe the condition in the image and how & when it occurs

occurs 3-14 days post-MI
-
papillary muscle rupture: severe mitral regurg. → pulm. veins → pulm. edema
- pan-systolic murmur loudest at apex (at the mitral valve)

describe the 2 types of the condition seen in the image

- 2 types:
-
transmural: full thickness of ventricular wall; associated with plaque disruption & superimposed completely occlusive thrombosis
- STEMI
-
subendocardial: inner 1/3 to 1/2 of ventricular wall;
- commonly caused by hypovolemic shock due to a gunshot wound
- subendocardium is a watershed area and receives blood last → infarction alone tends to be due to ischemia rather than complete occlusion of an artery
- NSTEMI
-
transmural: full thickness of ventricular wall; associated with plaque disruption & superimposed completely occlusive thrombosis

describe the presentation of the condition seen in the image

- presentation: most commonly asymptomatic
- incidental finding of a pulsatile and expansile abdominal mass or on ultrasound/CT

describe the organisms involved in the acute vs. subacute form of the condition seen in the image

- acute
- S. aureus in normal valves
- most common among IVDU → tricuspid valve
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa 2nd most common in IVDU
- candida in IVDU
- S. aureus in normal valves
- subacute
- S. viridans in abnormal valves → good prognosis w/ antibiotics
- S. bovis → tricuspid involvement + colon cancer
- HACEK group



describe investigations for the condition seen in the image

- investigation: ECG → will see unfused valve leaflets and LVH
- systolic ejection click followed by crescendo-decrescendo murmur → radiates to carotids

describe what is seen in the image


describe the condition in the image and how & when it occurs

occurs after scar is fulled formed
- left ventricular aneurysm after full formed scar
- stasis → mural thrombus → arrhythmia + embolism → most common place is legs, brain

describe the pathogenesis of the condition seen in the image

- pathogenesis:
- antero-superior displacement of the infundibular septum moves towards the RV → drags the aorta with it → overriding RV → creates large VSD

describe what is seen in the image


describe the type of hypertrophy seen in the image

- HCM = concentric hypertrophy → impaired diastolic filling → LV-outflow obstruction → anterior leaflet of MV

list other risk factors for the condition seen in the image

- other risk factors:
- homocystinuria, lipoprotein a, increased PA-1 inhibitor, CRP, decreased estrogen

describe investigations for the condition seen in the image

- investigations:
- markedly elevated ESR (>100) → nonspecific marker of inflammation
- temporal artery biopsy: the disease is focal and skips so need to take a segmental biopsy
- elastic trichrome stain
- negative biopsy does NOT rule out the disease

describe the most common form of the condition seen in the image and what it is associated with

membranous VSD is the most common VSD
- L → R shunt but most close with age
- associated with trisomy 21, 13, 18
- incidental finding on ECG

describe the unstable form of the condition seen in the image

- unstable = usually rupture → lefts off the cap and exposes core to lumen
- moderately stenotic (50-75%)
- thinner fibrous cap
- core rich in lipids, T cells and macrophages
-
less smooth muscle prolif.
- smooth muscle makes the collagen for the fibrous cap
- eccentric






















































































































































































