Cranial Nerve Testing Flashcards
(49 cards)
How to test CN1 (olfactory):
- Recognition of odors (avoid irritants).
- Test one nostril at a time.
- Be sure you are testing CN I and not CN V (olfaction, not general sensation).
Using a caustic substance when testing the olfactory nerve will stimulate:
- CN5: trigeminal general sensory innervation of the nasal mucosa
How to test CN2 (optic) visual field:
- Examiner holds one eye, patient holds same eye.
- Look at each other noses.
- Examiner brings hand from periphery while wiggling finger.
- Should see at same time.

Why is the finger moved/wiggled when testing the visual field?
- Rods detect peripheral vision.
- Rods are not good for visual acuity, but are very good for detecting movement.
Draw visual field diagram with optic chiasm:

What would this lesion lead to?

right anopsia
What would this lesion lead to?

left homonymous hemianopsia
What would this lesion lead to?

bilateral heteronymous hemianopsia
What kind of vision loss would occur from the pituitary gland tumor impinging the optic chiasm from below?
Bitemporal Heteronymous Hemianopsia
Type of pupil constriction in the eye the light is shined into during a pupillary reflex test:
direct constriction
Type of pupil constriction in the eye the light is NOT shined into during a pupillary reflex test:
consensual constriction
Pupillary light reflex afferent and efferent limbs:
- Afferent: CN2 (optic). Detects light.
- Efferent: CN3 (oculomotor). Causes pupillary constriction.
What kind of brain herniation will lead to a fixed, dilated pupil?
uncal herniation
Steps in uncal herniation:
- increasing intracranial pressure in supratemporal compartment pushes brain downward
- uncus herniates from supra-tentorium compartment into sub-tentorium compartment via tentorial notch.
- CN3 compressed against the brain stem (parasympathetics first).
- loss of pupil constriction.

What does the uncal herniate over to get from the supra-tentorium compartment into the sub-tentorium compartment?
tentorial notch

How to test both CN3 inferior and superior divisions:
capital H
How to test both CN3 inferior division only:
convergence/accomodation reflex
Accomodation reflex components and cranial nerves involved:
- convergence of eyes (CN3-inf; medial recti)
- thickening of lens (CN3-inf; parasympathetics)
- pupil constriction (CN3-inf; parasympathetics)
Oculomotor palsy will lead to:
- lateral strabismus
- (medial rectus will be paralyzed)
Abducens palsy will lead to:
- medial strabismus
- (lateral rectus will be paralyzed)
Label sensory innervation:
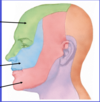

Sensation above the eyes:
V1: ophthalmic division
Sensation between eyes and mouth:
V2: maxillary division
Sensation below the mouth:
V3: mandibular division


