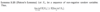Convergence of random variables Flashcards
What is the Markov Inequality lemma?
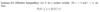
Prove the following lemma.
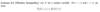

Define converges pointwise or surely.

Define converges to X in probability.

Define converges to X almost surely.

Define converges to X in the mean or in L1.
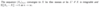
Define converges in Lr.

What are the main four types of convergence?
- In probability
- Almost surely
- In the mean/ in L1
- In Lr
What does the term almost surely mean?
It means that something occurs excpet on an event with probability zero.
What is convergence in probability similar to?
Convergence almost surely - except it is weaker
What is the sum convergence lemma?
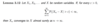
Prove the following lemma.


What is the lemma about convergence in Lr and convergence in probabiliity?

Prove the following lemma.
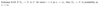
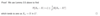
What is the lemma about convergence in probability and convergence almost surely?

Prove the following lemma.
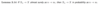

Does the converse to this lemma apply?
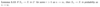
No - convergecne in probability does not imply convergence in L1 or Lr.
Does the converse to this lemma apply?
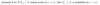
No - convergence in probability does not imply convergence almost surely
What is the weak law of larger numbers theorem?

Prove the following theorem.

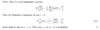
Why is the weak law of large numbers called weak?
Because the convergence is in probability
Why is the strong law of large numbers called strong?
The convergence is almost sure
What is the Cauchy-Schwarz theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


What is the strong law of large numbers theorem?

Prove the following theorem.


What is the Monotone Convergence theorem?

What are three important remarks of the following theorem?
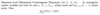

What is a corollary to the following theorem for nonnegative decreasing sequences?


Prove the following corollary.


What is the Dominated Convergence theorem?

What is the bounded convergence theorem corollary?

Prove the following corollary.


What is Fatou’s Lemma?
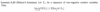
Prove the following Lemma.