Condensed Matter Physics Flashcards
How do you find the volume of the primitive cell?
- Need the primitive translation vectors of the crystal lattice a1, a2, a3
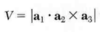
How do you find the primitive translation vectors of the reciprocal lattice b1, b2, b3?
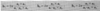
What is the structure factor?
- fj is the atomic form factor
- generally for the basis, f is used for the form factor of the atom (that is identical in the basis)
- xj, yj, zj are the posns in the basis of the idential atoms
- e.g. for the bcc basis atoms are identical at 0, 0, 0 and 1/2, 1/2, 1/2
- so S(v1v2v3) = f{1 + exp[-π(v1+v2+v3)]}
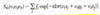
How do you calculate the structure factor for a certain structure?
What is the atomic form factor?
What is the atomic form factor if charge distribution is spherically symmetrical about the origin?
How to calculate the interplanar distance?
What is the equation for electric conductivity?
Why is the KE of a free e- at corner of first zone higher than that of an e- at midpoint of a side face of the zone in 2D? By what factor is it higher? And what is the factor in 3D?
How do you calculate the Fermi energy and density of states of a free e- gas in 1D and 2D?
What are the energy eigenvalues of a 3D gas of free e-s at 0K?
What is the relation connecting pressure and volume of an e- gas at 0K?
What are 2 ways of entering reciprocal space?
- diffraction
- Fourier analysis
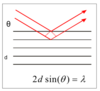
What is Bragg’s law?
How do energies of photon, neutron and electron compare? And what does wavelength vs energy graph look like?
- photon energy = keV
- neutron energy = 0.01 eV
- e- = 100 eV
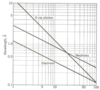
What is extinction?

What is a Brillouin zones?
What is spallation?
- fast protons e.g. 1 GeV approaching Pb
- intra-nuclear cascade with cascading particles then inter-nuclear cascade
- or highly excited nucleus
- then evaporation
- [still don’t really know what this is]
What is fission? Why are neutrons used? [don’t know why there are words listed under neutrons]
- neutron hits 235 U then fission of excited nucleus
- chain reaction by moderated nucleus
- neutrons
- light elements
- magnetism
- high penetration
- dynamics
What is a coolidge tube?

What is a rotating anode?
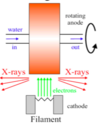
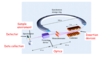
What is a Synchrotron?
What is brilliance in X-ray? And Moore’s law?
What do the width, area, position and background of a counts vs θ-θBragg show?
- posn => unit cell
- area, intensity => atomic arrangement
- width => corrections
- background => defects
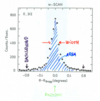
How are Debye-Scherrer Cones scattered?
- powder diffraction
- scan 2θ or λ then use Bragg’s law (λ=2dsinθ)
What is Low Energy Electron Diffraction (LEED)?
What are the different types of bonding?
- van der Waals e.g. crystalline argon
- neutral atoms with closed e- shells
- fluctuations in charge distributions
- ionic e.g. sodium chloride
- e-s transferred and ions held together by attractive electrostatic forces
- metallic e.g. sodium
- valence e-s taken from alkali atoms to form a communal e- sea
- covalent e.g. diamond
- overlapping parts of e- distribution
What are the different of solids?
- amorphous
- no recognisable long-range order
- polycrystalline
- completely ordered in segments
- grain/domain
- grain boundary
- completely ordered in segments
- crystal
- entire solid made up of atoms in orderly array

What is the difference between conventional and primitive cells?
What are the five distinct 2D Bravais lattices?
- oblique
- square
- triangular
- rectangular
- centred rectangular
What are the 14 Bravais lattices in 3D? 4 types of unit cell( P = primitive, B = body-centred, F = face-centred, S = side-centred) + 7 crystal classes
- cubic
- P, B, F [most important]
- tetragonal
- P, B
- orthorhomic
- P, B, F, S
- hexagonal
- P
- trigonal
- P
- monoclinic
- P, S
- triclinic
- P
Give examples of simple cubic, BCC, FCC, Hexagonal Closed Packed (HCP), diamond lattice, zinc blende structure
- simple cubic (rare) e.g. Po
- BCC e.g. Na, K, Fe, V, Cr
- FCC e.g. Al, Cu, Ni, Au, Pt, Ir, Ar, Xe, Kr
- HCP: ABABAB
- FCC: ABCABC
- Zn, Ti, Co
- diamond e.g. C, Si, Ge
- zinc blende structure e.g. GaAs, GaP, InAs + many more
*
What are nanowires?
- zinc blende: ABC
- twin: BAC
- wurtzite: AB
What do (100), (110), (111), (200), (1-00) planes look like in a cubic crystal?

How does thermal evaporation work?
- high vacuum created by diffusion pump; backed by rotary pump
- filament boat filled with evaporat
- clamps connected to high current source
- path of vapour is upwards towards the substrate holder and sample
- crystal detector is on top of the sample where the substrate table is
- glass bell jar contains the vapour
How does sputtering work?

How does Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD) work?

How does melt spinning work? Amorphous metals

How do you grow crystals?
- silicon does not occur alone in nature (man made)
- heating SiCl4 in hydrogen atmosphere to yield pure Si (polycrystalline)
- SiCl4 + 2H2 -> 4HCl + Si
- two methods to turn polycrystalline Si into single crystalline Si ingot
- Czochralski (CZ)
- melt high purity Si in a quartz crucible
- dips one end of seed on molten liquid
- seed slowly rotated and pulled
- by controlling temp. difference, seed crystal slowly grows
- Float zone (FZ)
- keep poly-Si rod and seed crystal vertically face to face
- partially melt by inducted heating from high RF power
- molten zone is rotated and gradually moved up
- entire polycrystalline rod is converted to single crystal
- Czochralski (CZ)
What is molecular beam epitaxy?

How do you grow nano wires?
- flux of gold condense to nanosize particles at surface of wafer
- enhanced growth of III and IV materials catalysed by gold particles
- freestanding III-V NWs with diameters specified by the catalyst
- what does NWs stand for? what are III and IV materials?
How does Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) work?

What are the defects and dislocations in crystals?
- edge dislocation
- Schottky
- Frenkel
- screw dislocation
What is there to know about impurities and alloys? What are ordered alloy phases?
- solid soln
- Si/Ge
- immiscible
- Ag/Cu
- ordered alloy phases
- disordered Cu3Au (“average” gold-copper atom)
- disordered because can’t distinguish?
- ordered; can tell gold and copper atoms apart (copper at centre of faces)
- I-tetragonal (what is this?)
- AuCu (copper at centre of sides instead of fcc)
- disordered Cu3Au (“average” gold-copper atom)
What is the Dulong and Petit heat capacity?
- older than Einstein model (1907) and Debye model - acoustic phonons (1914)

What is the dispersion relation?

What are phonons?
- Quasiparticles in QM that describe a quantised mode of vibration in a solid
- like sound-particles (oversimplified)
What are optical modes? What are acoustical modes?
- figure shows a transverse optical and acoustical acoustic waves in diatomic linear lattice; particle displacements at same wavelength

What are optical and acoustical branches of the dispersion relation for a diatomic linear lattice? And the limiting frequency?
- limiting frequencies at K=0 and K = Kmax = π/a
- lattice constant a

What is inelastic neutron scattering?
- triple axis geometry

What is lattice energy and specific heat?
- Dp(ω) = density of states

What is the Born-von Karman periodic boundary condition for linear chain?
- u ( [N+1] a) = u(a); u(0) = u(Na)
- like a ring
- length L=Na
How do you integrate in 2D square lattice with Fourier space? [answer doesn’t really explain it tbh]
- allowed values in Fourier space of phonon wavevector K for square lattice of lattice constant a
- periodic boundary conditions applied over a square of side L = 10 a
- one allowed value of K per area (2π/L)2 = (2π/10a)2
- so within circle of area πK2, number of allowed points is πK2(L/2π)2

What is the Debye model?
- assume only acoustic wave excited
- ω = vk

How does thermal expansion occur?
- as temp. increases, atomic vibration amplitude also increases
- cause an increase in bond lengths (avg. distance betwen atoms)
- hence leads to thermal expansion

What is thermal conductivity?
- it is similar betwen an ideal gas and phonons

What is the difference between normal process and Umklapp process in thermal conductivity?
- normal process
- G=0 => cause 0 thermal resistance directly
- Umklapp process
- G = reciprocal lattice vector = 2π/a hence not zero => cause thermal resistance
- selection rules
- K1 = K2 + K3 + G
- ћω1 = ћω2 + ћω3
- Dependance on crystal size (curve moves up before the peak)

What are trapped ion chains?
- EM fields in a “Paul trap” hold a small number of atomic ions in free space
- ions repel each other due to Coulomb interactions i.e. their motion is coupled
- ions can be interrogated and “kicked” using laser beams
How are phonons be used for “quantum logic” clocks?
- “quantum logic” clocks is an optical atomic clock: tune laser to a transition frequency of an ion & count oscillations of laser’s light field
- know laser is at resonance with atom
- when transfer electronic excitation from Al+ to Be+ using a “phonon bus” (excite Al+ if at resonance then convert into phonon then convert to Be+ excitation)
- know laser is at resonance with atom
How are electron gas formed?
- isolated atom have valence atoms
- whereas in a metal, nucleus and ion core retain their configuration in the free atom
- but valence electrons to form electron gas?
What is the Drude Model in Ohm’s law?

What does the Fermi-Dirac distribution look like at different temps?

What are the electronic states in reciprocal space (is that k space)?
- what’s k anyway?

What are the equations for Fermi wavevectors, Fermi energies and Fermi velocities?

What is the density of states (based on Fermi energy?) as a function of ε (which I’m guessing is energy)?

What is X-ray emission spectroscopy? What is photoelectron spectroscopy?
- width of the spectrum = Fermi energy
What is the specific heat of the electrons?


How do specific heat capacities of silicon and copper compare in Dulong and Petit law and Debye model?

What is a Fermi sphere?
- encloses occupied e- obritals in k space in ground state of e- gas?
What is the Drude-Sommerfeld Model?
- eqm Fermi surface has empty states below Fermi energy
- a displaced Fermi surface has full states above Fermi energy
- displacement is eEτ/ћ

What is the Umklapp process?
- electron-phonon scattering
- 2 Fermi spheres in adjacent zones
- construction shows the role of phonon umklapp processes in electrical resistivity

What is the Hall effect? Give its equation of motion.
- B field applied in z direction
- section perp. to z axis; drift velocity starts up
- then section perp. to z axis; drift velocity in steady state when Ey occurs

What happens to the Hall effect in steady state?
- steady state => d/dt = 0

What is the Hall coefficient?

What is Weidemann-Franz law?

What do the energy bands diagrams for metals, semiconductors and insulators look like?

What is Bloch’s theorem?

What is the general solution to the central equation?

What is the nearly free electron model?

How do you measure band structures?
- angle resolved photoemission
How do you construct 2D Fermi surfaces?
What is the effect of weak potential?
What is LCAO?


