Comparing Means and Proportions Flashcards
(23 cards)
Define Hypothesis test.
estimate the probability of obtaining the observed result, or one more extreme, f there is no true difference (P-value) –> use this informaiton to make decisions about the population
Paired vs. Unpaired data
- paired examples
- pre-post comparison
- cross-over trial (patients randomized to sequence of interventions; ex. race car drivers)
- matched case-control study
- twin study
- unpaired examples
- “traditional” randomized controlled trial
- epi study without matching
When to compare means, medians, or proportions?
- Compare Means: continuous, normally distrubuted data
- Compare Medians:
- continuous, not normally distributed data
- ordinal data
- Compare Proportions:
- ordinal data
- nominal data
What test do you use to compare means of normally distrubuted continuous UNPAIRED data?
unpaired t test
Unpaired T Test
- two-sided test, alpha = 0.05 (used to determine if p value is low enough for significance)
- H0: meanexperimental - meanplacebo = 0
- HA: meanexperimental - meanplacebo does not = 0
- find test statistic (difference in means/ SE of means), look up P-value in t table
What test do you use to compare medians (of non-normally distributed continuous UNPAIRED data OR of ordinal UNPAIRED data)?
Mann-Whitney U/ Wilcoxon rank-sum
Mann-Whitney/ Wilcoxon Test
- nonparametric test
- H0: Medianexperimental - Medianplacebo = 0
- same procedure as unpaired T test, but uses medians and a different table
Why use a nonparametric test?
- less sensitive to outliers
- don’t require a normal distribution
- good for ordinal data as well as interval/ratio data
- less powerful when using normally distrbuted data or complex hypotheses
What test do you use to compare means of normally distrubuted continuous PAIRED data?
Paired t test
Paired T test
What test do you use to compare medians (of non-normally distributed continuous PAIRED data OR of ordinal PAIRED data)?
Wilcoxon signifed rank test or Sign test
Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test
- H0 : median differences = 0
- nonparametric test
What test do you use to compare medians (of ordinal OR of nominal UNPAIRED data)?
Z test, Chi square, or Fisher’s exact
Z Test

Chi Square Test
- can be used to compare many different proportions (very vertasile for study design, not possible with T test)
- not useful for small sample size
- calculate expected frequencies as if the null hypothesis is true
- take overall percentages and apply to the experimental/ control groups
- calculate (observed-expected)2 / expected for each cell, sum resulkt across all cells
- look us results in chi square table
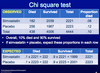
Chi Square & Epidemiological Studies (define null hypothesies)
- H0: p1 = p2; Ha: p1 ≠ p2
- Cohort study
- Odds ratio = p1/p2
- H0: If p1 = p2, p1/p2 = 1
- Risk difference = p1 – p2
- H0: If p1 = p2, p1 – p2 = 0
- Odds ratio = p1/p2
- Relative risk = p1/p2
- H0: If p1 = p2, p1/p2 = 1
Fisher Test
- good for small sample in one of the categories
- consider all possible 2x2 tables with the same row and column totals as your table
- how many of these are at least as extreme as your table?
What test do you use to compare proportions of ordinal or nomial PAIRED data?
McNemar’s Test
McNemar’s Chi Square Test
- chi square test, but use binomial categories
- ex. kids who have symptoms/ no symptoms at 12 and 14
- Does prevalence change with age?
- H0: Page 12 = Page14
- HA: Page 12 ≠ Page14
- α = 0.05, 2-sided test
- ex. If no change in prevalence, expect the same number of kids to switch from “no symptoms” to “symptoms” as vice versa
- use difference between kids who switched from symtoms to none from 12 to 14 and from none to symptoms from 12 to 14 to calcualte X2 value
ANOVA
- used to compare means in 3 or more groups of unpaired data
- Example:
- H0: no difference (rousuvastatin - atorvastatin = simvastatin)
- H0: rosuvastatin = atorvastatin
- H0: rosuvastatin = simvastatin
- H0: simvastatin = atorvastatin
- multiple comparisons can result in a higher chance of a result coming back significant even if it is not –> can use special adjustments, but this lowers power of statistical test (increases type II error)
Statistical vs. Clinical Significance

What does a P-value below 0.05 mean?
- we are unlikely to get this result purely by chance
- however, this result could occur w/ biased study
- gives no information about clinical significance
Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence!!!
- Just because you can’t reject the null hypothesis does not make it true


