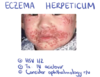
common dermatological conditions Flashcards
define macule vs papule?
What about a bulla or a nodule?
Macule–> FLAT area of altered colour (ex freckles)
Papule–> solid RAISED lesion <0.5cm in diameter
nodule–> solid RAISED lesion >0.5cm in diameter
bulla–>raised, clear fluid filled lesion >0.5 cm in diameter
types of skin infection based on pathogen type (ex virus etc:)
· Bacterial
- Impetigo
- Cellulitis/erysipelas
· Fungal
- Tinea (mold – dermatophyte/ringworm)
- Candida (yeast)
- Pityriasis versicolor (yeast
Viral
- Shingles - Herpes zoster
- Chicken pox - Varicella zoster
- Warts – HPV
· Parasite
- Scabies
Acne Vulgaris
definition
Cx
inflammatory disease of pilosebaceous follicle
Cx:
- hormonal
- increased sebum production
- abnormal follicular keratinisation
- bacterial colonisation
- inflammation
Acne Vulgaris
- Types
- locations
- complications
face, chest & upper back
Complix
- Post-inflam hyperpigmentation
- Scarring
- Deformity
- Psychological and social effects

Acne vulgaris
Mx
referral?
Retinoids r contraindicatd in breastfeeding & pregnacny
advice, topical therapies, oral therapies,
Referral: Refer to dermatology if multiple Tx have failed
Oral retinoids (roaccutane) (for severe acne)

Psoriasis
types , cause, triggers
Chronic inflammatory skin condition due to hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes & inflammatory cell infiltration
cx: gentic,enviromentsl, immunological
STREP in LAB
streptocoocus, trauma,retroviral,endocrine, pred, withdrawl, infliximab, nsaids, lithium, ace inhib, b blockers

Symptoms and signs of Psorasis
- well demarcated erythematous White and grey scaly plaques, itchy, burning, painful
- 50% nail involvment pitting, onchylosis oil drop sign,
- AUSPITZ sign
- if athropathy involved ( check for those)

ComplicX of Psoriasis
- Erythroderma : exfoliative dermatitis involving at least 90% of the skin surface
- Psychological and social effects

Psoarisis Mx
referal?
General Measure:
- Tx is only to relieve symp than cure
- given them Psoriasis info leaflet
- nail care: cutt nails, acetone free nail varnish, avoid manicure
- avoid triggers, dont smoke, check medications.
- Use emollients (epimax) reduce scale
- seek medical advice ofr unexplained swelling/joint pain
Topical treatment: may take several wks to work, if stopped suddenly may increase risk of relapse.
steroids (hydrocortisone, eumovate) vit D analogue, coal tar preparations, topical retinoids, keratolytics and scalp preparations.
REFFERAL: if after 4 weeks no symp improvment, severe Psoriasis & effecting phycologically>>REFER DERMOTOLOGY for 2nd line Tx
- Phototherapy
- Oral therapies (if severe extensive or systemic inlvolve): mycophenate mofetil, methotrexate, calcinuren inhibitors,retinoids,
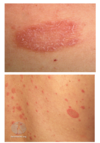
Allergic rashes & urticaria pathophys
- Urticaria is due to a local increase in permeability of capillaries & small venules
- A large number of inflammatory mediators (including prostaglandins, leukotriene & chemotactic factors) play a role but histamine derived from mast cells are the major mediator
- This can be induced by immunlogical and non-immunological mechanisms

Urticaria
symp
Ix
Pruritic wheals
Can progress to angioedema and anaphylaxis – see respiratory emergencies
Ix
if cause cannot be identified from Hx, symptom diaries can help to determine the frequency duration and severity of urticarial symptoms
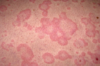
allergic rashes and Urticaria
Severe acute uritcaria/angioedema:
Mx
General measures: avoid trigger factors, avoid trigger medications (nsaids), it is self-limiting w/out Tx
Uriticaria: non-sedating anit-histamines ex: cetrizine
Severe acute uritcaria/angioedema: treat as above & add Oral corticosteroids 40mg pred for 7 days
Anaphylaxis: IM adren 1:1000 (repeat every 5 mins)
cholophenamine
hydrocortisone

Molluscum contagiosum
pearly papules with central umbillication
2ndry viral infection in eczema
complication
Candidiasis
symp, Ix, Mx,
if topical treatment not work?

White plaques on mucosal areas – can be scraped off · Erythema with satellite lesions in flexures
Ix: Skin swabs for MC&S (for yeasts)
Mx: as above for topical tx, If topical tx is ineffective, the infection is widespread or the person is significantly immunocompromised —-> Oral fluconazole

what is this showing?
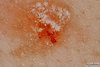
The Auspitz sign in psoriasis
scratch and removal of scales causes capillary bleeding