Colors of Oral Pathology II Flashcards
what is the “white” form of candidiasis?
pseudomembranous candidiasis
what is the “red” form of candidiasis, and what are the sub-categories?
- erythematous candidiasis
- central papillary atrophy of the tongue (median rhomboid glossitis)
- angular cheilitis
- denture stomatitis
what are basic forms that antifungals come in?
rinse, troche (dissolvable tablet - don’t want to use with patients with xerostomia), tablet, cream/ointment

- *need histo to diagnose*
- denture stomatitis (erythematous candidiasis)
- or hypersensitivity reaction
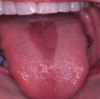
central papillary atrophy of the tongue aka median rhomboid glossitis (form of erythematous candidiasis)

angular cheilitis (form of erythematous candidiasis)

angular cheilitis (form of erythematous candidiasis)
what is another term for angular cheilitis?
perleche
what two things cause angular cheilitis?
reduced vertical dimension and salivary pooling
what are the basic treatment options for angular cheilitis?
- antifungals
- increase vertical dimension
what are antifungal prescription options for the treatment of angular cheilitis?
- mycolog II (triamcinolone 0.1% and nystatin 100,000 gram ointment)
- nystatin oral suspension (100,000 units/ml) aka mycostatin
- clotrimazole troche 10mg aka mycelex
what is the prescription for mycolog II?
- aka triamcinolone 0.1% and nystatin 100,000 units/gram ointment
- disp: 15g tube
- sig: apply tid until healing occurs
- refills: 1
what is the prescription for nystatin oral suspension (100,000 units/ml)?
- aka mycostatin
- disp: 240ml
- sig: rinse with 1-2tsp for 2 min then expectorate (or swallow, if affecting the soft pharynx)
- refills: 3
what is the prescription for clotrimazole troche 10mg?
- aka mycelex
- disp: 50 tabs
- sig: one troche 5 times a day (let dissolve in mouth)
- refills: 0

lymphoid hyperplasia (on floor of mouth because of waldeyer’s ring)

lymphoid hyperplasia
clinically blanches under pressure

hemangioma
clinically blanches under pressure

hemangioma
a ___ is a benign proliferation of blood vessels
hemangioma
hemangiomas affect ___% of children
10-12%
how is a hemangioma differentiated from a hematoma/petechiae?
a hemangioma will clinically blanch under pressure (dyoscopy)
what is the treatment for hemangioma?
surgery, laser, observation
history of placing candies in this area

hypersensitivity reaction
history of eating a scalding hot slice of deep dish pizza

thermal burn






























