CodeCademy Javascript notes Flashcards
(22 cards)
Which function returns a random number between 0 and 1?
Math.random();
Which function takes a decimal number and rounds it down to the nearest whole number?
Math.floor()
How to introduce a single line comment in Javascript?
By using two forward slashes
//
How to introduce a multiline comment in Javascript?
A multi-line comment will comment out multiple lines, and is denoted with /* to begin the comment, and */ to end the comment:
/* here goes the multilines blabla */
What is string interpolation?
It’s when you insert a variable into a string.
You do so using the ‘+’
Which logical operator do we use to say both must be true?
&&
(= and)
Which logical operator do we use to say either can be true?
||
(two pipes = or)
Which logical operator do we use to say I want to make sure this is the opposite of what it really is?
!
(=not)
Which logical operator do we use to say these should not be equal to each other?
!==
(not equal value or not equal type)
Using else if is a great tool for when we have a few different conditions we’d like to consider.
else if is limited however. If we want to write a program with 25 different conditions, like a JavaScript cash register, we’d have to write a lot of code, and it can be difficult to read and understand.
To deal with times when you need many else if conditions, we can turn to a […] statement to write more concise and readable code.
switch statement
The switch keyword initiates the statement, and is followed by ( … ), which contains the condition that each case will compare to. In the example, the condition is moonPhase.
Inside the block, { … }, there are cases. case is like the else if part of an if/else if/else statement. The word following the first case is ‘full’. If moonPhase equalled ‘full’, that case’s console.log would run.
moonPhase equals ‘full’, so the second and third case statements are skipped. The first case runs since the case is ‘full’ matches moonPhase’s value. This particular program will log out: ‘Howwwwlll’.
Then the program stops with the break keyword. This keyword will prevent the switch statement from executing any more of its code.
At the end of each switch statement, there is a default condition. If none of the cases are true, then this code will run.
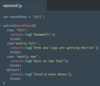
How to make a string interpolation/substitution in ES6?
using the ${ } syntax
Warning: CoffeeScript uses the #{ } syntax
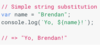
What is the difference between parameter and argument?
- inputNumber* is a parameter, but when we call multiplyByThirteen(9), the 9 is called an argument. Therefore, arguments are provided when you call a function, and parameters receive arguments as their value. So, inputNumber is a parameter and its value is the argument 9, since we wrote multiplyByThirteen(9).
- *Parameters** let us write logic inside functions that can be modified based on when we call the function, which will help make our functions more flexible.
Which verb do we use to mean that we’re giving arguments to a function?
“pass” / “pass in”
Passing in arguments to a function
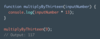
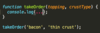
What should we put inside the takeOrder function to output
“Order: thin crust pizza topped with bacon”
function takeOrder(topping, crustType) {
console.log(**...**);
}
takeOrder(‘bacon’, ‘thin crust’);

What is the difference between Global Scope and Functional Scope?
Scope is the idea in programming that some variables are acessible/inaccessible from other parts of the program.
Global Scope refers to variables that are accessible to every part of the program.
Functional Scope refers to variables created inside functions, which are not accessible outside of its block.
What is the general purpose of a conditional statement?
Conditional statements evaluate code as either true or false
To make this statement valid, what operator belongs in the ___ space below?
if (coin ___ “heads”)
{console.log(‘coin is heads!’);}
else
{console.log(‘coin is tails…’);}
Is it =? Or ===? Or both will work?
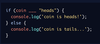
Answer is ===
The = operator is used to assign values to variables, it does not compare like the === operator.
What are function Default Parameters in ES6?
One of the features added in ES6 is the ability to use default parameters. Default parameters allow parameters to have a predetermined value in case there is no argument passed into the function or if the argument is undefined when called.
By using a default parameter, we account for situations when an argument isn’t passed into a function that is expecting an argument.

What differentiate function declarations and function expressions regarding hoisting?
Unlike function declarations, function expressions are not hoisted so they cannot be called before they are defined.
What is a function expression?
Another way to define a function is to use a function expression. To define a function inside an expression, we can use the function keyword. In a function expression, the function name is usually omitted. A function with no name is called an anonymous function. A function expression is often stored in a variable in order to refer to it.
What’s the benefit of ES6’s arrow function syntax?
ES6 introduced arrow function syntax, a shorter way to write functions by using the special “fat arrow” () => notation.
Arrow functions remove the need to type out the keyword function every time you need to create a function. Instead, you first include the parameters inside the ( ) and then add an arrow => that points to the function body surrounded in { } like this:

Given getComputerChoice is a function defined earlier, what will the below output?

The output is probably not what we’re expecting here:
[Function: getComputerChoice]
What is missing is the parenthesis to call the function!



