Clinical Knee Anatomy Flashcards
(20 cards)
What increases the mechanical advantage of the quadriceps and how?
- patella
- brings the extensor mechanism further from the knee joint.
Medial patellofemoral ligament:
- a thickening of the patellar ligament.
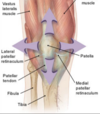
Which meniscus is least mobile and most likely to tear?
- medial meniscus
- attached to medial collateral ligament
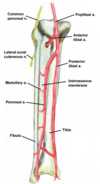
A proximal tibial fracture could lead to:
- a popliteal artery tear because the popliteal artery is so closely bound to the tibia.
The most common type of knee pain:
patellofemoral
- occurs when the patella is pressed against the femur
- Diffuse anterior tenderness
- Patellar tenderness
- Patellofemoral crepitus
- Overweight
Q-Angle:
The angle between the femur and the tibia.
Patella is always pulled laterally, and almost always dislocates:
laterally.
What is the only part of the menisci that can be repaired?
- lateral 1/3rd
- interior menisci (pink and white) are avascular
Symptoms of meniscal tears:
- Isolated joint line pain
- Mechanical symptoms
- Catching
- Locking
McMurrays sign is indicative of:
meniscal tear
What part of the meniscus has about 70% of the mensicus function?
- peripheral rim (splits load of femur)
- reason for partial meniscectomy
Most common knee ligament injury:
- MCL sprain
- pain at medial femoral epicondyle
How do you test for MCL sprain/tear?
- valgus stress
PCL is looser in ______ and ________ in flexion.
looser in extension and tighter in flexion.
ACL is _______ in flexion and ________ in extension.
looser in flexion and tighter in extension.
Why is Lachman’s test the most reliable for ACL tears?
- ACL is tighter at 20-30 degrees of extension than at 90 degrees. If you examine the ACL when it is loose, it won’t be reliable. You want to examine ligaments when they are the tightest.
ACL treatment:
surgical
hamstring graft or allograft
Which is more likely to tear during a direct fall to ground: ACL or PCL?
- PCL
- foot in plantar flexion, tibia head strikes ground first
- PCL tightest at 90 degrees
What is at risk during a knee dislocation?
- popliteal artery and common fibullar nerve are at risk.
- Skin is at risk due to loss of blood, which could lead to necrosis.
What injury can lead to foot drop?
- LCL tear or knee dislocation
- fibullar nerve compressed


