CIS275 - Chapter 11: SQL zyLabs Flashcards
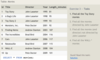
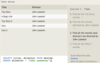
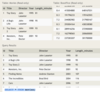
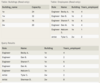
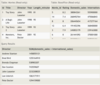
The Horse table has the following columns:
ID - integer, primary key
RegisteredName - variable-length string
Breed - variable-length string
Height - decimal number
BirthDate - date
Write a SELECT statement to select the registered name, height, and birth date for only horses that have a height between 15.0 and 16.0 (inclusive) or have a birth date on or after January 1, 2020.
SELECT RegisteredName, Height, BirthDate
FROM Horse
WHERE Height BETWEEN 15.0 AND 16.0
OR BirthDate >= ‘2020-01-01’;

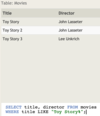
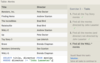
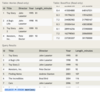
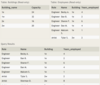
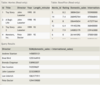
The Movie table has the following columns:
ID - integer, primary key
Title - variable-length string
Genre - variable-length string
RatingCode - variable-length string
Year - integer
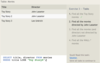
The Rating table has the following columns:
Code - variable-length string, primary key
Description - variable-length string
Write a SELECT statement to select the Title, Year, and rating Description. Display all movies, whether or not a RatingCode is available.
Hint: Perform a LEFT JOIN on the Movie and Rating tables, matching the RatingCode and Code columns.
SELECT Title, Year, Description
FROM Movie
LEFT JOIN Rating
ON RatingCode = Code;

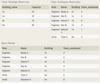
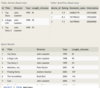
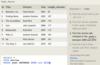
The database has three tables for tracking horse-riding lessons:
Horse with columns:
ID - primary key
RegisteredName
Breed
Height
BirthDate
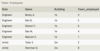
Student with columns:
ID - primary key
FirstName
LastName
Street
City
State
Zip
Phone
EmailAddress
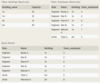
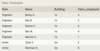
LessonSchedule with columns:
HorseID - partial primary key, foreign key references Horse(ID)
StudentID - foreign key references Student(ID)
LessonDateTime - partial primary key
Write a SELECT statement to create a lesson schedule with the lesson date/time, horse ID, and the student’s first and last names. Order the results in ascending order by lesson date/time, then by horse ID. Unassigned lesson times (student ID is NULL) should not appear in the schedule.
Hint: Perform a join on the Student and LessonSchedule tables, matching the student IDs.
SELECT LessonDateTime, HorseID, FirstName, LastName
FROM LessonSchedule
JOIN Student
ON LessonSchedule.StudentID = Student.ID
ORDER BY LessonDateTime ASC, HorseID;
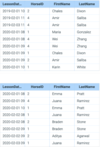
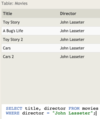
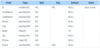
The Employee table has the following columns:
ID - integer, primary key
FirstName - variable-length string
LastName - variable-length string
ManagerID - integer
Write a SELECT statement to show a list of all employees’ first names and their managers’ first names. List only employees that have a manager. Order the results by Employee first name. Use aliases to give the result columns distinctly different names, like “Employee” and “Manager”.
Hint: Use INNER JOIN.
SELECT A.FirstName AS ‘Employee’,
B.FirstName AS ‘Manager’
FROM Employee A
INNER JOIN Employee B
ON B.ID = A.ManagerID
ORDER BY A.FirstName ASC;
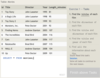



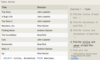

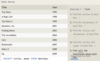
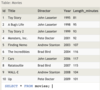
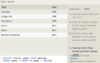
Standard numerical operators
=, !=, < <=, >, >=
col_name != 4
Number is within range of two values (inclusive)
BETWEEN … AND …
col_name BETWEEN 1.5 AND 10.5
Number is not within range of two values (inclusive)
NOT BETWEEN … AND …
col_name NOT BETWEEN 1 AND 10
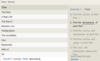
Number exists in a list
IN (…)
col_name IN (2, 4, 6)
Number does not exist in a list
NOT IN (…)
col_name NOT IN (1, 3, 5)
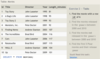




Case sensitive exact string comparison (notice the single equals)
=
col_name = “abc”
Case sensitive exact string inequality comparison
!= or <>
col_name != “abcd”
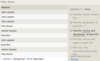
Case insensitive exact string comparison
LIKE
col_name LIKE “ABC”
Case insensitive exact string inequality comparison
NOT LIKE
col_name NOT LIKE “ABCD”
Used anywhere in a string to match a sequence of zero or more characters (only with LIKE or NOT LIKE)
%
col_name LIKE “%AT%”
(matches “AT”, “ATTIC”, “CAT” or even “BATS”)
Used anywhere in a string to match a single character (only with LIKE or NOT LIKE)
_ (underscore)
col_name LIKE “AN_”
(matches “AND”, but not “AN”)