Circular Motion and SHM Flashcards
(42 cards)
What kind of motion will a pendulum perform?
Simple harmonic motion
If the graph of displacement is cos(x), what will the respective graphs of velocity and acceleration look like SHM?
Velocity as -sin(x)
Acceleration as -cos(x)
Same as SVA in maths for differentiating / integrating
Describe a freely oscillating object
It oscillates with a constant amplitude because there is no external force acting on it
(Its energy is constant)
What is natural frequency?
The frequency of free oscillations of an oscillating system.
What are forced vibrations?
Making an object oscillate at a frequency that is not it’s natural frequency
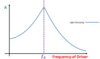
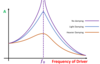
When does resonance occur?
When the frequency of driving force or oscillation matches the natural frequency of the system.
What is the outcome of resonance?
An increase in amplitude of the system’s oscillation.
What is damping?
The term used to describe the removal of energy from an oscillating system.
What are the three levels of damping?
Light
Heavy
Critical
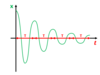
Describe the motion of a lightly damped system
The system oscillates over a long time frame before coming to rest.
The amplitude of the oscillations exponentially decay. But the time period of oscillations remains constant
Describe heavy damping (over damping)
System not allowed to oscillate.
Slowly returns to equilibrium.
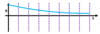
Describe critical damping
The oscillating system returns to the zero position of the oscillation after one quarter of a time period.
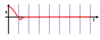
What are the two conditions for SHM?
- Acceleration must be proportional to displacement
- Acceleration must be opposite to displacement
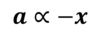
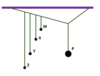
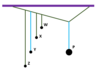
Label up the maximum and minimum velocities and accelerations on the simple pendulum…

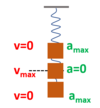
Label up the maximum and minimum velocities and accelerations on the mass spring system…
Label up the maximum and minimum potential and kinetic energies on the simple pendulum…
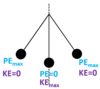
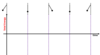
What are the kinetic energy, potential energy and total energy lines for one cycle of SHM?

When do you use?
x=Acos(wt)
When do you use?
x=Asin(wt)
x=Acos(wt) -> displacement in SHM when x=A when t=0
x=Asin(wt) -> displacement in SHM when x=0 when t=0
MUST BE IN RADIANS
How do you calculate KEmax or PEmax or ET in SHM?
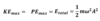
What two factors affect the time period of a mass spring system in SHM?
- Mass on the end of the spring
- Spring constant (stiffness) of spring
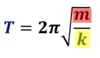
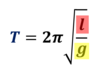
What two factors affect the time period of a simple pendulum in SHM?
- Length between top of string and centre of bob
- Gravitational field strength
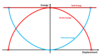
What could the graph of energy against displacement look like in SHM?
Does circular motion count as SHM?
When projected onto a flat surface, yes it does
When a SHM system is lightly damped what happens to its amplitude and time period?
Amplitude decreases (as it loses energy)
But time period remains constant