Chemistry/Physics (ours) Flashcards
Chromatography “Separation and Purification methods” OCR: p. 112
- the primary reason for chemical separation during a chromatographic separation on cellulose is that the relative amount of hydrogen bonding to the stationary phase will determine the relative rate of migration of the various components in the sample

The variety of opsins “How light and sound interact with matter”
enable the detection of different colors
Retinal Binding Site
BR p. 48
hydrophobic environment (retinal is mainly carbon and hydrogen)
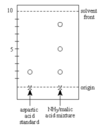
Rf Values with developed chromatography plates “Separation and purification methods.”
- Rf is the ratio of the distance travelled by the analyte relative to the solvent front during a chromatographic separation. - equation: distance of substance investigated / distance of solvent front
Stereospecific/ Stereospecific Reaction “Nature of molecules and intermolecular interactions.” OCR p. 45
- meaning rxn produces only one form of product - a rxn in which the stereochemistry of the reactant completely determines the stereochemistry of the product without any other option.
Rhodopsin “Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics.”
ATP (required for kinase activity): source of phosphate groups added to the molecule
Hybridization States
- “Nature of molecules and intermolecular interactions.”
Steric Number = Atoms + Lone pairs
4 = sp^3
3 = sp^2 2= sp

amine group “functional group” “Structure, function, and reactivity of biologically-relevant molecules.”
the functional group that forms during peptide bond formation is known as an amide group.
Aldehyde functional group

Carbonyl

Ketone

Acetal

Hemiacetal

Imine

Enamine

Aldol

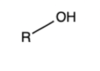
Alcohol
Carboxylic Acid

Amide

Ester

Lipase
BR: p. 48
hydrolyzes fatty acids
Anhydride

Phenol

What affects rate of subsitution in a reaction?
OCR:
The rate of substitution of protonated alcohols is subject to steric hindrance. This inhibits the ability of nucleophiles to collide with the reacting electrophilic center and slows the rate of reaction.
pH
BCR p. 51
pH = -log[H+]
[H+] = 10^-pH
pOH = -log[OH-]
pH + pOH = 14
difference of 3 pH units = 1000-fold difference in proton concentration
If Reaction 2 (Figure 4) is repeated with HCl and the compound shown next to the reaction, which of the following compounds is NOT a direct product (without rearrangement)?

the structure shown in this response requires an additional shift of hydride atoms prior to elimination and is therefore NOT a direct product.

In a gas-liquid chromatograph, the first peak observed in the gc trace is attributable to which compound?
OCR p.123
Whichever compound will exhibit the lowest molecular weight and also the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction will therefore migrate the fastest and be the first peak in the gas chromatograph (gc) trace.
Acid Dissociation
BCR p. 69
- higher Ka (acid dissociation)/ lower pka: stronger acid
- acid dissociation: net positive charge vs net negative charge acid - the net negative charge will be weaker acid / dissociate to a smaller extent

Glycogen/Glycogenesis
BCR: p. 123
- Most glucose units in glycogen are linked by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds
-branching with glycogen: α-1,6-glycosidic bond
- Glycogen: polymer of glucose in muscle/liver cells
- Glycogenesis: glu-6-p→ isomerized in reversible rxn to glu-1-P w/ phosphoglucomutase → glu-1-p is activated w/ UTP to form UDP-glucose→ added to glycogen polymer by glycogen synthase

What is the product of the reaction of Compound 1 (nxt to rxn) with HBr by the pathway shown in Figure 3?
OCR

(S)-1-bromo-1-deuteriopentane
because the incoming nucleophile displaces the leaving group form the opposite side of the reacting center during an SN2 reaction.
UDP
- deals with glycogen synthase
- contains uridine (nucleic acid used in RNA)
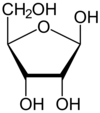
- structure of RNA contains ribose
- KNOW STRUCTURE OF RIBOSE
Phosphatase
- removes phosphate group from a protein
- removal of phosphate prior to gel electrophoresis –> decrease in band intensity
thin lens equation
an object O is at a distance of three focal lengths from the center of a convex lens. What is the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object?
- (1/o) + (1/i) = (1/f)
- magnification: -i/o
- if asked for ratio of height of image to height of object (given height of object): solve for i and then plug into magnification formula
- Object distance = 3f, focal length = f, image distance = i.
- 1/o + 1/i = 1/f –> 1/3f + 1/i = 1/f. R
- 1/i = 1/f - 1/3f ==> 1/i = 2/3f ==> i = 1.5f.
Plug this into the magnification formula m = -i/o and you get 1.5f/3f = (1/2)
Gamma decay
occurs when nucleus emits photons
spontaneous vs nonspontaneous reactions
- spontaneous: negative ΔG, positive ΔS°, negative ΔH ( - reaction that create gaseous products from solids and liquids = positive ΔS°)
- nonspontaneous: positive ΔG, negative ΔS°, positive ΔH
net sum of chemical reactions

catalysts
If a homogeneous catalyst cannot be separated from the products at the end of a reaction: products will be contaminated with the catalyst
If solid catalyst is finely ground before it is added to the reaction mixture:
- Faster rxn rate: a greater surface area of catalyst will be exposed.
- grinding a heterogeneous catalyst increases the amount of catalyst available to the reaction and therefore increases its rate
V = IR

oxidation-reduction reactions / metal strips in solutions
GCR p. 268
this link is very helpful:
https: //chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Analytical_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Analytical_Chemistry)/Electrochemistry/Redox_Chemistry/Balancing_Redox_reactions
- putting a metal strip in a solution: if it results in a solid –> metal strip is oxidized and the other ion has higher reduction potential…make two half-reactions and balance # e- (if solution is oxidized: e- go on right side) –> add together to get new equation
- spontaneous reaction: E° is greater than zero; 1) make half-reaction equation and take values (reverse signs based on which ion is oxidized in solution)
common ion effect with solubility
GCR: p. 216
If you have a solution and solute in equilibrium, adding a common ion (an ion that is common with the dissolving solid) decreases the solubility of the solute. This is because Le Chatelier’s principle states the reaction will shift toward the left (toward the reactants) to relieve the stress of the excess product. When equilibrium is shifted toward the reactants, the solute precipitates.

molarity (M)
mol/V
M = molar concentration
n = moles solute
v = liters solution
Units of Power (P)
watt, defined as J/s = ft•lb/s = kg•m2/s3
Amino acid substitution / pKa
-naming: original amino acid, position, new amino acid
- pH is less than pKa of acidic group = acidic group is in protonated form
- pH is greater than pKa of acidic group = deprotonated form
- Acids with low pKa deprotonate easily
radioactive decay
GCR p. 53
alpha decay: large nucleus wants to become more stable by reducing # protons and neutrons (atomic # -2; atomic mass -4)
beta decay: when unstable nucleus contains too many neutrons –> convert neutron to proton and electron (atomic # +1)
gamma decay: after the nucleus has undergone alpha or beta decay, it can “relax” to its ground state by emitting photons (atomic # stays same)

- Oxidizing and Reducing Agents
Ex question from mock MCAT 1 bio q. 53: When a strip of Zn is placed in a beaker containing 0.1 M HCl, H2(g) evolves. If a strip of Al is placed in a beaker containing 0.1 M HCl, does H2(g) evolve?
- Because Zn has higher reduction potential, since H2 gas evolves when in the presence of Zn(s), and Al(s) has an even higher oxidation potential than Zn(s), we know that H2 gas must evolve - or in other words, H+ must be reduced - when in the presence of Al(s).
(If Zn can reduce H+, then Al definitely can because it’s stronger than Zn.)
Note:
The more negative the reaction potential –> stronger reducing agent
nuclear localization signal
BR p. 176
- larger proteins cannot pass freely through nuclear pores and are excluded from nuclear interior unless they contain sequence of basic amino acids
- if they have sequence = translated on cytoplasmic ribosomes and then imported into the nucleus by specific transport mechanisms
- basically a signal that guides a protein molecule to the nucleus; useful to up/down regulate certain cellular processes and products
- permits proteins to enter the nucleus (not likely for transmembrane protein)
signal sequence
- what allows proteins to enter the rough ER (proteins that are either going to be secreted from the cell or perform their function within the cell membrane)
- transmembrane proteins: located in cell membrane (enter the endomembrane system by docking at the rough ER w/ signal sequence)
- definition: short sequence of AA (usually found at N-terminus) of a protein being translated, that directs the ribosome and its associated mRNA to the membranes of rough ER where translation will be completed; found on membrane-bound proteins, secreted proteins, and proteins destined for other organelles
mature mRNA
- has been spliced and processed; ready for translation
- not likely to contain introns or promoter sequences!
Transmembrane domains
similar to signal sequence, but they are located in middle of protein, not removed after translation, and occur on integral membrane proteins
Metric Units
There are 6 MCAT-relevant base units

Prefixes
6 prefixes, symbol, and “multiple”

Molarity
moles of solute per liter of solution
most common way of expressing solution concentrations
Liter units
1000L = 1m^3
1L = 1000cm^3
1mL = 1cm^3 = 1cc
Angstrom
unit of length = 10^-10 m
used with atomic radii and bond lengths

order of magnitude
Q: By how many order of magnitude is a centimeter longer than an angstrom?
An order of magnitude is a factor of 10.
Since 1cm = 10^-2 m and 1 Angstrom = 10^-10, a centimeter is 8 factors of ten greater than an angstrom.
Density
of a substance is its mass per volume
p = mass/volume = m/v
In SI units: (kg/m^3)
In chem: (g/cm^3)
g/cm^3 –> multiple by 1000 –> kg/m^3
Empirical formula
the smallest whole numbers that give the same ratio of atoms
to go from molecular formula to emperical, divide subscripts by their greatest common factor
Know the general “look” of these polyatmoic ions

formula weight
atomic mass unit
- is the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in the molecule
- is the unit for atomic weight (amu)
atomic number (Z)
- # protons
mass number (A)
protons + # neutrons
isotope
elements differ in # neutrons (different mass numbers)
molecular weight
when a compoudn exists as discrete molecules, this term is used instead of formula weight
ex) H2O molecular weight: 2(1) + 16 = 18
ex) NaCl formula weight (which is usually used to ionic compounds): 23 + 35.5 = 58.5
half-life
GCR p 59

mole
Avogador’s number
- 6.02 x 10^23 “entities”
- Na or No
- A’s number is the link between atmoic mass units and grams
- # moles = mass in grams / molecular weight (MW)
How to find percent composition by mass?
- a molecule’s molecular or emperical formula can be used to determine the molecule’s percent mass composition
ex) C2H2N
2(12) + 2(1) + 14 = 40
%C: 2(12)/40 = 60%
Concentration: Molarity (M)
expresses the concentration of a solution in terms of moles of solute per volume (in liters) of solution
Molarity (M) = # moles of solute / # liters of solution
concentratoin is denoted by enclosing the solute in brackets
Mole fraction
expresses the fraction of moles of a given substance
mole of fraction of S = Xs = # moles of substande S / total # moles of solution
useful way to express con when more than one solute is present; used when discussing composition of mixture of gases
Law of Conservation of Mass (or of Matter)
the amount of matter (mass) does not change in a chemical reaction
hydrogen absorption spectra
If a photon hits an atom and the energy of the photon is the same as the gap between two electron energy levels in the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level can absorb the photon and jump up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels then the photon will not be absorbed (it can still be scattered).
The absorbed photons show up as black lines because the photons of these wavelengths have been absorbed and do not show up!! (gaps in space correspond to photons getting absorbed)
Stoichiometric coefficients
tell us in what proportion the reactants react and in what proporiton the products are formed
they preceed each compound
ex) 2 Al + 6 HCL –> 2 & 6 are stoich coef
Balancing Equations
1) start with most complex molecule
2) do math lol
Stoichiometric relationships in balanced reactions
GCR: p. 44
know how to do equations like this
limiting reagent
GCR: p. 45
since we run out of this reactant first, it limits how much product the reaction can produce
know how to do probelms like this
Oxidation state (or oxidation number)
indicates how the atom’s “ownership” of it’s valence electrons changes when it forms a compound
ex) NaCl –> Na+1 bc it “donates” an electron in the covalent bond between itself and Cl, while Cl accepts the e- and has a -1 oxidation state
The _____state of an atom is the “charge” it would have if the compound were ionic.
Rules for Assigning Oxidation States
Exception to rule 6: in peroxides (H2O2 or Na2 O2), O2 is in a -1 oxidation state

hydrogen emission spectra
- light getting emitted
LIGHT BANDS on dark screen
The amount of energy absorbed by the electron to move into a higher level is the same as the amount of energy released when returning to the original energy level.
- refer to hydrogen absorption spectra for more info
Order of Electronegativities
FONClBrISCH (“fawn-cull-brish”)
most electronegative (F) –> least (H)
Bonds from H to anyting not found in the list will give H a -1 oxidation state
E photon = hf = h (c/wavelength)
h = Planck’s constant
- As energy goes up, wavelength decreases and frequency increases
In determining which reactant loses the –OH group, which of the following isotopic substitutions would be most useful?

Replace the hydroxyl oxygen of ethanol with O-18.
this experiment involves labeling a group which does not exchange with other groups present prior to reaction and will therefore give information about the true identity of the groups, which are exchanged during the reaction.
whether or not that O18 is in the final compound will give us the information we want. If it is in the compound, we know that the ethanol kept its -OH group and therefore acetic acid lost its -OH. If the O18 isn’t in the compound, that means ethanol lost its -OH instead.
A person, whose eye has a lens-to-retina distance of 2.0 cm, can only clearly see objects that are closer than 1.0 m away. What is the strength S of the person’s eye lens? (Note: Use the thin lens formula .)
Physics
51D
the strength of the eye lens is equal to the inverse of the focal length of the eye lens. Its numerical value is given by -1+(0.02 m)-1=1 D+50 D=51 D.
how enzymes affect chemical reactions
BCR
the stabilization of the transition state, not the substrate, provides binding energy that is used to lower the activation energy.
Which of the following will decrease the percentage ionization of 1.0 M acetic acid, CH3CO2H(aq)?
GCR
Adding concentrated HCl(aq)
HCl is a strong acid that will increase the amount of H+ in solution and thus decrease the percentage of CH3CO2H that ionizes.
Use Le Châtelier’s principle to identify that adding a strong acid to a solution of weak acid will decrease the amount of ionization of the latter
When the current in a circuit increases and the resistance of the circuit remains constant, the voltage of the circuit:
Physics
increases
according to Ohm’s law, current is equal to voltage divided by resistance. If current increases and resistance is constant, then voltage increases as well.
light spectra
Red: 750 nm (longest wavelength)
Violet: 400 nm (shortest wavelength)
Knowing that the speed of light in the vitreous humor is 2.1 × 108 m/s, what is the index of refraction of the vitreous humor? (Note: The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m/s.)
What is the index of refraction of a medium?
Physics
1.4
because the index of refraction of a medium is equal to the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in the medium, thus it is equal to (3.0 x 108 m/s)/(2.1 x 108 m/s) = 1.4.
Index of refraction: n = c (speed of light in vacuum) / v (speed of light in medium)
electron shell vs subshell
shell (n): circular orbits, n=3 has higher energy than e- in 2nd shell
subshell: comprised of one or more orbitals ((s-f); each subshell contains one or more orbitals of the same energy (degenerate); subshell higher than s has multiple orbital orientations
half-filled and filled orbitals: most stable
The intensity of the radiation emitted by the oxygen sensor is directly proportional to the:
Physics
the energy of electromagnetic radiation is directly proportional to the number of photons, and the intensity of electromagnetic radiation is defined as energy emitted per unit time. Thus, intensity is directly proportional to the number of photons emitted.
E (energy of the photon) = h (a constant) f (frequency of wave)
****need more info****
electron configurations
transition metals ionize from their valence s subshell before their d subshell
diamagnetic vs paramagnetic
diamagnetic: atom has all of its e- spin-paired (at the end of the block!); repelled by magnetic fields
paramagnetic: e- are not all spin paired; attracted to magnetic fields
What is the energy of the photons emitted by the LED at a frequency of 610 THz? (Note: h = 6.6 × 10–34 J·s)
Physics
4.0 × 10–19 J
the energy of a photon of frequency 610 THz is equal to 6.6 x 10-34 J•s x 610 x 1012 Hz = 4 x 10-19 J.
**equation isn’t given**
What percentage of standard atmospheric pressure is the pulse pressure of a healthy adult?
Provided: maximum and minimum blood pressures of a healthy adult (the systolic Psand the diastolic Pd pressures, respectively) are about Ps = 120 mmHg and Pd = 75 mm Hg.
Physics
6%
the pulse pressure in a healthy adult is (120 − 75) mmHg = 45 mmHg, and so the percentage is 45 mmHg/760 mmHg = 6%.
**note that 760mm Hg wasn’t provided in psg**
maximum # e- that can be present in n=3 shell
18 e-
excited vs ground state
ground state: lowest energy configuration
excited state: any of an infinite # of configurations that have a higher energy than the lowest energy e- configuration (not an ion; e- are not lost or gained; they jump to higher energy levels within the atom)
What fraction of a 15^O sample decays in 10 min?
Given: the half-life of 15^O is 2 minutes
Physics - half-life
thus, 10 minutes = 5 half-lives. Therefore, only (1/2)5 = 1/32 of the sample will be left after 10 minutes, while 31/32 of the sample will decay.
**need to go over**
valence e-
to form a cation (and in general) atoms will always lose their valence e- (the ones from the highest n level) first
Compared to micellular Compound 1, Compound 2 is structurally more rigid as a result of what type of interaction?
Given: multiple molecules of micellular Compound 1 come together to form Compound 2, which is a solid. An oxidant causes the formation of Compound 2
BCR
It can be reasoned that the interaction described is intermolecular in nature. Multiple pieces of information (from the psg) point to the fact that the interaction is disulfide bond formation, including the fact that an oxidant causes the formation of Compound 2, which can be reversed by the addition of a reducing agent.
The graph below shows the relationship between the predominant form of iron as a function of solution pH and applied potential. Based on the graph, which of the following statements is true?
GCR

At a potential of –0.44 V, the equilibrium between Fe and Fe2+ is independent of solution pH below pH 6.
At an applied potential of −0.44V and pH below 6, there is an equilibrium between Fe(s) and Fe2+(aq), as shown by the line of demarcation. The fact that this line moves horizontally with increasing pH up until pH = 6 means that this equilibrium is unaffected by changing the pH.
Trends

elements in same group show similar reactivity (all have same # e- in outermost shell)
metalloids: possess qualities of metals and nonmetals
Which of the following types of orbitals of the central atom are involved in bonding in octahedral compounds?
GCR
d2 sp3
octahedral compounds have six σ bonds and no lone pairs. According to valence bond theory, the central atom requires the hybridization of six atomic orbitals, d2sp3.
“Ideal Gas”
GCR
since a property of an “ideal” gas is that it is composed of particles that have negligible volume and do not exert intermolecular forces, individual molecular volume and intermolecular forces are negligible.
Periodic Trends - radius
as we go across a period, e- are added, but new shells are not –> e- feel greater effective nuclear charge –> radius decreases
as we go down a group, as new shells are added –> v e- experience increased shielding (smaller effective nuclear charge)–> RADIUS decreases
if we form an ion, the radius will decrease as e- are removed (the ones that are left are drawn in more closely to the nucleus); radius will increase as e- are added

periodic trends - IE
across a period / up a group: IE (amt of energy necessary to remove least tightly bound e- from isolated atom) increases since v e- are more tightly bound
electronegativity
ability of atom to attract e- to itself in covalent bond
(greater tendency to attract e- –> greater electronegativity
- increases from L to R and from bottom to top
F > O > N > Cl > Br > I > S > C =(ish) H
shielding effect

Z eff = effective nuclear charge
Z - core e-
base units to know

power-of-ten prefixes you should know

displacement
physics
is its change in position
position(f) - position(I)
net distance traveled by the object, regardless of the path the obj took; net distance plus diraction
velocity
the magnitude of the velocity vector is called the _____
physics
tells us how fast an object’s position changes (vector)
displacement/time
speed = scalar (has no direction)
acceleration
how fast an object’s velocity changes
= change in V/time
an object can be accelerating even if its speed is constant bc velocity changes if speed or direction change
average acceleration: delta V/delta t
a sprinter runs 300 meters north, then 400 meters east, which takes 100 seconds. What is his average speed? What was the magnitude of his average velocity?
average speed: 700m(total distance covered) /100s = 7 m/s
bc displacement is 500m, average velocity: 500m/100s = 5 m/s
the direction of a tells v how to change
phsyics
**know this**

uniformly accelerated motion equations !
this is motion in which the object’s acceleration, a, is constant
The big five (bolded = most used on exam):
1) d = 1/2 (vo + v)t = missing a
2) v = vo + at = missing d
3) d = vot + 1/2 at^2 = missing v
4) d = vt - 1/2 a t^2 = missing vo
5) v^2 = vo^2 + 2ad = missing t
kinematics with graphs
position vs. time graph
velocity vs. time graph
p vs t: slope gives velocity
v vs. t: slope gives acceleration, area gives displacement
free fall
physics
object moving only under the influence of gravity (ignoring air resistance, etc. )
near the surface of the earth, the magnitude of g, the gravitational acceleration = 10m/s^2
not a description of a downward velocity but as a description of a downward acceleration
direction of objects displacement = pos. (but it’s your choice)
projectile motion
the motion of an obj, experiencing only the constant, downward acceleration due to gravity (free fall) = proj motion
throw ball up at angle, path = trajectory and would be parabola
obj’s velocity is always tangent to its path; for a projectile moving in a parabolic path, it’s only the verticle velocity that’s zero at the top; the horizontal velocity is still there
for a parabola: the projectile’s total flight time will be twice the time required to reach the top

In which organ are sickled red blood cells most likely to be hemolyzed?
One of the key functions of the spleen is to remove old or deformed red blood cells from circulation. The capillaries of the spleen are much smaller than the diameter of a red blood cell, helping to induce lysis of fragile or old cells. If the spleen is removed, more damaged cells remain in circulation.
other options were: thymnus (a specialized primary lymphnoid organ of immune system), lymph nodes (have immune system cells), and kidneys (filter blood)
hemolyzed = the state of being broken down
isoelectric point
(Acids/Bases & pH)
The isoelectric point is the solution pH at which an amphoteric molecule (a molecule that can act either as an acid or a base) has a net electric charge of zero.
Which of the following best explains why the separation occurs?
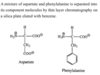
Phenylalanine will move farther with the mobile phase, because it has a nonpolar side chain.
The side chain on aspartate is –CH2COO–, which is very polar, while the side chain on phenylalanine is –CH2Ph, which is nonpolar. Since “like dissolves like,” and the mobile phase is nonpolar, the molecule which is less polar (phenylalanine, in this case) will move farther with the mobile phase.
If a silent mutation occurs at position 6 in the β chain of hemoglobin, what will be the overall charge of the resulting tryptic peptide in a solution buffered to pH 5?

A silent mutation within the coding region of DNA does not alter the amino acid sequence of a protein.
By determining the charge states on each individual amino acid in the tryptic peptide at pH 5, the overall charge on the peptide can be calculated. Recall that when the pH of a solution exceeds the pKa of a functional group, that group is deprotonated. This applies only to the acidic residues in the peptide. So, from left-to-right: the N-terminal Val bears a +1 charge on its α-amino group; His bears a +1 charge on its side chain; Leu, Thr, and Pro are uncharged; each Glu bears a –1 charge on its side chain; and the C-terminal Lys is neutral overall (+1 on its side chain and –1 on its α-carboxyl group). The sum total of these charges [(+1) + (+1) + (–1) + (–1) + (0)] is 0

According to the figures, decreasing which of the following would create the greatest increase in charge stored per unit voltage on an axon membrane in its rest state?

“Charge stored per unit voltage,” Q / V, is the definition of capacitance, C. The equation for the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor is C = κε0A / d, where κ is the dielectric constant, ε0 is a universal constant (the permittivity of free space), A is the area of each plate, and d is the distance between the plates. Of the choices given, decreasing the thickness of the membrane (that is, decreasing d), would increase the capacitance
Ouabain irreversibly inhibits the Na+/K+ pump. The effect of this on the equivalent circuit model for the resting axon would be to cause:

decreased potential difference across the resistors and the capacitor.
The resistors and the capacitor are in parallel, so they must have the same potential difference (The voltage difference between any two points in a circuit is known as Potential Difference and it is this potential difference which makes current flow). If the source of potential difference (the Na+/K+ pump) is prevented from operating, then the common potential difference across the resistors and the capacitor would decrease.
properties for parallel: voltage is the same, current is sum
properties for series: voltage is sum, current is same
Across the membrane of an axon in its rest state:
Based on psg: Course Exam 1, Chem: #8
the potential is higher on the outside of the cell than the inside, and electric field lines run from the outside to the inside
The passage states that “the voltage across the membrane is –70 mV from the exterior to the interior of the cell.” That is, there is a 70 mV drop in electric potential in going from the exterior to the interior; thus, the potential is higher on the exterior of the cell. Since the potential is higher on the exterior than in the interior, the electric field lines must point from the outside to the inside.
**read psg carfully, understand voltage/potential**
The change in Q, the magnitude of charge on each surface of the axon membrane shown in the graph, could be produced by which of the following?
**circuit pic on other side**

Inactivity of the Na+/K+ pump
The graph shows how the charge decreases as a capacitor discharges, which occurs when the voltage between the plates is no longer maintained. If the Na+/K+ pump (the voltage source) stopped working, the voltage between the sides of the membrane would no longer be maintained. It would be wrong to say “a steady decrease in the voltage”; if V decreased steadily, then, since Q ∝ V, Q would also decrease steadily and its graph would be a straight line.
33%
If the absolute pressure of a gas is increased from 3 atm to 4 atm at constant volume, then the absolute temperature of the gas will increase by:
Assuming the validity of the Ideal-Gas law, PV = nRT, an increase in pressure by a factor of 4/3 at constant volume will result in an increase in temperature by the same factor (since P is proportional to T if V and n are constant). Multiplying the temperature by 4/3 = 133% implies an increase by 33%.
Which one of the following best represents the phase diagram of water?
The characteristic that distinguishes the phase diagram for water from the phase diagram for virtually all other substances is that the solid–liquid boundary line in the phase diagram for water has a negative, rather than a positive slope.

RNA Molecules compared to DNA (just a general facts)
RNA molecules have decreased stability compared to DNA in part because of their susceptibility to alkaline hydrolysis due to the presence of hydroxyl group at 2’-C position
Some RNAs have enzymatic function (such as in telomerase) and they are termed ribozymes.
tRNA has unique and modified bases apart from the traditional four bases A,U,C, and G (such as inosine)
rRNA is synthesized in the nucleolus
Two blocks are suspended from the ends of a massless meter stick as shown below:
How far from the center of the stick must the rope be attached in order to maintain rotational equilibrium?

30 cm
Intuitively, the rope must be closer to the heavier block to balance the stick. Since the block on the left is 4 times heavier, the rope must be attached at a point which is 4 times closer to the left-hand block than to the right-hand block to balance the torques due to the weights of the blocks. So, letting x denote the distance from the 4 kg block to the rope’s suspension point, the distance from the 1 kg block to the suspension point is 4x. Thus, x + 4x = 100 cm, which implies x = 20 cm. The rope is therefore suspended at a point which is 50 – 20 = 30 cm from the center of the stick.
if overall energy of something doesn’t change, neither will the _____, ______, nor ____ done by the object
**know connection between power, energy, and work**
neither will the frequency, wavelength, nor work done by the object
Concentrating the energy into a shorter time period increases the power of each pulse (since power equals energy delivered per unit time, by definition).
A CO2 laser used as a laser scalpel produces a beam of laser light with a wavelength of 10.6 µm. Compared to the excited electrons in the laser shown in Figure 1, the excited electrons in the CO2 laser most likely have:
a smaller energy difference between their normal state and their excited state.
The wavelength of the CO2 laser is 10 times greater than the wavelength of the laser shown in Figure 1. Therefore, the frequency and the energy of the CO2 laser are 10 times lower. Since the laser light is the energy released by transitions of electrons dropping to a lower energy level, less emitted energy implies a smaller difference between the energy levels. The mass of an electron is independent of its atomic or molecular energy state (Fyi).
If the front mirror in Figure 1, which is made of glass of refractive index 3/2, were repositioned so that the laser beam strikes at an angle of 30° to its normal, what would be the angle of reflection?
physics

30°
If the laser beam strikes the mirror at an angle of 30° relative to the normal, then this is the angle of incidence, and, by the Law of Reflection, it is also the angle of reflection. The refractive index of the mirror is irrelevant.
angle of incidence = angle of reflection: the angle that a straight line, ray of light, etc. that is meeting a surface, makes with the “normal” line and the surface
the “normal” line: is an imaginary line at 90° to where the ray touches the surface
hydrolase
enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of, among other bond types, the phosphoric anhydride bonds found in GTP
Lyases
enzymes that cleave bonds without the addition of water (non-hydrolytically)
Transferases
class of enzymes involved in the transfer of a functional group from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule
Oxidoreductase
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
conjugate base example
look at picture: the side-chain carboxylic acid groups of Glu23 and Glu57 function catalytically in ADP-ribosylation in their conjugate base form
What change in cytosolic conditions would most directly disrupt the catalytic function of the Glu23, and Glu57 residues?
- w/ decreased pH: increase the likelihood of protonating and inactivating either residue, thus most directly disrupting enzyme function
- w/ increased pH: Increasing cytosolic pH would not interfere with the conjugate base states of Glu23 and Glu47
- w/ increased or decreased temp: neither change is likely to have a direct effect on the catalytic ability of either residue
Which one of the following is true of Reaction 1?
**know what a redox reaction is**

The oxidation state of Ag does not change.
Reaction 1 is not a redox reaction. The oxidation states of Ag and I in AgI(s) are +1 and –1, respectively, and neither changes during dissolving.
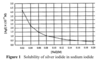
How many grams of NaI should be added to 500 mL of a saturated solution of AgI to make a solution that is 1.5 x 10–15 M Ag+?
4.5 g
Figure 1 indicates that when [AgI] = 1.5 x 10–15 M, the concentration of NaI = 0.06 M. In 500 mL (0.5 L), this solution should contain 0.030 mol NaI. Since the molar mass of NaI is 150 g/mol, this amounts to 4.5 g of NaI.
common ion effect
consequence of Le Châtelier’s Principle
refers to the decrease in solubility of an ionic precipitate by the addition of a soluble compound with an ion in common with the precipitate
ex) AgI and adding NaI –> A higher [I–] shifts Reaction 1 to the left.

If a fully saturated solution of AgI, with precipitate present, were treated with NaCl instead of NaI, which of the following observations is likely?
**know solubility/equilibrium and interactions between compounds**

The concentration of [I–] increases.
Unlike NaI, NaCl does not have a common ion with AgI and will therefore NOT cause a decrease in the solubility for AgI with increasing concentration. The following will act as a competing reaction when [Cl–] concentrations become sufficiently large:
Ag+ (aq) + Cl– (aq) → AgCl (s)
With this in mind, there will be no situations wherein the solution is free of precipitate. As the dissolved [NaCl] concentration increases, AgCl will be precipitated from solution, which will enable additional AgI to dissolve. The increased dissolution (“dissolvability”) of AgI will cause the increase in [I–], even as [Ag+] levels remain low.
Raclopride-H+ can best be described as:

an amphiphilic molecule that has two stereoisomers
In the reaction shown in figure 1, raclopride-H+ donates a proton in the first step (acting as a Brønsted–Lowry acid). Raclopride-H+ has a hydrophobic halogenated aromatic portion, and a hydrophilic side chain (protonated amine), making it an amphiphilic or amphipathic molecule. The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound may have is given by the formula 2n, where n is the number of chiral centers present. Raclopride-H+ has one chiral center, so it has two stereoisomers.
amphiphilic and amphipathic
is that amphipathic describes a molecule that has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups
amphiphilic has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic (or lipophilic) groups
**end answer? both mean the same thing**
sterioisomers
The maximum number of stereoisomers a compound may have is given by the formula 2n, where n is the number of chiral centers present.
is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
Nucleophiles, Electrophiles, and Leaving Groups
Nucleophilic functional groups are those which have electron-rich atoms able to donate a pair of electrons to form a new covalent bond.
An electrophilic atom is usually a carbon which is bonded to an electronegative atom, usually oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or a halogen. An electron-poor atom is an attractive target for something that is electron-rich, i.e. a nucleophile.
A leaving group is a molecular fragment that departs with a pair of electrons.
In the second step of the reaction shown in Figure 1, the role of water can best be described as a(n):
**ligand vs. nucleophile vs. electrophile vs. leaving group**

Protonation of the carbonyl group at the oxygen atom in the first step of the reaction in Figure 1, makes the carbonyl-carbon a good electrophile. As the protonated carbonyl was an ester, a carboxylic acid derivative, it will undergo an addition-elimination reaction. Water acts as the nucleophile, attacking the electrophilic carbonyl at the carbon atom as shown below. The carboxylate is then eliminated as the leaving group. A ligand is a molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. There are no metal atoms involved in the reaction, so ligand would be the wrong answer.

Which of the following occur(s) in the reaction shown in Figure 1?
** Oxidation vs. Elimination vs. Saponification**

Elimination
Oxidation is false. There is no change in the oxidation states in any of the individual atoms in the reaction shown in Figure 1. Elimination is true. During the reaction, an ester is converted into a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo an addition reaction followed by an elimination reaction. Saponification is false bc it is the base-mediated hydrolysis of an ester. While an ester is hydrolyzed in the reaction, it is achieved under acidic conditions.
A converging glass lens forms a real image of a red object at a distance equal to twice its focal length. If a blue object is placed adjacent to the red object, will its image form closer to the lens or farther from the lens than the image of the red object?
**Light: Wave Effects and Optics: Mirrors/Lenses**
Closer, because blue light is refracted more due to its shorter wavelength
blue light has a shorter wavelength than red light. The refractive index of a transparent medium increases with increasing frequency of the transmitted light. Thus, the refractive index of the lens for blue light would be slightly higher than for red light. This would imply that blue light experiences more refraction than red light. Since the lens is a converging one (because diverging lenses cannot form real images), the blue light would be bent more sharply toward the axis than the red light, so the image of the blue object would be formed closer to the lens.
As an ideal fluid flowing in a narrow pipe passes from a region of cross-sectional diameter d to a region of cross-sectional diameter d / 2, the flow speed of the fluid will:
**Fluids: Flow Rate and Continuity**
increase by a factor of 4
If the diameter of the flow tube decreases by a factor of 2, the cross-sectional area decreases by a factor of 22 = 4. Since the Continuity Equation implies that flow speed is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the flow tube, the flow speed will increase by a factor of 4.
Which of the following is true about the molecule shown?
**Isomerism**

It is meso
The pictured epoxide has two chiral centers, but it also has a plane of symmetry. For this reason, it is a meso compound, and its two chiral centers must have opposite configurations (one is R while the other must be S).
meso vs absolute configuration (R vs. S)
Which one of the following statements concerning the SN2 reaction mechanism is true?
**Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: SN1 and SN2 Reactions**
It proceeds best with primary substrates and is a one-step reaction.
SN2 cannot operate with a tertiary substrate because the nucleophile must attack at the same time the leaving group leaves, and tertiary substrates are too sterically hindered. SN2 goes with inversion of stereochemistry, not retention. SN1 reactions have Unhindered substrates allow the nucleophile to attack while the leaving group leaves.
Strongest dipole moment
a bond has a dipole moemnt when the two atoms involved in the bond differ in electronegativity. However, an entire molecule can only have a dipole if it contains bond dipoles and is asymmetrical


