Chapter_01 Flashcards
(71 cards)
What is digital marketing?
Achieving marketing objectives through applying digital technologies
Customer-centric digital marketing involves:
- Applying digital technologies which form online channels… (Web, e-mail, databases, mobile, iPTV)
- to Contribute to marketing activities aimed at achieving profitable acquisition and retention of customers (within a multi-channel buying process
and customer lifecycle) - through Improving customer knowledge (of their profiles, behaviour, value and loyalty drivers), then delivering integrated targeted communications and online services that match their individual needs
Marketing is the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitability
How do digital technologies support marketing?
- Identifying – the Internet can be used for marketing research to find out customersʼ needs and wants
- Anticipating – the Internet provides an additional channel by which customers can access information and make purchases
- Satisfying – a key success factor in e-marketing is achieving customer satisfaction through the electronic channel, which raises issues such as: is the site easy to use, does it perform adequately, what is the standard of associated customer service and how are physical products dispatched?
What are the Applications of digital marketing?
- advertising medium
- direct-response medium
- platform for sales transactions
- lead-generation method
- distribution channel
- customer service mechanism
- relationship-building medium
Give a summary and examples of transaction alternatives between businesses, consumers and governmental organisations

What are the challenges of managing a digital marketing strategy?
- Unclear responsibilities for digital
- Setting objectives
- Lack of budget
- Budget wasted through experiments/duplication
- Developing new propositions and campaigns to compete
- Lack of measurement u i.e. No plan!
Why is a digital strategy needed?
- To set clear goals for digital channels
- To align with business strategy (avoid ad-hoc
- approaches)
- Create a specific online value proposition (OVP) u Specify communications tools to drive visitors
- Integrate digital and traditional channels
- Manage customer lifecycle (e.g. through email marketing)
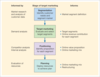
What does a generic digital marketing strategy development process look like?

What do the communication models for traditional media and new media look like?
traditional media:
new media:
(unique messages and more information exchange between customers)
(same message to every customer)

What are two fundamental digital marketing concepts?
Customer engagement:
- Repeated interactions that strengthen the emotional, psychological or physical investment a customer has in a brand” cScape
- the level of involvement, interaction, intimacy, and in;uence an individual has with a brand over time” Forrester
Permission marketing:
- A value exchange in return for communications and profiling, e.g. Email opt-in, Like of brand on Facebook
What does The Internet marketing environment look like?

What are the issues for digital marketers in the micro-environment?

Evaluating demand levels
Level of Internet access
Includes type of access – broadband and mobile
Consumers influenced by using online channel
Includes understanding type of sites which have influence
Transact online
Includes different types of transactions, not just sales, e.g. support, forum comments, etc.
What are the different Information / experience seeking consumer behavior models?
Directed information-seekers. These users will be looking for product, market or leisure information such as details of their
football clubʼs fixtures. They are not typically planning to buy online.
Undirected information-seekers. These are the users, usually referred to as ʻsurfersʼ, who like to browse and change sites by following hyperlinks. Members of this group tend to be novice users (but not exclusively so) and they may be more likely to click on banner advertisements.
Directed buyers. These buyers are online to purchase specific products online. For such users, brokers or cybermediaries that compare product features and prices will be important locations to visit.
Bargain hunters. These users (sometimes known as ʻcompersʼ) want to find the offers available from sales promotions such as free samples or competitions. For example, the MyOffers site (www.myoffers.co.uk) is used by many brands to generate awareness and interest from consumers.
Entertainment seekers. These are users looking to interact with the Web for enjoyment through entering contests such as quizzes, puzzles or interactive multi-player games.
Hierarchy of response buying process models

In what categories can competitors be benchmarked?

What are the different types of portals and their characteristics?

Disintermediation of a consumer distribution channel

What are the five forces of Porter?
Competitive Rivalry. This looks at the number and strength of your competitors. How many rivals do you have? Who are they, and how does the quality of their products and services compare with yours?
Where rivalry is intense, companies can attract customers with aggressive price cuts and high-impact marketing campaigns. Also, in markets with lots of rivals, your suppliers and buyers can go elsewhere if they feel that they’re not getting a good deal from you.
On the other hand, where competitive rivalry is minimal, and no one else is doing what you do, then you’ll likely have tremendous strength and healthy profits.
Supplier Power. This is determined by how easy it is for your suppliers to increase their prices. How many potential suppliers do you have? How unique is the product or service that they provide, and how expensive would it be to switch from one supplier to another?
The more you have to choose from, the easier it will be to switch to a cheaper alternative. But the fewer suppliers there are, and the more you need their help, the stronger their position and their ability to charge you more. That can impact your profit.
Buyer Power. Here, you ask yourself how easy it is for buyers to drive your prices down. How many buyers are there, and how big are their orders? How much would it cost them to switch from your products and services to those of a rival? Are your buyers strong enough to dictate terms to you?
When you deal with only a few savvy customers, they have more power, but your power increases if you have many customers.
Threat of Substitution. This refers to the likelihood of your customers finding a different way of doing what you do. For example, if you supply a unique software product that automates an important process, people may substitute it by doing the process manually or by outsourcing it. A substitution that is easy and cheap to make can weaken your position and threaten your profitability.
Threat of New Entry. Your position can be affected by people’s ability to enter your market. So, think about how easily this could be done. How easy is it to get a foothold in your industry or market? How much would it cost, and how tightly is your sector regulated?
If it takes little money and effort to enter your market and compete effectively, or if you have little protection for your key technologies, then rivals can quickly enter your market and weaken your position. If you have strong and durable barriers to entry, then you can preserve a favorable position and take fair advantage of it.
What impact does the Internet have on the five competitive forces

What are some Publisher revenue models?
- Revenue from subscription access to content.
- Revenue from Pay Per View access to documents.
- Revenue from CPM display advertising on site (e.g. banners ads, skyscrapers or rich media).
- CPM stands for ʻcost per thousandʼ where M denotes ʻMilleʼ. u Revenue from CPC advertising on site (pay per click text ads)
- CPC stands for ʻCost Per Clickʼ. Advertisers are charged not simply for the number of times their ads are displayed, but according to the number of times they are clicked.
- Revenue from Sponsorship of site sections or content types (typically fixed fee for a period) –
- Affiliate revenue (typically CPA, but could be CPC)
- Affiliate revenue is commission based, for example if you display links to Amazon books on your site, you can receive around 5% of the cover price as a fee from Amazon.
Why should one review the macro-environment
The main reason for keeping track of changes in the macro-environment is to be aware of how changes in social behaviour, new laws, technological innovation can create opportunities or threats. Organisations that monitor and respond effectively to their macro-environment can create differentiation and competitive advantages which enable the business to survive and prosper.
What are some Key macro-environment factors?
- Political forces
- Economic forces
- Social forces
- Technological forces
- Legal forces
- Environmental forces
What does the Information exchange between a web browser and a web server look like?

Explain the relationship between access to intranets, extranets and the Internet text editor