Chapter 7: Neoplasia Flashcards
What kind of tumor is derived from glands and applied to benign epithelial neoplasms?
Adenoma
What benign epithelial neoplasm has visible finger like or warty projections?
Papilloma
A polyp with glandular tissue is called what?
Adenomatous polyp
Malignant tumors arising from solid mesenchymal tissues are called what?
Sarcoma
Malignant neoplasms of epithelial cell origin, derived from any of the 3 germ layers, are called what?
Carcinomas
What is the most common mixed tumor?
Capable of producing what and is designated?
- Salivary gland mixed tumor
- Epithelial and myoepithelial cells = pleomorphic adenoma
What is the term applied to a heterotopic rest of cells?
i.e., a small nodule of well-developed and normally organized pancreatic tissue found in the submucosa of the stomach, duodenum, or SI.
Choristoma
Lack of differentiation, or anaplasia, is considered a hallmark of?
Malignancy
What refers to variation of size and shape of cancer cells?
Pleomorphism
What best describes carcinoma in situ?
- Dysplastic changes are marked and involve the full thickness of the epithelium
- Lesions DO NOT penetrate the BM
What malignant cancers invade early but rarely metastasize?
- Gliomas
- Basal cell carcinoma of the skin
Once tumor cells breach the basement membrane they are said to be?
Invasive
How is dysplasia related to malignant transformation?
Is all metastatic epithelium dysplastic?
- May be a precursor to malignant transformation
- Does NOT always progress to cancer
- Not all metastatic epithelium is dysplastic
What are the 3 pathways of spread of cancer?
1) Direct seeding of body cavities or surfaces
2) Lymphatic spread
3) Hematogenous spread
In direct seeding of body cavities, sometimes appendiceal carcinomas or ovarian carcinomas fill the peritoneal cavity with what?
Pseudomyxoma peritonei
What is the most common pathway for the initial dissemination of carcinomas?
Lymphatic spread
Where do carcinomas of the breast in the upper outer quadrant disseminate 1st to?
Inner quadrants?
- Axillary LNs
- LNs along internal mammary arteries
Where do carcinomas of the lung in the major respiratory passages metastasize first to?
Perihilar tracheobronchial and mediastinal nodes
Renal cell carcinoma invades what structure?
Renal vein —> IVC —-> right side of the heart (sometimes)
Hepatocellular carcinoma often penetrates what?
Portal and hepatic radicles
Breast carcinoma preferentially spreads to where?
Bone
Bronchogenic carcinoma preferentially spreads to where?
Adrenals and brain
Neuroblastoma preferentially spreads to where?
Liver and bones
To avoid the considerable surgical morbidity associated with full LN dissection, which technique is often used to assess the presence of metastatic lesions in the LNs?
- Biopsy of sentinel nodes
*The first node in a regional lymphatic basin that receives lymph flow from the primary tumor
Which organs are most frequently involved in hematogenous dissemination of cancer?
Liver and lungs
Describe the following for benign cancers:
- Differentiation
- Rate of growth
- Local invasion
- Metastasis
- Well differentiated; structure sometimes typical of tissue of origin
- Progressive and slow growth
- Cohesive, expansile, well-demarcated masses that do not invade
- Absent metastasis
Describe the following for malignant cancers:
- Differentiation
- Rate of growth
- Local invasion
- Metastasis
- Lack differentiation (anaplasia); structure often atypical
- Erratic, slow or rapid growth
- Locally invasive
- Frequent metastasis
Cancers arising in close proximity to the vertebral column often embolize through where?
This pathway is involved in the frequent vertebral metastases of carcinomas of?
- Paravertebral plexus
- Thyroid and prostate
What are the most common tumors in Men?
Woman?
Men = prostate, lung, and colon
Woman = breast, lung and colon
What is responsible for a large majority of cervical carcinoma and increasing fraction of head and neck cancers?
HPV
What cancer is associated with benzene (i.e., light oil, paint, printing, dry cleaning, adhsives. etc.)?
Acute myeloid leukemia
What cancer is associated with beryllium (i.e., missle fuel, space vehicles)?
Lung carcinoma
What cancer is associated with cadmium (i.e., yellow pigments and phosphors; used in batteries, etc.)?
Prostate carcinoma
What cancer is associated with vinyl chloride (i.e., refrigerant, vinyl polymers, plastic adhesives, etc.)?
Hepatic angiosarcoma
What cancer is associated with chromium (i.e., metal alloys, paints, pigments, and preservatives)?
Lung carcinoma
What cancers are associated with nickel?
Lung and oropharyngeal carcinoma
What cancers are associated with Arsenic?
Lung carcinoma
Skin carcinoma
What is the etiologic agent of osteomyelitis?
What neoplasm?
- Bacterial infection
- Carcinoma in draining sinuses
What is the etiologic agent of Chronic Cystitis?
What neoplasm?
- Schistosomiasis
- Bladder carcinoma
What is the associated neoplasm of Sjorgen syndrome and Hashimoto thyroiditis?
MALT lymphoma
What is the classic example of a benign, neoplastic, precursor lesion?
Colonic villous adenoma
What are 2 examples of epigenetic modifications that contribute to the malignant properties of cancer cells?
1) DNA methylation: silencing of tumor suppressor genes
2) Histone modification
What are the 4 classes of regulatory genes that are principal targets of cancer-causing mutations?
1) Growth-promotong proto-oncogenes
2) Growth-inhibiting tumor suppressor genes
3) Genes that regulate apoptosis
4) DNA-repair genes
What are the 8 fundamental changes in cell physiology, which are considered the hallmarks of cancer?
1) Self-sufficiency in growth signals
2) Insensitivity to growth-inhibitory signals
3) Altered cellular metabolism
4) Evasion of apoptosis
5) Limitless replicative potential (immortality?)
6) Sustained angiogenesis
7) Ability to invade and metastasize
8) Ability to evade host immune response
Define Oncoprotein
A protein encoded by an oncogene that drives increased cell proliferation through one of several mechanisms
What is MYC known as and what are its important functions?
- The master transcription factor that regulates genes needed for rapid cell growth by deregulation through chromosomal translocations
90% of what type of cancer contains RAS mutations?
Pancreatic adenocarcinomas
What is the major function of CDK4; D cyclins?
Form a complex that phosphorylates RB, allowing the cell to progress through the G1 restriction point
What is the major function of the cell cycle component, RB?
- Tumor suppressive “pocket” protein that binds E2F transcription factors in its hypophosophorylated state, prevents G1/S transition
- Interacts with several transcription factors that regulate differentiation
What induces the cell cycle inhibitor p21?
p21 is induced by tumor suppressor p53
What responds to growth suppressors such as TGF-B?
p27
What chromosome is p53 located on?
Acts mainly through what?
What negatively regulates p53?
- Chromosome 17
- Acts mainly through p21
- Negatively regulated by MDM2
What inhibits MDM2 activity?
What does this do?
- p14
- Increases p53 activity
What specifically binds to cyclinD-CDK4, blocking CDK4/cyclin D-mediated phosphorylation of RB; thereby reinforcing the RB checkpoint?
p16
What occurs in the familial form of retinoblastoma?
Inherited how?
- All somatic cells inherit one mutated copy of RB gene from a carrier parent (first hit)
- Only one additional RB mutation in a retinal cell is required for complete loss of RB function (second hit)
- Autosomal dominant
What occurs in sporadic cases of Retinoblastoma?
- Both normal RB alleles must undergo somatic mutation in the same retinoblast (two hits)
- Probability of this event is low (explaining why this tumor is uncommon in th general population)
What is the “two-hit” hypothesis of oncogenesis as it relates to retinoblastoma?
Which chromosome involved?
- Two mutations (hits) involving both alleles of RB at chromosome locus 13q14 are required to produce retinoblastoma
- In familial cases, children inherit one defective copy of the RB gene in the germline (first hit), and the other copy is normal. Retinoblastoma develops when the normal RB allele is mutated in retinoblasts as a result of spontaneous somatic mutation (second hit)
What are the key initiators of p53 activity following DNA damage or cellular exposure to hypoxia?
How do they act; what is p53 released from?
- ATM/ATR family
- These kinases phosphorylate p53, liberating it from inhibitors such as MDM2
What affect does the active hypophosphorylated RB in complex with E2F transcription factors have?
- Binds DNA, recruits chromatin-remodeling factors (histone deacetylases and histone methyltransferases)
- Inhibits transcription of genes who products are required for the S phase of the cell cycle

What phosphorylates RB (inactivating it)?
What occurs when RB is phosphorylated?
- Phosphorylated by cyclin D-CDK4 and CDK6; also cyclin E-CDK2
- Causes RB to release E2F
- E2F is then able to activate transcription of S-phase genes

Virtually all cancer cells show dysregulation of the G1-S checkpoint as a result of mutation in one of four genes that regulate the phosphorylation of RB; what are these genes?
- RB (loss of function mutations)
- CDK4 (gene amplifications)
- -* Genes encoding cyclin D proteins (gene amplifications)
- CDKN2A (p16): loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors
Which GFs activate Cyclins D/CDK4,6 and Cyclin E/CDK2 leading to hyperphosphorylated RB (inactive)?
EGF and PDGF

Explain the interaction between the E7 protein of HPV and RB, where does it bind?
Which form of HPV is higher risk and why?
- Binds to hypophosphorylated form of RB in the same pocket which normally sequesters E2F transcription factors
- HPV16 confers a high risk for development of cervical carcinoma and expresses E7 protein variants with higher affinity for RB than do lower risk viral types
- RB protein is unable to bind E2F transcription factors and is functionally inactivated by these viral oncoproteins, and the E2F factors are free to cause cell cycle progression
Normal GF signaling leads to RB _______ and __________, thus promoting cell cycle progression
Normal GF signaling leads to RB hyperphosphorylation and inactivation, thus promoting cell cycle progression

Tumors with wild type or mutated TP53 alleles are more susceptible to chemotherapy?
What kind of cancers?
- Wildtype
- Testicular Teratocarcinomas and Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Activation of normal p53 by DNA-damaging agents or by hypoxia leads to cell cycle arrest in which phase?
Causes induction of DNA repair by transcriptional upregulation of what?
- Arrest in G1
- Upregulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, CDKN1A (encoding p21): inhibitor of CDK4/D cyclin
- Upregulation of GADD45 genes (DNA repair)

If DNA repair fails, what does p53 trigger?
- Apoptosis (through BAX and PUMA)
- Senescence

Mutated TP53 alleles are mostly resistant to chemotherapy and irradiation and include what cancers?
Lung and colorectal cancers
What do cells with defective p53 acquire and what does this result in?
- Mutator phenotype
- Tendency to acquire additional mutations at a higher rate
Rare patients with Li-Fraumeni syndrome inherit how many defective copies of TP53?
Inherit one defective copy of TP53 and have a very high incidence of a wide variety of cancers
The majority of human cancers demonstrate ________ mutations in TP53
The majority of human cancers demonstrate biallelic loss-of-function mutations in TP53
Like RB, p53 can also be inactivated by?
Viral oncoproteins, such as the E6 protein of HPV
What is the “gatekeeper of colonic neoplasia?”
Functions by?
- Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)
- Downregulates growth-promoting signaling pathways
Germline loss-of-function mutations involving APC (5q21) locus are associated with what disorder?
Inheritance pattern?
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis = Autosomal Dominant
- Individuals born w/ one mutant allele develop thousands of adenomatous polyps in the colon during their teens or 20s
What is the role of APC in regulating the stability and function of β-catenin in both resting and WNT activated colonic epithelial cells?
Forms what?
What does β-catenin do?
- In resting colonic epithelial cells (not exposed to WNT), β-catenin forms macromolecular complex containing the APC protein. This complex leads to destruction of β-catenin, and intracellular levles are low
- When stimulated by WNT, the destruction complex is deactivated, β-catenin degradation does not occur, and cytoplasmic levels increase
- β-catenin translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to TCF, a TF that activates genes involved in cell cycle progression and proliferation

Germline loss-of-function mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene on chromosome 3p are associated with what?
- Hereditary renal cell cancers
- Pheochromocytomas
- Hemangioblastomas of the CNS
- Retinal angiomas
- Renal cysts
When APC is mutated or absent, as frequently occurs in colonic polyps and cancers, what happens to β-catenin?
How do they cells behave?
- The destruction of β-catenin cannot occur.
- β-catenin translocates to nucleus and coactivates genes that promote entry into the cell cycle and cells behave as if they are under constant stimulation by the WNT pathway
VHL encodes what, which is reponsible for?
How does this function in oxygen rich and hypoxic enviornments?
- Encodes a component of a ubiquitin ligase that is responsible for the degradation of hypoxia-induced factors (HIFs)
- In presence of oxygen, HIF1α is hydroxylated and binds to VHL, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation
- In hypoxia the hydroxylation rxn does NOT occur and HIF1α escapes recognition by VHL and accumulates in nuclei of hypoxic cells turning on genes encoding VEGF, PDGF, and GLUT1
In chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and some acute lymphoblastic leukemias (ALL), which translocation occurs?
What does this fusion create?
- ABL gene is translocated from chromosome 9 to chromosome 22 where it fuses with the BCR gene
- Encodes a constituitively active, oncogenic BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase

Which portion of the BCR-ABL fusion has the tyrosine kinase activity?
What is the function of the other gene?
- ABL has tyrosine kinase activity
- BCR drives self association of BCR-ABL and unleashes activity of ABL
What 6 ways are tumor cells able to evade cell death by apoptosis?
1) Loss of p53 –> reducedfunction of pro-apoptotic factors such asBAX
2) Reduced egress of cytochrome c as a result of upregulation of anti-apoptotic factors such as BCL2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1
3) Loss of apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 (APAF1)
4) Upregulation of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP)
5) Reduced CD95 level
6) Inactivation of death-induced signaling complex FADD, needed for Fas-FasL

Which pathway of apoptosis is most commonly affected in cancer cells?
Intrinsic (mitochondrial)
In >85% of follicular B-cell lymphomas, what gene is overexpressed?
Due to what translocation?
- Anti-apoptotic gene BCL2
- (14;18) translocation
What are the most common general category of tumor in adults?
Children?
Adults = Carcinomas
Children = Acute Leukemia and distinctive neoplasms of CNS
What is an abundant collagenous stroma called?
How can this also be described?
- Desmoplasia
- Scirrhous
What chromosome is the RB gene located?
How is it inherited?
- Chromosome 13
- Autosomal dominant
What cancer is specific to a mutation in BRCA2?
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
What is the function of GADD45?
What induces it?
- DNA repair
- p53
What does CDKN2A activate?
p16 and p14
What is a novel gene expression assay that is being used to predict prognosis and treatment response in cancer patients?
- Expression of CEN/KT (centromere and kinetochore) genes
- Centromere and kinetochore gene expression score (CES) signature
How does the Warburg effect work (3 signaling mechanisms)?
1) PI3K/AKT signaling
2) RTK activity
3) MYC
What opposes the actions of the Warburg effect via blockage of PI3K/AKT signaling?
PTEN
Mutation of PTEN results in what?
Located on what chromosome?
- Cowden syndrome
- Chromosome 10
Hypoxia triggers angiogenesis through the actions of?
HIF1α on the transcription of the proangiogenic factor VEGF
How does p53 regulate angiogenesis?
RAS, MYC, and MAPK?
- p53 Induces synthesis of the angiogenesis inhibitor thrombospondin-1
- RAS, MYC, MAPK all upregulate VEGF expression and stimulate angiogenesis
Invasion of the ECM, a hallmark of malignancy, occurs in what 4 steps?
1) Loosening of cell-cell contacts
2) Degradation of ECM
3) Attachment to novel ECM components
4) Migration and invasion of tumor cells
Via which enzymes and factors are tumor cells able to degrade the basement membrane and interstitial CT during the second step of invasion?
- Tumor cells may secrete proteolytic enzymes themselves
- May induce stromal cells (i.e., fibroblasts and inflammatory cells) to elaborate proteases, such as MMP, Cathepsin D, and Urokinase plasminogen activator

What is loss of adhesion to the BM called?
Triggers what?
- Anoikis
- Apoptosis
Solid tumors and normal T lymphocytes is use what to spread to LNs and other metastatic sites?
- Binding of CD44 to hyaluronate on high endothelial venules
- Solid tumors express CD44, which appears to enhance their spread to LNs and other metastatic sites
What mechanisms may account for the organ tropism exhibited by tumor cells and why metastasis sometimes occurs in locations unrelated to the initial site of the tumor?
- Tumor cells may have adhesion molecules whose ligands are expressed preferentially on the endothelial cells of the target organ
- Chemokines may play an important role. Some breast cancer cells express the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7
- In some cases, the target tissue may be a nonpermissive enviornment - “unfavorable soil”
The prolonged survival of micrometastases without progression (dormancy) like in breast cancer metastases to bone is accomplished how?
- Breast cancer cells secrete PTHRP, which stimulates osteoblasts to make RANKL
- RANKL activates osteoclasts, which degrade the bone matrix and release GFs embedded within, like IGF and TGF-B
- GFs help make the metastatic site habitable for the cancer cells.
What protein is often found overexpressed in drug-resistant cancers?
MCL-1
What areas of the body rarely have metastasis?
Why?
- Spleen and Skeletal muscle
- Represent “unfavorable soil”
What are the main pro angiogenic factors?
GOF mutations in what may upregulate them?
- VEGF, bFGF
- GOF mutations in RAS or MYC
What are the oncofetal antigens whose expression at high levels serve as markers that aid in tumor diagnosis and clinical management?
- CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
- AFP (α-fetoprotein)
The first step in invasion of the ECM by tumor cels involves loss of?
E-cadherin function
Where do most metastasis occur?
What organs?
- First capillary bed available
- Lung and liver
Which oncogene products and tumor suppressor gene products may enter MHC class I and class II for detection by the immune system?
Mutated RAS, p53, and BCR-ABL

Which overexpressed and aberrantly expressed cellular proteins may lead to detection of tumor cells by the immune system?
Overexpressed: tyrosinase, gp100, MART in melanomas
Aberrantly expressed: cancer-testis Ags (MAGE, BAGE)

Which T lymphocytes have a clear protective role against virus-associated neoplasms and increased number of these cells correlates with a better prognosis in a variety of cancers?
CD8+ CTLs
Which immune cells may collaborate in anti-tumor reactivity?
T cells, NK cells, and Macrophages
Which cytokines activate NK cells and what is their effect on tumor cells?
- IL-2 and IL-15
- NK cells can lyse a wide range of human tumors, including many that seem to be nonimmunogenic for T cells
What mode of inheritance is hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC)?
Defect in what?
Genome shows what?
- Autosomal dominant
- Mismatch repair system
- Microsatellite instability (hallmark) = changes in length of short repeats throughout the genome
Antibodies against which transmembrane protein expressed on the surface of all normal B-cells have been used in the treatment of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias?
What are these antigens called?
- CD20
- Differentiation antigens
Which mutations leading to genomic instability are important causes of lymphoid neoplasms?
Mutations in lymphoid cells due to expression of gene products that induce genomic instability (RAG1, RAG2, AID)
What leads to anemia in patients with advanced cancers?
Inflammation-induced sequestration of iron and downregulation of EPO production
What has been shown to decrease the incidence of colonic adenomas and are now approved for tx of patients with familial adenomatous polyposis?
COX2 inhibitors
What mucins are expressed on ovarian carcinomas?
Colon and pancreatic?
Breast?
CA-125
CA19-9
CA15-3
Which gene responsible for nucleosome positioning/chromatin remodeling is mutated in 100% of Malignant rhabdoid tumors?
SNF5
Which genes responsible for histone methylation are seen in 90% of Acute leukemia in infants and Follicular Lymphomas?
- MLL1 =* Acute leukemia in infants
- MLL2* = Follicular lymphoma
In the molecular model for the evolution of colorectal cancers through the adenoma-carcinoma sequence what are the steps?
What are the “first hit” and “second hit”?
“First hit” = loss of APC tumor suppressor genes at 5q21
“Second hit” = methylation abnormalities; APC – β-catenin
- Activation of RAS
- Loss of TP53 at chromosome 18

Where is MUC-1 expressed?
Ovarian and breast carcinomas
What is expressed on T cell lymphomas and Hodgkin lymphomas and antibodies to it may be used as treatment?
CD30
People with xeroderma pigmentosum are at increased risk for what?
Defect in what?
- Cancer of skin due to UV radiation –> pyrimidine dimers
- Nucleotide excision repair (NER)
Mutations in what genes account for 30% of HNPCC?
MSH2 and MLH1
Defects in the homologous recombination DNA repair system results in what 3 disorders?
1) Bloom syndrome
2) Ataxia-Telangiectasia
3) Fanconi anemia
Infiltrating cancers invoke chronic inflammatory states with what classic symptoms?
- Anemia
- Fatigue
- Cachexia
What miR is believed to be important in invasiveness and metastasis?
MiR-200
What miR is overexpressed in B cell lymphomas and upregulates MYC?
miR-155
Deletions of what miRs lead to CLL?
Their deletion upregulates what?
- miR-15 and miR-16
- BCL-2
Defects in DICER lead to what cancers?
Rare Ovarian and Testicular tumors
Which genotype seen in 10% of the white population increases the risk of developing lung cancer in light smokers nearly 7-fold?
CYP1A1
What carcinogen does Aspergillus make?
Causes what cancer?
- Aflatoxin B1
- Hepatocellular carcinoma in Africa and the Far East
Aflatoxin B1-associated hepatocellular carcinomas have which particular mutation in TP53?
G:C –> T:A transversion in codon 249 producing an arginine –> serine substitution in the p53 protein
What is responsible for the induction of cutaneous cancers?
Due to the formation of?
What wavelength?
- UVB
- Formation of pyrimidine dimers in DNA (NER); particularly adjacent thymidine residues in the same strand of DNA
- 280-320 nm
What are the most frequent radiation-induced tumors?
- Myeloid leukemias, Thyroid cancer (only in the young)
- Intermediate category: breast, lungs, and salivary gland cancers
What sites are relatively resistant to radiation-induced neoplasia?
Skin, bone, and GI tract
What is the main oncogenic RNA virus?
What does it cause?
Endemic where?
HTLV-1
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL)
Japan, Caribbean, South America, Africa
What protein is responsible for the transforming activity and essential for viral replication in HTLV-1?
Tax
How does the protein Tax produced by the HTLV-1 virus contribute to increased pro-growth signaling and cell survival?
- Interacts with PI3K and thereby stimulates AKT
- Directly upregulates expression of cyclin D2 and represses function of CDK inhibitors
- Activates the TF NF-kB
What are the high-risk DNA viruses associated with squamous cell carcinomas of the cervix, anogenital region, and head/neck?
HPV 16 and 18
What binds to and mediates the degradation of p53?
What does it stimulate?
Polymorphism of Arg72 in p53 leads to what?
- E6 protein
- Stimulates expression of TERT, catalytic subunit of telomerase
- Cervical carcinomas

What binds RB protein and displaces E2F?
What can it inactivate?
What can it activate?
- E7 protein
- Inactivates CDK inhibitors p21 and p27
- Activates cyclins E and A
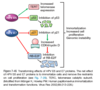
HPV itself is not sufficient for Carcinogenesis, what else does it need for full malignant transformation?
Co-transfection with mutated RAS
What are the most common EBV associated tumors?
- Those derived from B cells (i.e., African Burkitt Lymphoma and B-cell lymphomas)
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
What does EBV use to infect B cells?
Complement receptor 2 (CR2, CD21)
What does EBV use as an oncogene?
How does it act?
- LMP-1
- Behaves like a constituitively active CD40 receptor = stimulates B cell growth
- Activates NF-kB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways and promotes B cell survival and proliferation
- Prevents apoptosis by activating BCL2
What is the most common childhood tumor in central Africa and New Guinea?
Burkitt lymphoma (EBV related)
In the case of Burkitt lymphoma it seems that EBV is not directly oncogenic, but instead acts how?
Acts as a polyclonal B-cell mitogen setting the stage for acquisition of the (8;14) translocation and other mutations that ultimately produce full-blown cancer
Which tumor is endemic in Southern China, some parts of Africa, and in the Inuit population?
Association with what virus?
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- EBV
While the oncogenic effects of HBV and HCV are multifactorial, what is the dominant effect in the development of hepatocellular carcinomas?
Immunologically mediated chronic inflammation and hepatocyte death leading to regeneration and, over time, genomic damage
Which key molecular step within hepatocytes blocks apoptosis, allowing the dividing hepatocytes to incur genotoxic stress and to accumulate mutations characteristc of HBV induced hepatocellular carcinoma?
Activation of NF-kB pathway
Which protein of HBV and the HCV core protein can activate signal transduction pathways that may contribute to carcinogenesis?
Where is HBV endemic?
- HBx protein
- Endemic in: Far East and Africa (highest incidences of hepatocellular carcinoma)
H.pylori causes what cancers?
What associated gene is present?
- Gastric adenocarcinoma and MALT (gastric) lymphomas
- CagA, stimulates growth factor pathways
Chronic H.pylori infection leads to polyclonal B-cell proliferations that may give rise to a?
Monoclonal B-cell tumor (MALT lymphoma) of the stomach
What is characteristic of neoplasms in the gut and urinary tract?
Melena (blood in stool) and Hematuria
Cancer cachexia is associated with what 3 events?
1) Equal loss of both fat and lean muscle
2) Elevated BMR
3) Evidence of systemic inflammation (i.e., increase in acute phase reactants)
Grading of tumors is based on what?
Cytologic appearance; based on idea that behavior and differentiation are related
What are the 3 things staging is graded on?
T - size of primary lesion
N - extent of spread to regional LNs
M - presence or absence of blood-borne metastases
T0 means what?
Indicative of In situ lesion
What are the major forms of underlying cancer associated with Cushing Syndrome?
Small-cell carcinoma of lung
Pancreatic adenoma
Neural tumors
Lung cancer patients with Cushing syndrome have elevated serum levels of?
- POMC
- Corticotropin
What are the 2 general processes involved in cancer-associated hypercalcemia?
Which of the 2 is considered to be paraneoplastic?
1) Osteolysis induced by cancer
2) Production of calcemic humoral substances by extraosseous neoplasms (only one considered paraneoplastic)
Which factors have been causally implicated in the hypercalcemia of malignancy?
Which is the most important?
- PTHRP = most important
- IL-1
- TGF-α
- TNF
Which tumors are most often associated with paraneoplastic hypercalcemia?
- Squamous cell carcinoma of lung
- Breast carcinoma
- Renal carcinoma
- Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
What are the 2 major forms of underlying cancer seen in Myasthenia?
1) Bronchogenic carcinoma
2) Thymic neoplasms
What is the major form of underlying cancer seen in disorders of the CNS and PNS?
Breast carcinoma
What are the 3 major forms of underlying cancer seen in patients with Acanthosis nigricans?
Due to what?
- Gastric carcinoma
- Lung carcinoma
- Uterine carcinoma
- Due to EGF secretions
What are the 2 major forms of underlying cancer seen in patients with Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and clubbing of the fingers?
1) Bronchogenic carcinoma
2) Thymic neoplasms
*Also seen in Myasthenia syndromes
Big Ten Hype
What are the 2 major forms of underlying cancer seen in patients with Migratory thrombophlebitis (Trousseau phenomenon)?
1) Pancreatic carcinoma
2) Bronchogenic carcinoma
Disseminated intravascular coagulation is most commonly associated with what 2 cancers?
1) Acute promyelocytic leukemia
2) Prostatic adenocarcinoma
DICAP-itated
What screening technique is used for carcinoma of the cervix, endometrial carcinoma, lung carcinoma, bladder and prostatic tumors, etc
Cytologic smears
What technique is used for assessment of breast, thyroid, and LN cancer?
Fine needle aspiration (FNA)
Presence of cytokeratins, detected by immunohistochemistry points to?
An epithelial origin (carcinoma)
What does presence of ALK in a immunohistochemical stain indicate?
Lung cancer and lymphomas
Flow cytometry is mainly used to identify cellular antigens expressed by what kind of tumors?
- “Liquid” tumors, those that arise from blood-forming tissues
- B- and T-cell lymphomas and leukemias, as well as myeloid neoplasms
HCG is a marker for what tumors?
- Trophoblastic tumors
- Testicular tumors
CA-125 is a marker for what?
- Ovarian tumors
- Immunoglobulin in multiple myeloma
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a marker for what?
- Hepatocellular carcinomas
- Embryonal cell carcinomas (yolk sac tumors)
Neuron specific enolase is a marker for what 2 tumors?
1) Small-cell cancer of lung
2) Neuroblastoma
TP53, APC, RAS mutants in stool and serum used as marker for what cancer?
Colon cancer
Chronic Inflammatory Bowel disease increases the risk for what cancer?
Colorectal carcinoma
What is one major differenc between Burkitt Lymphomas and Nasopharyngeal carcinomas associated with EBV?
- Burkitt lymphomas associated with EBV do NOT express LMP-1
- Nasopharynheal carcinomas associated with EBV DO express LMP-1
What are the 2 major forms of underlying cancers associated with Dermatomyositis?
1) Bronchogenic carcinoma
2) Breast carcinoma
What is the major form of underlying cancer associated with Red cell aplasia?
Thymic neoplasms
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy is characterized by what 3 abnormalities?
1) Periosteal new bone formation, primarily at distal ends of long bones, metatarsals, metacarpals, and prox. phalanges
2) Arthritis of the adjacent joints
3) Clubbing of the digits
Advances mucin-secreting adenocarcinomas often show lesions of the heart where?
Known as?
- Often left-sided heart valves
- Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
CA-15-3 is used as a marker for what cancer?
Breast cancer


