Chapter 7- Carbohydradrates and Glycobiology Flashcards
1
Q
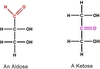
- 2.
A
- Aldose 2. Ketone
2
Q

A
D-Glyceraldehyde
3
Q

A
L-Glyceraldehyde
4
Q

A
D-Glucose
5
Q

A
D-Fructose
6
Q

A
D-ribose
7
Q

A
D-Erythrose
8
Q

A
D-Mannose
9
Q

A
2-deoxy-D-ribose
10
Q

A
D-Galactose
11
Q
What are Carbohydrates?
A
- Named because Cn(H2O)n
- Produced from CO2 and H20 via photosynthesis in plants.
- Polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones that yield such as compounds on hydrolysis.
12
Q
What are carbohydrates function ?
A
- INFOMATIONAL MOLECUES IN CELL-CELL SIGNALING !
- Energy source
- structural component of cell walls and exoskeletons.
13
Q
- What are Glycoconjugates ?
A
Complex carbohydrates polymer covalently attached to proteins or lipids act as signals that determine the intracellular destination or metabolic fate of these hybrid molecules.
14
Q
- What are the most famous Hexoses and why are they so important ?
A
- D-glucose (aldohexose) and D-fructose (ketohexose) are the most common monosaccharides in nature. The product of photosynthesis and key intermediates in the central energy yielding reaction sequence in most organisms.
15
Q
What are Enantiomers ?
Which is the only monosaccharide that does not have a chiral center?
A
- Stereoisomers, mirror images
- dihydroxyacetone
16
Q
What type of stereoisomers are most of the hexoses ?
A
D-stereoisomers
17
Q
What are the enantiomers in sugar ?
A
- D and L isomers of a sugar are enantiomers and have similar physical properties.
- e.g. L and D glucose have the same water solubility.
18
Q
What are Diastereoisomers ?
A
- are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other.
19
Q
Epimers
A
Two sugars that differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom.
20
Q
Name (2) examples of epimers
A
- D-Glucose and D-Mannose
- D-Glucose and D-Galactose
21
Q
A


