Chapter 6 - Enterprise LAN Design and Technologies Flashcards
In the Cisco hierarchical network model, which layer is responsible for fast transport?
- Network layer
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
B. The core layer is responsible for fast transport.
What is the maximum segment distance for Fast Ethernet over UTP?
- 100 feet
- 500 feet
- 100 meters
- 285 feet
C. The maximum distance for 100BASE-T is 100 meters.
In the hierarchical network model, at which layer do security filtering, address aggregation, and media translation occur?
- Network layer
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
C. The distribution layer is responsible for security filtering, address and area aggregation, and media translation.
Which type of cable is the best solution in terms of cost for connecting an access switch to the distribution layer requiring 140 meters?
- UTP
- Copper
- Multimode fiber
- Single-mode fiber
C. Multimode fiber provide a cost-effective solution for that distance. Single-mode fiber is more expensive. UTP’s maximum distance is 100 meters.
Which mechanism transitions an access port directly to the forwarding state?
- UplinkFast
- Root Guard
- PortFast
- AccessPortFast
C. PortFast bypasses the listening/learning phase for access ports and goes directly to the port-forwarding state.
You have powered devices that require a maximum power of 60 watts per PSE port. Which PoE solution do you recommend?
- PoE
- PoE+
- Cisco UPOE
- Cisco UPOE+
C. The maximum power per PSE port for Cisco UPOE is 60W; for PoE it is 15.4W, for PoE+ it is 30W, and for Cisco UPOE+ it is 90W. B.
Which solution remotely powers up a machine?
- PoE
- WoL
- OOB switch
- ON switch
Wake on LAN (WoL) is a combination of hardware and software technologies to wake up sleeping systems. The WoL feature allows an administrator to remotely power up all sleeping machines so that they can receive updates.
High availability, port security, and rate limiting are functions of which hierarchical layer?
- Network layer
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
D. The access layer functions are high availability, port security, rate limiting, ARP inspection, and trust classification.
True or false: The core layer of the hierarchical model does security filtering and media translation.
False
True or false: The access layer provides high availability and port security.
True
True or false: You can implement a full-mesh network to increase redundancy and reduce a WAN’s costs.
False. A full-mesh network increases costs.
How many links are required for a full mesh of six sites?
Use n(n − 1)/2, where n = 6. 6(6 − 1)/2 = (6 × 5)/2 = 30/2 = 15.
What are four benefits of hierarchical network design?
Cost savings, ease of understanding, easy network growth (scalability), and improved fault isolation.
True or false: Small to medium campus networks must always implement three layers of hierarchical design.
False. Small campus networks can have collapsed core and distribution layers and implement a two-layer design. Medium campus networks can have two-tier or three-tier designs.
How many full-mesh links do you need for a network with 10 routers?
Use the formula n(n − 1)/2, where n = 10. 10(10 − 1)/2 = 90/2 = 45 links.
Which layer provides routing between VLANs and security filtering?
- Access layer
- Distribution layer
- Enterprise edge
- WAN module
B. The distribution layer provides routing between VLANs and security filtering.
Which of the following describe the access layer? (Choose two.)
- Transports data at high speed
- Applies network policies
- Performs network aggregation
- Concentrates user access
- Provides PoE Avoids data manipulation
D and E. The access layer concentrates user access and provides PoE to IP phones.
Which of the following describe the distribution layer? (Choose two.)
- Transports data at high speed
- Applies network policies
- Performs network aggregation
- Concentrates user access
- Provides PoE
- Avoids data manipulation
B and C. The distribution layer concentrates the network access switches and routers and applies network policies with access lists.
Which of the following describe the core layer? (Choose two.)
- High-speed data transport
- Applies network policies
- Performs network aggregation
- Concentrates user access
- Provides PoE
- Avoids data manipulation
A and F. The core layer provides high-speed data transport without manipulating the data.
Which are two benefits of using a modular approach? (Choose two.)
- Simplifies the network design
- Reduces the amount of network traffic on the network
- Often reduces the cost and complexity of the network
- Simplifies the network by using full-mesh topologies
- A and C.
Which topology is best used for connectivity in the building distribution layer?
- Full mesh
- Partial mesh
- Hub and spoke
- Dual ring
- EtherChannel
B. Partial-mesh connectivity is best suited for the distribution layer.
Which are key features of the distribution layer? (Choose two.)
- Aggregates access layer switches
- Provides a routing boundary between the access and core layers
- Provides connectivity to end devices
- Provides fast switching
- Provides transport to the enterprise edge
- Provides VPN termination
- A and B.
Which Cisco solution allows a pair of switches to act as a single logical switch?
- HSRP
- VSS
- Spanning Tree Protocol
- GLB
B. VSS allows a Catalyst switch pair to act as a single logical switch.
What are the three layers of the hierarchical model? (Choose three.)
- WAN layer
- LAN layer
- Core layer
- Aggregation layer
- Access layer
- Distribution layer
- Edge layer
C, E, and F. Core, distribution, and access layers.
Which is the recommended design geometry for routed networks?
- Linear point-to-point networks
- Rectangular networks
- Triangular networks
- Circular networks
C. Build in triangles.
Which layer performs rate limiting, network access control, and broadcast suppression?
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
- Data link layer
- C.
Which layer performs routing between VLANs, filtering, and load balancing?
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
- Application layer
B.
Which topology allows for maximum growth?
- Triangles
- Collapsed core–distribution
- Full mesh
- Core–distribution–access
D.
Which layer performs port security and DHCP snooping?
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
- Application layer
C.
Which layer handles Active Directory and messaging?
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
- Application layer
D.
Which layers provide redundancy? (Choose two.)
- Core layer
- Distribution layer
- Access layer
- Data link layer
A and B.
Which statement is true regarding hierarchical network design?
- It makes the network harder since there are many submodules to use.
- It provides better performance and network scalability.
- It prepares the network for migration from IPv4 to IPv6.
- It secures the network with access filters in all layers.
B.
You need to connect a building access switch to the distribution switch. The cable distance is 135 meters. What type of cable do you recommend?
- UTP
- Coaxial cable
- Multimode fiber
- Single-mode fiber
C. Multimode fiber provides the necessary connectivity at the required distance. UTP can reach only 100 meters. Single-mode fiber is more expensive.
Which of the following is an access layer best practice?
- Reduce switch peering and routing.
- Use HSRP and summarize routes.
- Disable trunking and use RPVST+.
- Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers.
C. Disabling trunking on host ports and using RPVST+ are best practices at the access layer.
Which of the following is a distribution layer best practice?
- Reduce switch peering and routing.
- Use HSRP and summarize routes.
- Disable trunking and use RPVST+.
- Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers.
B. The use of HSRP and summarization of routes are best practices in the distribution layer.
Which of the following is a core layer best practice?
- Reduce switch peering and routing.
- Use HSRP and summarize routes.
- Disable trunking and use RPVST+.
- Offload SSL sessions and use load balancers.
A. Best practices for the core include the use of triangle connections to reduce switch peering and using routing to prevent network loops.
What is the recommended method to connect the distribution switches to the core?
- Redundant triangle links
- Redundant cross-connect links
- Redundant Layer 3 squares
- Redundant Layer 2 links
A. The core and the distribution layers should be connected using redundant Layer 3 triangular links.
Which are best practices for the access layer? (Choose four.)
- Disable trunking in host ports.
- Limit VLANs to one closet.
- Use PVST+ with multilayer switches.
- Enable trunking on host ports.
- Use VLAN spanning to speed convergence of Spanning Tree Protocol.
- Use VTP Server mode in hierarchical networks.
- Use VTP Transparent mode in hierarchical networks.
- Use RPVST+ as the Spanning Tree Protocol with multilayer switches.
- A, B, G, and H.
- Which are best practices for the distribution layer? (Choose three.)
- Use HSRP or GLBP.
- Provide fast transport.
- Use Layer 3 routing protocols to the core.
- Use Layer 2 routing protocols to the core.
- Summarize routes to the core layer.
- Summarize routes to the access layer.
A, C, and E.
Which are best practices for the core layer? (Choose three.)
- Use routing with no Layer 2 loops.
- Limit VLANs to one closet.
- Use HSRP. Use GLBP.
- Use Layer 3 switches with fast forwarding.
- Use Layer 3 routing to the core.
- Use two equal-cost paths to every destination network.
- Use RPVST+ with multilayer switches.
- A, E, and G.
- What is a major requirement if you use a Layer 3 access layer design?
- The distribution switches are configured as a VSS pair.
- The core switches need to support EIGRP.
- The access layer switch needs to be able to route.
- HSRP is configured on the distribution switches.
- C.
What is an advantage of using the updated Layer 2 access layer design over the traditional model?
- There is an increase in uplink bandwidth.
- The updated model adds routing between the distribution and access layers.
- The access layer switch needs to be able to route.
- Layer 3 load balancing is enabled.
A.
Which Cisco STP Toolkit mechanisms are recommended on user access ports? (Select two.)
- PortFast
- RootGuard
- UplinkFast
- Loop Guard
- BPDU Guard
A and E.
You want to enable physical device virtualization. Which feature provides that?
- VLAN
- VFR
- VSS
- VPN
C.
A network has two distribution switches, A and B, connected via a Layer 2 trunk. Distribution A switch is the HSRP active gateway and Spanning Tree Protocol root. Layer 2 links are used to connect access layer switches to both distribution switches.
Which version of spanning tree is recommended?
- PVST+
- Rapid PVST+
- MST
- VSS
B.
A network has two distribution switches, A and B, connected via a Layer 2 trunk. Distribution A switch is the Spanning Tree Protocol root, and distribution B is the active HSRP gateway. Layer 2 links are used to connect access layer switches to both distribution switches.
Which statement is true?
- Traffic will transit from the access switches through distribution switch A through the Layer 2 trunk to distribution switch B. A
- Spanning Tree Protocol loop will be created.
- The access switches will not be able to communicate.
- Loop Guard will prevent the loop from being created.
A.
Which is true in regard to using UDLD? (Choose three.)
- It is used instead of Loop Guard.
- It should be used in aggressive mode.
- It should be enabled in global configuration mode.
- It prevents blackholing and loops.
- It should be used only on UTP links.
- It cannot protect against miswiring.
B, C, and D.
What is true regarding Spanning Tree Protocol design?
- Best practice is for the network to determine the root bridge.
- All ports should be configured with PortFast to enable root bridge selection.
- The root bridge and HSRP primary router should be on the same distribution switch.
- It is best practice to disable the toolkit when setting the root bridge.
C. The Spanning Tree Protocol root bridge and HSRP active router should match.
Match each campus design model with its description.
- Routed access layer
- Traditional Layer 2 access layer
- Layer 2 access with VSS
- Hybrid access layer
- Legacy design
- Access layer using Layer 3 capabilities
- Layer 2 design improvement
- Not recommended
A = ii
B = i
C = iii
D = iv.
Which statement is correct regarding Local VLANs? (Select two.)
- It is the preferred design.
- Users are grouped into VLANs depending on their physical location.
- VLAN membership does not change if the user moves to another building within the campus.
- VLANs are dispersed throughout the campus.
A and B.
Which statements are correct regarding end-to-end VLAN design? (Choose two)
- It is the preferred design.
- Users are grouped into VLANs based on their physical location.
- VLAN membership does not change if the user moves to another building within the campus.
- VLANs are dispersed throughout the campus.
C and D.
You need to power a PD that requires 50 watts. Which solution is preferred?
- PoE
- PoE+
- UPOE
- UPOE+
C. UPOE provides up to 51W to a powered device.
An administrator requests a way to do remote maintenance on desktops. What solution would allow the administrator to power up end devices to do maintenance?
- PoE
- ON switch
- WoL
- Cisco
- UPOE
C. Wake on LAN.
Which statement regarding campus design is correct?
- Connect access switches directly to summarize via the uplinks.
- Build using triangles rather than squares.
- Configure a security ACL in the core.
- Avoid summarization at the distribution layer.
B. Build triangles.
What is the minimum cable requirement for Cisco UPOE+?
- CAT 5
- CAT 5e
- CAT 6a
- CAT 7
C. Category 6a.
What is correct regarding Spanning Tree Protocol stability mechanisms? (Choose two)
- Apply PortFast to all end-user ports.
- Apply RootGuard to all ports where a root is never expected.
- Apply RootGuard to all end-user ports.
- Apply PortFast to all ports where a root is never expected.
- Apply PortFast to all end-user ports.
- Apply RootGuard to all ports where a root is expected.
- Apply Loop Guard to all end-user ports.
- Apply RootGuard to all ports.
A and B are correct.
- Apply PortFast to all end-user ports.
- Apply RootGuard to all ports where a root is never expected.
The benefits of using hierarchical models for your network design include the following, except one. Which one does not belong?
- Cost savings
- Redundancy
- Ease of understanding
- Modular network growth
- Improved fault isolation
While important, Redundancy is not a benefit of hierarchical design.
What layer of the three layer hierarchical model provides policy-based connectivity?
Distribution: The distribution layer provides policy-based connectivity.
What layer is the backbone?
The core layer is the backbone.
What is ‘diameter’ in a network design?
When a network uses routers, the number of router hops from edge to edge is called the diameter.
It is considered good practice to design for a consistent diameter within a hierarchical network. The trip from any end station to another end station across the backbone should have the same number of hops. The distance from any end station to a server on the backbone should also be consistent.
This provides predictable performance and ease of troubleshooting.
What layer of the three layer hierarchical model applies policies?
Distribution.
Policy-based connectivity (for example, ensuring that traffic sent from a particular network is forwarded out one interface while all other traffic is forwarded out another interface)
What layer of the three layer model implements load balancing?
Distribution.
Which of these belong to the distribution layer’s responsibilities? (Choose three.)
- Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)
- Redistribution between routing domains (for example, between two different routing protocols)
- High availability
- Demarcation between static and dynamic routing protocols
1, 2 and 4
High availability is part of the access layer.
Which of the following duties fall to the acces layer? (Choose three.)
- Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring)
- Virtual access control lists (VACLs)
- Spanning tree
- Trust classification
2, 3, and 4.
Media translations (for example, between Ethernet and Token Ring) are part of the distribution layer.
Which of the following roles fall in the access layer? (Choose three)
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) and auxiliary VLANs for VoIP
- Network access control (NAC)
- Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes
- Auxiliary VLANs
1, 2, 4
Avoidance of slow packet manipulation caused by filters or other processes is a core layer function.
Redistribution between routing domains (for example, between two different routing protocols) happens at what layer?
Distribution.
Broadcast suppression happens at which layer?
Access layer.
The __________ layer is the boundary between the Layer 2 domains and the Layer 3 routed network.
Inter-VLAN communications are routed in the _________ layer.
Route summarization is configured under the routing protocol on interfaces toward the core layer.
The distribution layer is the boundary between the Layer 2 domains and the Layer 3 routed network.
Inter-VLAN communications are routed in the distribution layer.
Route summarization is configured under the routing protocol on interfaces toward the core layer.

See the attached ‘Switched Hierarchical design’.
SPT is great for redundancy. What is a drawback of STP when using multiple links to connect access and distribution switches?
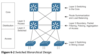
The drawback with this design is that Spanning Tree Protocol allows only one of the redundant links between the access switch and the distribution switch to be active. In the event of a failure, the second link becomes active, but at no point does load balancing occur.
See the attached ‘Routed Hierarchical design’. What is the benefit of this design?

The benefit of this design is that load balancing occurs from the access layer because the links to the distribution switches are routed.
- In this design, the Layer 3 boundary is pushed toward the access layer. Layer 3 switching occurs in the access, distribution, and core layers.
- Route filtering is configured on interfaces toward the access layer.
- Route summarization is configured on interfaces toward the core layer.
What is VSS? What problem does it solve with STP?
Virtual Switching System (VSS): This provides redundancy between the access and distribution switching layers. VSS solves the Spanning Tree Protocol looping problem by converting the distribution switching pair into a logical single switch.
It removes Spanning Tree Protocol and eliminates the need for Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP), Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), or Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP).
One of the main benefits of VSS is MEC. What is this?
Multichassis EtherChannel (MEC) creating loop-free technologies and eliminating the need for Spanning Tree Protocol

What is a VSL?
With VSS, the physical topology changes as each access switch has a single upstream distribution switch rather than two upstream distribution switches.
As shown in Figure 6-4, the two switches are connected via 10 Gigabit Ethernet links called virtual switch links (VSLs), which makes them seem as a single switch. The key benefits of VSS include the following:
- Layer 3 switching used toward the access layer to enhance nonstop communication
- Simplified management of a single configuration of the VSS distribution switch
- Better return on investment (ROI) thanks to increased bandwidth between the access layer and the distribution layer

Which of the following topology designs is easier to manage and scales better?
- full mesh
- ring
- hub and spoke
The hub-and-spoke network design (see Figure 6-5) provides better convergence times than ring topology. The hub-and-spoke design also scales better and is easier to manage than ring or mesh topologies. For example, implementing security policies in a full-mesh topology would become unmanageable because you would have to configure policies at each point location.

What is a two-layer hierarchy used with smaller networks called?
One alternative to the three-layer hierarchy is the collapsed core design, which is a two-layer hierarchy used with smaller networks. It is commonly used in sites with a single building with multiple floors.
As shown in Figure 6-6, the core and distribution layers are merged, providing all the services needed for those layers.
Design parameters to decide if you need to migrate to the three-layer hierarchy include not enough capacity and throughput at the distribution layer, network resiliency, and geographic dispersion.

When you build in __________, you take advantage of equal-cost redundant paths for best deterministic convergence.
When you build in triangles, you take advantage of equal-cost redundant paths for best deterministic convergence.
In the networks shown in Figure 6-7, when the link at location A goes down, the design with triangles does not require routing protocol convergence because each switch has two routes and two associated hardware Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency entries. In the design with squares, routing convergence is required.

What is the recovered state of the network if the link fails as shown in the diagram?

When designing a hierarchical campus, using redundant links with triangles enables equal-cost path routing. In equal-path cost design, each switch has two routes and two Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency entries.
This allows for the fastest restoration of voice, video, and data traffic flows.
As shown in Figure 6- 8, there are two Cisco Express Forwarding entries in the initial state. When there is a switch failure, the originating switch still has a remaining route and associated Cisco Express Forwarding entry; because of this, it does not trigger or wait for routing protocol convergence and is immediately able to continue forwarding all traffic.

What is ‘end-to-end’ VLAN deployment? What are the pros and cons?
The term end-to-end VLANs refers to the design that allows VLANs to be widely dispersed throughout the enterprise network.
The advantage of this design is that a user can move from one building to another and remain in the same VLAN.
The problem is that this does not scale well for thousands of users, which makes it difficult to manage. The recommended solution is to implement local VLANs where users are grouped into VLANs based on their physical locations.
What is 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet?
100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet
- The 100BASE-TX specification uses CAT 5 or 6 UTP wiring.
- Fast Ethernet uses only two pairs of the four-pair UTP wiring.
- RJ-45 connectors are used (the same as in 10BASE-T).
- Punchdown blocks in the wiring closet must be CAT 5 certified.
- 4B5B coding is used.
What is 100BASE-T4 Fast Ethernet?
100BASE-T4 Fast Ethernet
- The 100BASE-T4 specification was developed to support UTP wiring at the CAT 3 level.
- This specification takes advantage of higher-speed Ethernet without recabling to CAT 5 UTP.
- Transmission occurs over CAT 3, 4, 5, or 6 UTP wiring.
- Three pairs are used for transmission, and the fourth pair is used for collision detection.
- No separate transmit and receive pairs are present, so full-duplex operation is not possible.
- 8B6T coding is used.
What is 100BASE-FX Fast Ethernet?
100BASE-FX Fast Ethernet
The 100BASE-FX specification for fiber is as follows:
- It operates over two strands of multimode or single-mode fiber cabling. It can transmit over greater distances than copper media.
- It uses media interface connector (MIC), stab and twist (ST), or stab and click (SC) fiber connectors defined for FDDI and 10BASE-FX networks.
- 4B5B coding is used.
What is 1000BASE-LX Long-Wavelength Gigabit Ethernet?
1000BASE-LX Long-Wavelength Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 1000BASE-LX uses long-wavelength optics over a pair of fiber strands. The specifications are as follows:
- It uses long wavelengths (1300 nm [nanometers]).
- It can be used on multimode or single-mode fiber. Maximum lengths for multimode fiber are as follows:
- 62.5-micrometer fiber: 440 meters 50-micrometer fiber: 550 meters
- The max length for single-mode fiber (9 micrometers) is 5 km.
- It uses 8B10B encoding with simple NRZ.
What is 1000BASE-SX Short-Wavelength Gigabit Ethernet?
1000BASE-SX Short-Wavelength Gigabit Ethernet
IEEE 1000BASE-SX uses short-wavelength optics over a pair of multimode fiber strands. The specifications are as follows:
- It uses short wavelengths (850 nm). It can be used on multimode fiber. Maximum lengths are as follows:
- 62.5-micrometer fiber: 260 m 50-micrometer fiber: 550 m
- It uses 8B10B encoding with simple NRZ.
What is 1000BASE-CX Gigabit Ethernet over Coaxial Cable?
1000BASE-CX Gigabit Ethernet over Coaxial Cable
The IEEE 1000BASE-CX standard is for short copper runs between servers. The specifications are as follows:
- It is used on short-run copper.
- It runs over a pair of 150-ohm balanced coaxial cables (twinax). The maximum length is 25 meters.
- It is mainly for server connections.
- It uses 8B10B encoding with simple NRZ.
What is 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet over UTP?
1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet over UTP
This IEEE standard uses the four pairs in a CAT5 cable. (100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T Ethernet use only two pairs.) The specifications are as follows:
- It uses CAT 5 four-pair UTP.
- The maximum length is 100 meters.
- The encoding defined is a five-level coding scheme. One byte is sent over the four pairs at 1250 MHz.
Short-wavelength multimode fiber is ______ nm. Long-wavelength is ______ nm, and extra-long-wavelength is ______ nm.
Short-wavelength multimode fiber is 850 nm. Long-wavelength is 1310 nm, and extra-long-wavelength is 1550 nm.
The Cisco _____________ implementations provide a method to increase the bandwidth between two systems by bundling Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet links.
Depending on your hardware, you can form an __________ with up to ______ compatibly configured ports on the switch.
The Cisco EtherChannel implementations provide a method to increase the bandwidth between two systems by bundling Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, or 10 Gigabit Ethernet links.
Depending on your hardware, you can form an EtherChannel with up to eight compatibly configured ports on the switch.
T/F: The participating ports in an EtherChannel trunk must have the same speed and duplex mode and belong to the same VLAN.
True.
EtherChannel can be established by using three mechanisms. Define these:
- LACP:
- PAgP:
- Static persistence configuration:
EtherChannel can be established by using three mechanisms:
LACP: Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is defined in IEEE 802.3ad. It protects against misconfiguration but adds overhead and delay when setting up a bundle.
PAgP: Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP) is a Cisco-proprietary negotiation protocol. PAgP aids in the automatic creation of EtherChannel links.
Static persistence configuration: This does not add overhead as LACP does, but it can cause problems if not configured properly.
How much power is delivered py PoE and PoE+?
PoE provides 15.4W at the power sourcing equipment (PSE) side (LAN switch); due to power dissipation, only 12.95W is assured to the powered device (PD).
PoE+ provides up to 30W on the PSE side, with 25.5.W assured to the PD.
What pin pairs is power provided over with PoE and PoE+?
PoE and PoE+ provide power using two pairs: pins 1 and 2 and pins 3 and 6.
What are UPOE and UPOE+? How much power can they deliver?
Cisco has developed Universal Power over Ethernet (UPOE) to provide power to higher-level devices, such as telepresence systems, digital signage, and IP turrets.
Cisco UPOE uses four twisted pairs (instead of two pairs for PoE) to provide additional power.
UPOE provides 30W + 30W = 60W of PSE power over Category 5e UTP, assuring 51W to the PD. Cisco
UPOE+ provides 45W + 45 W = 90W of PSE power over Category 6a UTP cabling, assuring 71.3W of power to the PD.
What is a magic packet?
Wake on LAN (WoL)
When a PC shuts down, the NIC still receives power and is able to listen to thenetwork. WoL allows an administrator to remotely power up sleeping machines in order to perform maintenance updates.
WoL sends specially coded network packets, called magic packets, to systems equipped and enabled to respond to these packets. If you send WoL packets from remote networks, the routers must be configured to allow directed broadcasts.
Spanning Tree Protocol is defined by IEEE ______.
RSTP is defined by IEEE ______.
MST is defined by IEEE _______.
Spanning Tree Protocol is defined by IEEE 802.1D
RSTP is defined by IEEE 802.1W.
MST is defined by IEEE 802.1S.
Spanning Tree Protocol is implemented by switches exchanging ______ messages with other switches to detect loops, which are removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces.
Spanning Tree Protocol is implemented by switches exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, which are removed by shutting down selected bridge interfaces.
This algorithm guarantees that there is one and only one active path between two network devices.
A __________ port would cause a switching loop if it were active.
A blocking port would cause a switching loop if it were active.
No user data is sent or received over a blocking port, but it may go into forwarding mode if the other links in use fail and the spanning tree algorithm determines that the port may transition to the forwarding state.
BPDU data is still received in the blocking state. It prevents the use of looped paths.
What STP state does this describe?
The switch processes BPDUs and awaits possible new information that would cause it to return to the blocking state. It does not populate the MAC address table and does not forward frames.
Listening: The switch processes BPDUs and awaits possible new information that would cause it to return to the blocking state. It does not populate the MAC address table and does not forward frames.
What STP state does this describe?
While the port does not yet forward frames, it does learn source addresses from frames received and adds them to the filtering database (switching database). It populates the MAC address table but does not forward frames.
Learning: While the port does not yet forward frames, it does learn source addresses from frames received and adds them to the filtering database (switching database). It populates the MAC address table but does not forward frames.
A __________ port receives and sends data in normal operation. Spanning Tree Protocol still monitors incoming BPDUs that would indicate it should return to the blocking state to prevent a loop.
A forwarding port receives and sends data in normal operation. Spanning Tree Protocol still monitors incoming BPDUs that would indicate it should return to the blocking state to prevent a loop.
T/F: A network administrator can manually disable a port, although this is not strictly part of Spanning Tree Protocol.
True.
What are the STP metrics, the updated 32 bit values, for the following:
- 1M
- 10M
- 100M
- 1G
- 10G
- 100G
- 1T
- 10T
- 20,000,000 - 1M
- 2,000,000 - 10M
- 200,000 - 100M
- 20,000 - 1G
- 2000 - 10G
- 200 - 100G
- 20 - 1T
- 2 - 10T
PVST+ is a Cisco proprietary protocol.
True.
Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+) provides the same functionality as PVST using 802.1Q trunking technology rather than ISL. PVST+ is an enhancement to the 802.1Q specification and is not supported on non-Cisco devices.
PVST+ is based on the IEEE 802.1D and adds Cisco-proprietary features such as BackboneFast, UplinkFast, and PortFast.
T/F: With RPVST+ all the switches generate BPDUs and send out on all the ports every 2 seconds, whereas with 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol, only the root bridge sends the configuration BPDUs.
True.
All the switches generate BPDUs and send out on all the ports every 2 seconds, whereas with 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol, only the root bridge sends the configuration BPDUs.
T/F: RPVST+ is backward compatible with STP.
True.
Rapid PVST+ uses RSTP to provide faster convergence. When any RSTP port receives a legacy 802.1D BPDU, it falls back to legacy Spanning Tree Protocol, and the inherent fast convergence benefits of 802.1W are lost when it interacts with legacy bridges.
Cisco recommends that Rapid PVST+ be configured for best convergence.
What must you remember when configuring STP with a FHRP?
Remember to align the STP root with the Active/Primary FHRP router!
You should manually assign the root bridge of a Spanning Tree Protocol network to match the Layer 3 First-Hop Resiliency Protocol (FHRP) active/primary/master router..
The root bridge is assigned by manually lowering its root bridge priority from the default.
What is PortFast? Where is it used?
PortFast causes a Layer 2 LAN access port to enter the forwarding state immediately, bypassing the listening and learning states. When configured for PortFast, a port is still running Spanning Tree Protocol and can immediately transition to the blocking state, if necessary.
PortFast should be used only when connecting a single end station to the port. It can be enabled on trunk ports.
What is UplinkFast? Where is it deployed?
UplinkFast provides fast convergence after a direct link failure.
UplinkFast cannot be configured on individual VLANs; it is configured on all VLANs of a LAN switch.
It is most useful when configured on the uplink ports of closet switches connecting to distribution switches. This mechanism is enabled when RSTP is enabled on a switch.
What is BackboneFast? Where is it configured?
BackboneFast provides fast failover when an indirect link failure occurs. It is initiated when a root port or blocked port on a network device receives inferior BPDUs from its designated bridge.
It is configured on distribution and core switches.
As with UplinkFast, this mechanism does not need to be enabled when RSTP is configured.
What is LoopGuard? Where is it deployed?
Loop Guard helps prevent bridging loops that could occur because of a unidirectional link failure on a point-to-point link.
It detects root ports and blocked ports and ensures that they keep receiving BPDUs from the designated port on the segment.
When Loop Guard is enabled, if a root or blocked port stops receiving BPDUs from its designated port, it transitions to the loop-inconsistent blocking state.
T/F: LoopGuard must be configured on point- to-point links only.
True.
Loop Guard can be enabled on a per-port basis. It must be configured on point- to-point links only. When Loop Guard is enabled, it is automatically applied to all active instances or VLANs to which that port belongs. When enabled on an EtherChannel (link bundle) and the first link becomes unidirectional, it blocks the entire channel until the affected port is removed from the channel. Loop Guard cannot be enabled on PortFast ports, dynamic VLAN ports, or Root Guard–-enabled switches. It does not affect UplinkFast or BackboneFast operation.
What is Root Guard? Where is it deployed?
Root Guard prevents a port from becoming a root port or blocked port.
When a Root Guard port receives a superior BPDU, the port immediately goes to the root-inconsistent (blocked) state.
Root Guard is configured on access switches so that they do not become a root of the spanning tree.
What is BPDU Guard? Where is it used?
BPDU Guard shuts down a port that receives a BPDU, regardless of PortFast configuration.
This is used on access ports.

What is BPDU Filter? Where is it used?
BPDU Filter prevents a port from sending or receiving BPDUs.
It can be configured on a per-port basis. When configured globally, it applies to alloperational PortFast ports.
This should only be used on ports connected to hosts.
Match the following recommended practices for Spanning Tree Protocol stability mechanisms:
- PortFast:
- Root Guard:
- Loop Guard:
- Apply to all ports where a root is never expected.
- Apply to all end-user ports. To secure PortFast-enabled ports, always combine PortFast with BPDU Guard.
- Apply to all ports that are or can become non-designated ports.
PortFast: Apply PortFast to all end-user ports. To secure PortFast-enabled ports, always combine PortFast with BPDU Guard.
Root Guard: Apply Root Guard to all ports where a root is never expected.
Loop Guard: Apply Loop Guard to all ports that are or can become non-designated ports.
What is UDLD? How is it useful.
UDLD detects unidirectional links on optical fiber links before a forwarding loop is created. Loop Guard and UDLD functionality overlap, partly in the sense that both protect against Spanning Tree Protocol failures caused by unidirectional links.
A Spanning Tree Protocol loop can occur on fiber networks if an SFP module fails. Unidirectional Link Detection (UDLD) can be configured on a per-port basis on all redundant links. Because Loop Guard does not work on shared links, UDLD should also be configured to prevent loops.


