Chapter 6 Flashcards
Premature Atrial Complexes (PAC)
Characteristics:
Atria generate premature impulse
Clinical significance:
Occasional PAC’s are benign, cause palpitations
Management:
Recurrent PAC’s treated with digitalis

Atrial Tachycardia
- Common forms are paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) and multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) aka wandering pacemaker.
- Diminishes atrial kick
PAT
Characteristics:
Sudden onset of three or more beats of narrow complex tachycardia
Heart rate 150-250 bpm
Clinical significance:
isolated PAC’s are normal
Management:
Avoid caffine or cigarette smoking
Treatment if symptomatic: digoxin

MAT aka wandering pacemaker
Characteristics:
More than one shaped P wave
Usually more than 3 types of identifiable types of P waves
Heart rate 100-150 bpm
Clinical significance:
mostly seen in patients with COPD.
Management:
improving underlying cause
Verapamil, Flecainide, Propafenone
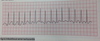
Atrial flutter
Characteristics:
Atrial rate of 250-400 bpm
most characteristic pattern is “saw tooth” shaped P waves called flutter waves
Clinical significance:
Commonly seen in patients with heart disease
Risk of thromboembolic events are high
Management:
Diltiazem, Verapamil, Digoxin

Atrial fibrillation
Characteristics:
rapid, disorganized and irregular atrial activation
atrial rate above 400 bpm
Clinical significance:
fast ventricular response
loss of atrial appendage contractility leading to risk of clot formation
some patients present with severe dizziness or syncope
Treatment:
Direct current (DC) cardioversion; rate control, prevention of thromboembolic event, rhythm control



