Chapter 34: Thyroid Disease + Surgery Flashcards
How much does the thyroid weigh?
30 g
Where does the isthmus usually lie?
Midline
Main anatomical points of thyroid:
Right lobe, left lobe, isthmus
What is most common issue with thyroid gland?
Enlargement
Parathyroid glands: How many? Size?
4 4 mm x 6 mm
Most common source of problems in parathyroid gland?
Endocrine disorder
Which nerves are contiguous with the thyroid gland?
RLNs
What increases risk for injury or loss of nerve?
Thyroid malignancy
What adjunct is necessary when operating on thyroid?
Nerve testing and NMB monitoring
Range of testing device for RLNs in thyroid surgery?
0.5-2 mA
The thyroid gland is contiguous with what airway structure?
Trachea
What is a goiter?
Enlargement of thyroid gland
Where can goiters grow? What are they called in their respective positions?
Can grow in chest (intrathoracic) or in neck (extrathoracic)
What is your biggest concern regarding goiters?
They tend to shift the trachea and therefore shift the glottis.
What type of disease may deviate and/or compress the trachea?
Thyroid disease
In what thyroid case would the patient require intubation post-operation?
Only the patient with tracheal malasia would remain intubated for 2-5 days as the surrounding tissue healed.
Immediate risk to thyroid disease/surgery?
Interruption/injury to one/both RLNs
This tool is used for:

Mediastinoscopy
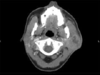
Condition demonstrated in this picture

Intrathoracic goiter

Mediastinoscopy
Pathway of the RLNs:
Transverses chest (right vs. left difference)
Ascends in neck lateral to airway
Which cranial nerve is contiguous with thryoid gland?
Vagus (CN X)
Origin of RLNs?
Vagus nerve (CN X)
What anatomical structures protect RLNs?
Protected in larynx by thyroid cartilage
RLNs serve what?
posterior cricoarytenoid muscle and other laryngeal muscles EXCEPT cricothyroid
What muscle is the only primary vocal cord abductor?
posterior cricoarytenoid muscle
RLN runs along track of which artery?
Laryngeal branches of superior and inferior thyroid arteries
If the RLN is interrupted, position of the VCs?
Paramedian
If RLN is injured (but not interrupted), VC at what position?
Abducted (lateral)
What are some destructive effects of the thyroid gland on mechanical integrity of the upper airway? Where might these effects occur?
Cartilaginous destruction
Extrinsic compression
Can occur in neck and/or mediastinum
What are three questions you should ask yourself if patient has previously had thyroid surgery?
Where is the lesion(?)
Where will the ETT cuff be(?)
What will happen after extubation(?)
What routine actions may cause INJURY to RLNs?
Retraction, clamping, or electrocautery
What routine surgical actions/tools may cause INTERRUPTION to RLNs?
scalpel or electrocautery
INJURY to RLN: overall effect to vocal cords?
VC adduction
In ACUTE UNILATERAL injury to RLN:
Affected VC will move to the median position, opposed by the normal VC
In LONGTERM UNILATERAL injury to RLN:
Affected VC may force the normal VC away from the midline
BILATERAL ACUTE injury to RLNs:
Upper airway obstruction
Result of LONGTERM BILATERAL injury to RLNs:
Dyspnea, aspiration, but then resolution of edema, no problem
Position of VCs during inspiration after RLN paralysis:
Normal
Position of VCs during phonation during after RLN paralysis (compensated):
Closed (midline)
Position of VCs during inspiration in the case of bilateral RLN paralysis
Paramedian
What are some possible diagnoses for stridor after parathyroid or thyroid surgery?
Edema in the supraglottic or glottic regions
RLN damage
Hypocalcemia
How much does a parotid gland weigh?
20 g
Why must you use NMB monitoring when working with the parotid glands?
To ensure no damage was done to the facial nerve
Name the two lobes of the parotid gland:
Superficial
Deep
Which duct mediates secretions from the parotid gland?
Stenson’s duct
What are the branches of the facial nerve?
Temporal
Zygomatic
Buccal
Mandibular
Cervical
Branches of the buccal nerve?
Upper + lower
What is the most common disease of the parotid gland?
The other source?
Benign adenoma (75%)
Other: malignancies (25%)
What disorder do these images demonstrate?
Parotitis
What is trismus?
Lock jaw (TMJ issue)
Facial nerve branches require how many stimulators for each branch the surgeon wishes to monitor?
One
Describe the optimal positioning of a NMB nerve monitor.
Close to the nerve being monitored
Maximal current density
Minimal current dispersion
Best way to monitor sensory threshold while using an NMB nerve stimulator on the facial nerve?
Watch facial expressions prior to induction
Explain the premise of the supramaximal stimulus using an NMB nerve stimulator:
Activate all muscle fibers served by the stimulated nerve without directly stimulating the muscle fibers
Describe the empiric setting of the NMB nerve stimulator.
We want to set it to be 25 mA above motor threshold, which is 15 mA: so we set it to 40 mA.
How should you give rocuronium? How long after dosing should you wait to test? What should your TOF ratio be?
Give in 5 minute increments.
Wait 4-6 minutes in order to test.
TOF ratio: >0.4
End point for ending case following reversal of NMB: TOF ratio should be what?
>0.9


