Chapter 3: Sodium and Water Flashcards
What is the normal osmolality (range) for a dog? What is the normal osmolality (range) for a cat?
Dogs: 290-310 mOsm/kg Cats: 290-330 mOsm/kg
What is the definition of specific gravity?
The ratio of weight of a volume of liquid to the weight of equal volume of distilled water.
Which of the following does specific gravity not depend on? A. Number of particles B. Size of particles C. Weight of particles D. How well your refractometer is calibrated.
C. Size of particles (depends on # of particles and molecular weight)
What is the definition of solute, or osmotic diuresis? What is the specific gravity of urine in this state?
Increased urine flow due to excess non-reabsorbable solutes. USG = approaches plasma osmolality
What is the definition of water diuresis? What is the specific gravity of urine in this state?
Increased urine flow due to decreased reabsorption of (solute-free) water. USG = less than plasma osmolality
Fill in the blanks:

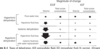
Where are the high pressure baroreceptors?
Aortic arch
Carotid Sinus
Where is renin released in the kidney?
This is released in response to what?
Renin is released in the juxtaglomerular apparatus in response to changes in perfusion (blood flow)
What is glomerulotubular balance?
Mechanism incompletely understood.
Describes how kidneys take into account small changes in GFR and maintain static FF.
Spontaneous increase in GFR increases filtered load of all sultues and their increased concentration in the proximal tubules enhances Na+ reabsorption.
Change in peritubular hydrostatic and oncotic pressure proabbly play a role
Autoregulation plays a role.
However…this does not occur as a secondary increase in GFR tue to increased ECF [Na+]; only works as primary mechanism
Approximately 67% of filtered sodium is reabsorbed isosmotically with water where?
Proximal tubules
Where are the volume receptors (low pressure mechanoreceptors)
Cardiac atria
Pulmonary vessels
In the early proximal tubule, sodium crosses luminal membrane by cotransport with __________? In exchange for what?
Sodium crosses early proximal tubule with glucose, amino acids, phosphate.
In exchange for H+ ions (via Na-H antiporter). HCO3- is reabsorbed during this process.
25% of filtered load of sodium is reabsorbed where?
Loop of Henle
Primarily in thick ascending limb
5% of the filtered load of sodium is reabsorbed where?
Distal convoluted tubule and connecting segment. Sodium enters passively.
3% of filtered load of sodium is reabsorbed where?
Collecting ducts
What are thiazide diuretics MOA?
Inhibit Na+-Cl- cotransporter in early distal tubule
In the late proximal tubule, Na+ is reabsorbed primarily with what?
Chloride
Here the luminal Na+-H+ antiporter works in parallel with a luminal Cl--anion- antiporter
Net effect = NaCl reabsorption
Sodium is reabsorbed in the thin descending and ascending limbs of LOH by what mechanism?
passively reabsorbed
Sodium is reabsorbed in the thick ascending LOH by what mechanism?
Na+-H+ antiporter and Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter
Aldosterone alters sodium reabsorption how?
In response to dietary sodium intake, aldosterone increases the number of open luminal Na+ channels in the cortical collecting ducts.
This increases sodium reabsorption.
Aldosterone is produced and released in response to what?
Angiotensin II, hyperkalemia, and ACTH
Aldosterone is inhibited by what?
Dopamine
Atrial natriuretic peptide
Catecholamines stimulate proximal tubule reabsorption of Na+ through what effect?
directly stimulate alpha 1 adrenergic effect
stimulates renin release from granular cells of JGA via beta 1 adrenergic effect
This mechanism is important, as there is typically an increase in systemic BP and this offsets pressure natriuresis
Angiotensin II directly stimulates what in the proximal tubules, facilitating Na+ reabsorption and stimulating secretion of aldosterone from adrenals.
Renin release leads to production of what?
Angiotensin II
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is released in response to what?
atrial distension caused by volume expansion
Atrial natriuretic peptide facilitates excretion of Na+ how?
Causes dilation of afferent arterioles.
Constriction efferent arterioles
= increase in GFR
Relaxes mesangial cells ⇒ increase in surface area
Inhibits sodium reabsorption in cortical/inner medullary collecting ducts
Inhibits renin secretion
Inhibits aldosterone secretion by zona glomerulosa
True or false:
Pressure natriuresis is entirely intrarenal (it could occur in the isolated denervated kidney)
True
Osmoreceptors live where?
What is released in response to plasma hyperosmolality?
Osmoreceptors shrink =
Osmoreceptors swell =
Hypothalamus
Vasopressin
vasopressin is released
vasopressin release is inhibited
Vasopressin is synthesized where (specifically?)
Released specifically where?
Neurons of supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei in the hypothalamus.
Vasopressin travels down axons of these neurons and released at the level of the neurohypophysis.
Vasopressin increases reabsorption of water how?
Increases reabsorption of water in collecting ducts
Increases permeability of medullary collecting ducts to urea
Why may vasopressin not be as effective in chronic PU/PD cases?
In these cases, there can be medullary washout ⇒
depletion of urea from medullary interstitium ⇒
impaired urea reabsorption in medullary collecting ducts
Changes in plasma osmolality of ____% can lead to maximal vasopressin release
1-2%
In addition to plasma osmolality, vasopressin is also released in response to:
Volume depletion
Left atrium, aortic sinus, carotid sinuses
A decrease of _____% of volume (actual or perceived) lowers the threshold for vasopressin release.
5-10%
Other than hyperosmolality and decrease in volume status, what are three other stimuli for vasopressin release?
Nausea
Pain
Emotional anxiety
What three disease states cause hyponatremia secondary to perceived hypovolemia
(yet there is hypervolemia)
Nephrotic syndrome
Heart failure
Liver failure
What three conditions must be met for the kidneys to excrete a water load normally?
- Adequate delivery of tubular fluid to distal diluting sites (ascending LOH), where Na+ is removed without water.
- Ascending LOH must function normally
- In the absence of vasopressin, the collecting ducts must remain impermeable to water
How does the brain defend itself from a drop in tonicity?
Immediately forces Na+ containing water into CSF (minutes)
Movement of K+ out of cells (24 hours)
Reduction in cellular content of organic solutes/osmolytes (>24→48 hours)
List some organic osmolytes (idiogenic osmoles)
TIGGS =
Taurine
Inosine
Glutamate
Glutamine
Sorbitol
Others: myoinositol, phosphocreatine
Which is more common in veterinary medicine?
Hypernatremia or hyponatremia
Hyponatremia
Increased thirst normally protects against hypernatremia (unless water not available or thirst mechanism not intact)
What are three mechanisms to hypernatremia?
Pure water deficit
Hypotonic fluid loss
Impermeant solute gain
What are some mechanisms of pure water deficit?
Primary hypodipsia
Diabetes insipidus (central & nephrogenic)
High environmental temp
Fever
Inadequate access to water
What are some mechanisms to hypotonic fluid loss?
Extrarenal & renal (many in both)
What are some causes of impermeant solute gain?
Salt poisoning
Hypertonic fluid administration
Hyperaldosteronism
Hyperadrenocorticism
Which typically takes precedence - response to changes in osmolality or changes in volume?
Usually response to osmolality.
This response is not typically seen with diabetes insipidus when administered HTS
How can one differentiate between renal or non-renal sodium losses?
Fractional excretion of sodium
FeNa <1% (non-renal losses)
FeNa >1% (renal losses)
What is the definition of CDI?
What are some causes of CDI?
CDI is a partial or complete lack of vasopressin production and release from the neurohypophysis
Causes: trauma, neoplasia, idiopathic, visceral larval migrans, congenital (rare)
What is the USG typically with CDI?
Hyposthenuric
With CDI, plasma osmolality is typically ______.
With psychogenic PU/PD, plasma osmolality is typically ______.
CDI–>higher
psychogenic PU/PD–>lower
What is the MOA of chlorpropramide and how may it be useful in management of patients with partial CDI?
Sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agent that can potentiate the renal tubular effects of small amounts of vasopressin
How do thiazide diuretics potentially help treat animals with CDI and NDI?
Results in mild dehydration, enhanced proximal tubular reabsorption of sodium, decreased delivery of tubular fluid to distal nephron and reduced UOP.
List some causes of acquired nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Drugs (glucocorticoids, lithium, E. coli endotoxin, diuretics)
Electrolyte disturbances (hypokalemia, hypercalcemia)
Altered medullary hypertonicity (hypoadrenocorticism)
Hepatic insufficiency, hyperthyroidism, hyperadrenocortism
Post-obstructive diuresis
Acromegaly
Structural- medullary interstitial amyloidosis, polycystic kidneys, pyelonephritis, chronic interstitial nephritis
In which conditions can pseudohyponatremia occur?
Hyperlipidemia and hyperproteinemia.
What should be your suspicion if you have an abnormal osmolal gap with normal measured osmolality?
Pseudohyponatremia. (Measured osmolality will be normal, but calculated osmolality will be low)
What is the change in sodium for every change in glucose concentration?
There is a 2.4 mEq/L decrease in sodium for each 100 mg/dL increase in glucose.
What 3 physiologic events need to happen in order to have a hypovolemic hyponatremic patient?
- Decreased GFR: volume depletion decreases GFR, enhances isosmotic reabsorption of sodium and water in the proximal tubules, and decreases delivery of tubular fluid to distal diluting sites. These events impair excretion of water.
- Vasopressin release: volume depletion is a strong nonosmotic stimulus for vasopressin release, and the increased plasma vasopressin concentration further impairs water excretion.
- Thirst
Why patients with atypical hypoadrenocorticism may have hyponatremia without hyperkalemia?
Because glucocorticoids are necessary for complete suppression of vasopressin release, and in their absence impaired water excretion and hyponatremia can occur.
In what 3 clinical conditions can you have hypervolemic hyponatremia?
Congestive heart failure, severe liver disease, and nephrotic syndrome.
What type of water shift between ECF/ICF does hypotonic fluid loss cause?
hypotonic fluid loss –> increases osmolality of ECF –> osmotic stimulus driving water from the ICF to ECF compartment
Which patient will show more severe cardiovascular compromise: the patient with free water loss of the patient with hypotonic fluid loss? Explain your answer
- Patient with hypotonic fluid loss
- free water loss from ECF causes a more significant osmotic drift because of higher ECF osmolality –> more water moves from ICF to ECF and replenishes intravascular losses
What type of fluid loss does postobstructive diuresis cause?
hypotonic fluid loss
What type of fluid loss do vomiting, diarrhea, SI obstruction, peritonitis, glucosuria or postobstructive diuresis cause?
hypotonic fluid loss
Does the gain of an impermeable solute cause Hypo- or Hypernatremia?
- initially hyponatremia: gain of solute draws water from ICF to ECF –> dilutional effect on [Na]
- then: hypernatremia: the solute takes over Na’s place in tubular excretion and more Na is retained in ECF
What has to be absent/dysfunctional for an animal with increased NaCl intake to actually develop hypernatremia?
hypernatremia unlikely from increased NaCl intake if thirst mechanism intact and access to water
what is the pathophysiologic mechanism of neurologic damage from hypernatremia
increased ECF hypertonicity –> draws fluid from ICF to ECF –> shrinkage of brain cells from loss of water
clinical signs of hypernatremia
- anorexia
- vomiting
- muscular weakness
- behavioral changes
- ataxia
- seizures
- death
equation for Water Deficit
Water deficit = total body water (0.6xbw) x [(Napresent/Nadesired)-1]


