Chapter 3 Flashcards
(33 cards)
Expression?
Combination of numbers, operators and variables that, when understood by the computer, result in an answer of some form.
Number Comparison Operators in Ruby?
x > y Greater than
x < y Less than
x == y Equal to
x >= y Greater than or equal to
x <= y Less than or equal to
x <=> y Comparison; returns 0 if x and y are equal, 1 if x is higher, and −1 if y is higher
x != y Not equal to
Basic loop
.times 5.times
Iterator
Progresses through a list of items one by one. ..or different multiples:
.each
- upto(5)
- downto(5)
- step(50, 5)
- upto(5) { |number| puts number }
String Literal
When a string is embedded directly into code, using quotation marks.
Interpolation
Embedding expressions and even logic into strings
x = 10 y = 20
puts “#{x} + #{y} = #{x + y}”
String Methods


Regular Expression
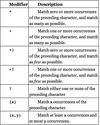
is a string that describes a pattern for matching elements in other strings.
Operator
Something that’s used in an expression to manipulate objects such as+(plus), - (minus), * (multiply), and / (divide). You can also use operators to do comparisons, such as with <, >, and &&.
Arrays
A collection of objects or values with a defined, regular order.
x = [1, 2, 3, 4]
Array Index
position within the array.
Array Literal
Square brackets are used to denote an array literal.
Array Element Reference
To access a particular element, an array (or a variable containing an array) is followed by the index contained within square brackets.
puts x[2]
Array <<
is the operator for pushing an item onto the end of an array. It’s equivalent to the push method.
Array Push
equivalent to <<
x.push(“word”)
Array Pop
is the process of retrieving and removing items from the end of the array.
x = []
x << “Word”
x << “Play”
x << “Fun”
puts x.pop
puts x.pop
puts x.length
Fun
Play
1
Hash
A collection of objects or values associated with keys. A key can be used to find its respective value inside a hash, but items inside a hash have no specific order. It’s a lookup table, much like the index of a book or a dictionary.
dictionary = { ‘cat’ => ‘feline animal’, ‘dog’ => ‘canine animal’ }
Regular Expresion
A way to describe patterns in text that can be matched and compared against.
Code block
A section of code, often used as an argument to an iterator method, that has no discrete name and that is not a method itself, but that can be called and handled by a method that receives it as an argument
Range
The representation for an entire range of values between a start point and an endpoint.
(‘A’..’Z’).to_a.each { |letter| print letter }
Symbol
A unique reference defined by a string prefixed with a colon (for example, :blue or :name). Symbols don’t contain values as variables do, but can be used to maintain a consistent reference within code.
person1 = { :name => “Fred”, :age => 20, :gender => :male }
You might want to consider symbols to be literal constants that have no value, but whose name is the most important factor.
Substitutions
puts “foobar”.sub(‘bar’, ‘foo’)
gsub does multiple substitutions at once, as this example demonstrates: puts “this is a test”.gsub(‘i’, ‘’)
x = “This is a test” puts x.sub(/^../, ‘Hello’)
.scan
example. What if you want to iterate through a string and have access to each section of it separately? scan is the iterator method you require:
“xyz”.scan(/./) { |letter| puts letter } x y z
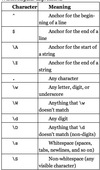
Basic Special Characters and Symbols Within Regular Expressions