Chapter 26 Pt 2 Flashcards
(51 cards)
In what process are myelin ovoids formed?
Axonal neuropathies: Wallerian degeneration => Schwann cells will catabolize myelin => unravel and disintegrate into spherical structures.
What do we see on histology in demyelinating neuropathies?
Onion bulbs: excess proliferation of Swchwann cells => concentric layers of cytoplasm of Schwann cells and redundant BM wrapped around thinly myelinated axons, like an onion
Type 1 Muscle Fibers
- Color
- Action
- Strength
- Physiology
- Red
- Sustained force
- Weight-bearing
- Slow-twich
Type 2 Muscle Fibers
- Color
- Action
- Strength
- Physiology
- White
- Sudden movements
- Purposeful motion
- Fast-twitch
What causes Type 2 Fiber Atrophy (group atropgy)?
- Inactivity or disuse (limb fracture, degeneration of pyramidal tract)
- Neurodegenerative disease
- Corticosteroids => steroid myopathy
What type of reactions do muscle fibers undergo?
- Segmental necrosis
- Vacuolization
- Regeneration
- Hypertrophy
When a muscle fiber undergoes segmental necrosis, briefly describe the process?
- Necrosis of segment
- Myophagocytosis
- Replaced with collagen and fat
Characteristics of muscle fibers that are regenerating
- Centrally located nuclei
- Cytoplasm is red with trichrome stain because alot of RNA
Characteristics of muscle fibers that are undergoing hypertrophy
Muscle fiber splitting: cell membrane splits it down middle with adjacent nuclei
What can cause a neurogenic bladder? (6)
- MS
- Parkinsons
- DB
- Infection of brain/SC
- Spina bifida
Course of Bells Palsy
- Occurs 48-72 hours after a URI/DM and resolves spontaneously in pts who are 15 - 60YO
Inflammatory neuropathies: how do we differentiate them?
- Guillian Barre Neuropathy
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy
Differentiate by: time course and whether htey respond to steroids.
MC AQUIRED Inflammatory Peripheral Neuropathy
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Peripheral Polyradiculoneuropathy
2/3’s of Guillain-Barre Syndrome cases are preceded by what; which etiologies have been implicated?
Acute, influenza-like illness
- Campylobacter
- CMV,
- EBV,
- Mycoplasma penumoniae,
- Prior vaccination
How is CIDP and AIPD different from one another?
CIDP
- Chronic: persists more than 2 months and has remissions and relapses
- Responds to steroids
Pathophysiology of CIDP?
IgM and IgG Ab on myeling sheath
Infectious Polyneuropathies (5)
- Leprosy (Hansen Disease)
- Diptheria
- Varicella-Zoster Virus
- Lyme Diseae
- HIV
MC Viral Infection of the PNS
- Varicella Zoster
What is Leprosy, Hanson Disese?
Mycobacterium Leprea invades Schwann cells and other cells => symmetric polyneuropathy in COOL extrememties
In lepromatous leprosy (Hansen Disease) Schwann cells are invaded by Mycobacterium leprae and what pattern of peripheral nerve damage will be seen?
- Segmental demyelination and remyelination
- Loss of myelinated AND unmyelinated fibers
- Endoneurial fibrosis
- Multi-layered thickening of perineural sheaths.
What are the clinical symptoms of Leprosy (Hansen Disease)?
- Symmetric polyneuropathy of pain fibers COOL extremeties => loss of sensation in hands and toes, but nose is often affected first.
- Large, traumatic ulcers => pt does not feel it.
Leprosy Findings
- AFB (+): multuple uniform-staining acid-fast slender baccili
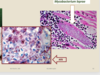
More localized nerve involvement + granulomatous nodules in the dermis is characteristic of what form of leprosy?
Tuberculoid leprosy = TH1 (cell-mediated) response
Peripheral nerve dysfunction as a result of Diptheria is due to what; what are the early sx’s and later findings?
Result of diptheria exotoxin
- Early loss of proprioception and vibratory sensation
- Bulbar and respiratory muscle dysfunction -> dealth or long-term disability due to suffocation.


