Chapter 2 Microscopy Flashcards
(19 cards)
Bright Field/Light Microscopy
Dark object against a light-filled field or background
Light travels directly through the object at low contrast
Pigmented cells can create enough contrast to be seen, however others need Gram stain to reveal something about the envelope
Shows cell shape and allows for pigmentation (if present) to be viewed via wet mount
Cells are usually dead, however are live if pigmented or large
Can view cells 1 micrometer to 1 mm
Compound microscope that needs objective and condensor lense
4x, 10x, 40x objectives are dry. 100x objective is oil-immersion
Total magnification: magnification of ocular lense x magnification of objective lense

Dark Field Microscopy
Show motility/live cell movemenet
Can view small features of a cell eg. flagella or appendages
Cells are live
Light comes from around the objects themselves
Hollow cone of light 8 mm - 20 mm in diameter

Phase Contrast Microscopy

Can view large/prominent internal structures such as the eukaryotic nucleus or bacterial endospore
Shows motility
Cells usually live
Light that bends around the object creates a halo effect around the cells - easier to observe
higher contrast between light and dark
Frits Zernike (1888 - 1966) thought to block the direct source of light to your eyes
Light passes through and around sample; light that passes through sample is refracted

Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Microscopy
Light emits waves in multiple directions
Polarized light passes through specimen from two different angles (90 degree offset)
Gives shadowing and 3D appearance
Parallel slits allow only waves with the same orientation as the slits to pass through (parallel to the slits)
Cell shape is clearly discerned
Can see surface textures; can visualize motility
Cells are live
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Electrons scan the surface of the sample
Can see surface texture (S layer or fuzzy pili)
Can see appendages such as flagella, pili, stalks, or other surface structures
Cells are dead
Sample is coated with heavy metal
Not sliced so it retains 3D structure and gives 3D image
Only examines surface of sample

Transmission Electron Microscopy
Electrons travel through the sample
First sample is fixed to reinforce structure (dead!): either through aldehydes to cross-link proteins, flash-freezing, and high intensity microwaves
Fixed sample is either: 1. Stained with a heavy metal (Uranium, Osmium) negative staining or 2. Sliced very thin using a microtome/diamond knife: thin sectioning
Can see internal bodies (magnetosomes, storage granules)
Can see layers of cell envelope (membranes, periplasm, s-layers, etc..)
Cells are dead

Fluorescence Microscopy
Absorb high energy (short wavelength)
Emit lower energy (longer wavelength)
Label specific molecules or organisms
Can see DNA or ribosomal hybridization for identification of speicies or visualization
Can view labeled antibodies for identification or localization; used for gene transcription; in situ hybridization for identification of species
Cells are usually dead except for fluorescence protein fusion (eg. GFP/YFP)
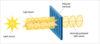
What limits the minimum object that humans can see?
The distance between 2 foveal “pixels” (groups of cones with neurons) limits resolution to about 100 micrometers (1/7 of a mm)
Raptors: tightly pacted photoreceptor cones
more tightly packed cones = better vision
What type of bacteria is this?
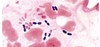
Bright field
Same as picture below
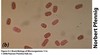
As you get closer and closer to an object with the lens, the light is less and less concentrated.
How can you increase resolution with bright field microscopy?
Solution: wider lense closer to specimen; higher numerical aperture (NA)
Solution 2: immersion oil (collects more light from specimen

What happens to the light in bright field microscopy?
The light travels directly through the object at low contrast
What happens to light with dark field microscopy?
Light is scattered at a very oblique angle that makes visible objects below resolution limit
What microscopy is this an example of?

Dark Field Microscopy
What microscopy is this an example of?

Phase-Contrast
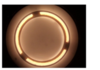
Phase Contrast vs. Dark Field
PC: light is bent at minor angle and light goes through object
DF: light is scattered at very oblique angle and light bounces or reflects off object
Picture is example of phase contrast

What type of microscopy is this?

Differential Interference Contrast

Electron Microscopy
Magnification: 15x - 100,000x
Resolution: .2nM
Uses electrons instead of light and magnets instead of lenses
Under normal conditions, the electrons would be scattered by molecules in the air (N2, O2, etc..) so the sample is placed in a vacuum
Samples are dead
Magnetic lenses focus the beam
Metals used to coat specimens - similar to staining
Heavy metals provide a coating for electron collision (ex. gold, uranium)
Very high frequency/high powered electron beam
Sample will disintegrate if exposed too long
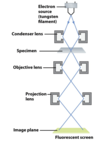
Thin-Section Transmission EM
High resolution
Can detect molecular complexes and internal structure such as ribosomes, flagellar base, and strands of DNA
Need many slices to determine 3D structure


