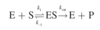Chapter 2. Enzymes Flashcards
Fill in the blank.
The molecules that are acted on by enzymes are called ____.
substrates
What are ribozymes?
Biological catalysts composed of RNA instead of peptides.
What is the activation energy (Ea) of a reaction?
The input of energy needed to overcome the barriers in the reaction.
Finish the sentence.
Enzymes decrease the activation energy, so molecular collisions ____.
occur more often
What are the six classes of enzymes?
- Oxidoreductases
- Transferases
- Hydrolases
- Lyases
- Isomerases
- Ligases
What are oxidoreductases?
- Class of enzymes that catalyze redox reactions.
- Transfer electrons between biological molecules.

When looking at oxidoreductases, the ____ is the electron donor and the ____ is the electron acceptor.
reductant; oxidant
Fill in the blank.
Oxidoreductases often have a cofactor that acts as an ____.
electron carrier
Oxidoreductases often have a cofactor that acts as an electron carrier. Give an example of three cofactors associated with oxidoreductases.
NAD+, NADP+, and heme
Which class of enzyme catalyzes the movement of a functional group from one molecule to another?
Transferases

Fill in the blank.
Transferases often employ ____.
coenzyme donors
Transferases often employ coenzyme donors. Give an example of one common coenzyme donor associated with transferases.
Coenzyme A
Fill in the blank.
Kinases and polymerases are classified as a ____ enzyme.
transferase
What are kinases?
- Transferase enzyme.
- Catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group, generally from ATP, to another molecule.
What is a polymerase?
- Transferase enzyme.
- Catalyze the transfer of nucleotides.
Which class of enzyme catalyzes the breaking of a compound into two molecules using the addition of water?
Hydrolases

What is the reverse reaction of hydrolases?
Dehydration synthesis
What is a phosphatase?
- Hydrolases enzyme.
- Cleaves a phosphate group from another molecule.
Which type of enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of a single molecule into two products?
Lyases
Which group of enzymes often forms rings or multiple bonds to reform octets?
Lyases
Fill in the blanks.
Lyases require ____ phosphate group(s) to cleave molecules, and ____ phosphate group(s) to bring molecules together.
one; two
Which class of enzyme catalyzes the rearrangement of bonds within a molecule?
Isomerases

Fill in the blanks.
Isomerases interconvert between ____ and ____.
constitutional isomers and stereoisomers
Which class of enzyme catalyzes addition or synthesis reactions, generally between large similar molecules, and often require ATP?
Ligases
Which class of enzyme is typically encountered in the context of DNA repair/synthesis?
Ligases
What are the five ways that enzymes decrease the activation energy of a reaction?
- Stabilize the transition state.
- Microenvironment adjustments.
- Adjustment of the local’s environment pH.
- Through the exclusion of water.
- Adjusting substrate proximity.
- Increases the frequency of favorable collisions.
- Transient covalent bonding.
- Substrates briefly contact active site residues subsequentially.
- Reactant destabilization.
What are the three types of interactions that occur in the active site to stabilize the spatial arrangement and contribute to the efficiency of the enzyme?
- Hydrogen bonding
- Ionic interactions
- Transient covalent bonding
What is the Lock and Key Theory?
The enzyme’s active site (lock) is already in the appropriate conformation for the substrate (key) to bind.