Chapter 16 Endocrine & Neuroendocrine Physiology Flashcards
Endocrine Glands
- A.A. Berthold speculated that the testes of a rooster secreted something that was responsible for its male characteristics in 1849
- In 1905, Starling described 3 characteristic properties of hormones:
- Hormones are synthesized by specific tissues or glands
- Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream, which carries them to their site(s) of action
- Hormones change the activities of target tissues or organs

Endocrine Glands: Hormone Structure
- There are 3 criteria determining if a tissue has endocrine function:
- Removal of the tissue produces a deficiency syndrome
- Replacement of the removed tissue reverses the deficiency syndrome
- Injection of the putative hormone should also relieve deficiency symptoms
- Hormones belong to 4 structural classes:
1. Amines - Catecholamines & Thyroid Hormone
2. Steroid hormones
3. Peptide hormones
4. Eicosanoids

Amines
Catecholamines
- Made from tyrosine
- Water soluble
- Stored in chromaffin granules
- Interact with binding proteins in plasma
- Receptors on cell membrane
- Secreted from adrenal medulla
Thyroid Hormone
- Iodinated tyrosine
- Fat soluble
- Stored in colloid
- Interact with binding proteins in plasma
- Intracellular receptors
- Secreted from thyroid gland
Steroid Hormones
- Made from cholesterol
- Fat soluble
- Not stored
- Interacts with binding proteins in plasma
- Intracellular receptors (most)
- Secreted from adrenal cortex, gonads, placenta


Steroid & Lipophilic Hormones

Peptide Hormones
- Made from amino acids
- Water soluble
- Made in RER
- Stored in secretory granules
- Transported as free hormone
- Extracellular receptors
- Many secretion sites

Hormone Effectiveness
- Several things alter hormone effectiveness
- Amount of free hormone
- Rate of synthesis
- Rate of secretion
- Concentration of binding proteins
- Dilution of hormone in plasma
- Number of receptors
Endocrine Glands: Negative-Feedback Loops
- The endocrine system runs on negative-feedback systems:
- Short-loop feedback: the response of the target tissue (1) feeds back to the endocrine tissue
- Long-loop feedback: secondary targets (2) feed back to the endocrine tissue

Posterior Pituitary and Hormones


Anterior Pituitary & Hormones

Growth Hormone (somatotropin)
- Effects depend on age
- Triglyceride catabolism
- GH induces the liver to produce insulin-like growth factors (IGF-1) which further promote tissue growth
- Increases cell size (hypertrophy) and cell number (hyperplasia)
- Bone growth (thickness & length)
- Cartilage is a primary target tissue for GH resulting in bone growth; growth hormone and thyroxine are synergistic hormones in development
- In adults, GH effects are similar to those of glucagon (these effects also occur in immature animals)

Prolactin
- Causes milk production (lactogenesis)
- Stimulates crop milk
- Reproductive behaviors (incubation behavior)
- Brood patch
- Osmoregulation
- Control differs in mammals & birds
Thyroid Hormone
- Thyroxine causes increased metabolism in skeletal and cardiac muscle, the liver, and the kidney; this causes the metabolic production of heat.
- T4 is most abundant, T3 is most active
- Increases response to catecholamines (from sympathetic system)
- Increases heart rate
- Acts permissively with GH
- Controls metamorphosis


The HPA Axis

Catecholamines
The adrenal medulla is physiologically equivalent to a giant postganglionic sympathetic neuron which releases epinephrine &/or norepinephrine into the circulation

Stress

Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- Vasopressin
- Stimulated by hypothalamic osmoreceptors
- Pressor effect
- Antidiuretic effect
- Arginine Vasotocin
- Lower vertebrates
- Oviposition in birds
- Stimulates ACTH-induced steroidogenesis in tadpoles
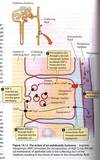
Calcitonin and Parathyroid Hormone Effects
Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone have opposing effects on blood Ca2+ levels

Mammalian Hormones Involved in Water and Electrolyte Balance

Insulin

Insulin & Glucagon

Insulin, Glucogon, & Steak

Prostaglandins
- Prostaglandins are arachidonic acid-derived substances which tend to have paracrine as well as endocrine effects that are short-lived unlike other lipid-soluble hormones
- Prostaglandins have varied effects including mediating the inflammatory response

Invertebrate Endocrinology
- Mollusks
- Juxtaganglionar organ secretes peptides into hemolymph during egg laying
- Bag cells secrete egg-laying hormone (ELH)
- Annelids
- Annetocin causes egg-laying behavior
- Crustaceans
- X-organ (in eyestalks)
- Chromatophorotropins: change color of cuticle
- Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone: releases glucose and glycogen from hepatopancreas
- Vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone: inhibits egg production
- X-organ (in eyestalks)
- Y-organ (in head)
- Crustecydsone: causes molting
Insect Hormones
- Prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) is made in the brain.
- Neurohormone
- Released into circulation at corpora cardiaca and corpora allata
- Travels through hemolymph to prothoracic glands
- Prothoracic gland
- At back of head or thorax
- Secretes ecdysone
- A steroid (ecdysteroid)
- Induces molting: Replacing exoskeleton with another
- Ecdysis: Removal of old exoskeleton
- At back of head or thorax

- Corpora allata
- Behind brain
- Secretes juvenile hormone (JH)
- Bursicon
- Neurohormone
- Cuticle development after molting
- Eclosion hormone
- Neurohormone
- Emergence from pupa




