Chapter 1: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins Flashcards
What are molecules that contain these two functional groups: an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH)?
Amino acids.
In a-amino acids, the amino group and carboxyl group are bonded to which carbon
The a-carbon of the carboxylic acid.
The a-carbon has two other groups attached to it. What are they?
A hydrogen atom and a side chain (-R group) which is specific to each amino acid.
Side chains determine what about amino acids?
They determine the properties of amino acids, and therefore their functions.
The 20 a-amino acids that are encoded by the human genetic code are also called what?
Proteinogenic amino acids.
For most amino acids, the a-carbon is a what center, as it has four different groups attached to it?
Chiral (stereogenic) center.
Because most amino acids have a chiral a-carbon, most amino acids are what?
Optically active.
What amino acid has an achiral a-carbon atom due to hydrogen being its R group?
Glycine
The stereochemistry for all chiral amino acids used in eukaryotes is?
L-amino acid, thus the amino group is draawn on the left in a Fischer projection.
In the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system, L-amino acids translates to which absolute configuration?
(S) absolute configuration.
What L-amino acid has an (R) absolute configuration due to the -CH2SH group having higher priority over the -COOH group?
Cysteine.
What are the 7 proteinogenic amino acids that have nonpolar, nonaromatic side chains?
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline.
Glycine has what as it’s side chain?
Hydrogen atom in its side chain, thus making it achiral.
Which amino acids have alkyl side chains containing one to four carbons?
Valine, alanine, leucine, isoleucine.
Why is methionine relatively nonpolar?
Methionine is one of two amino acids with a sulfur atom in its chain and because a methyl group is attached to the sulfur, it’s relatively nonpolar.
Why is proline special?
Proline forms a cyclic amino acid. The amino nitrogen becomes a part of the side chain, forming a five-membered ring. The ring places constraints on the flexibility of proline, which limits where it can appear in a protein and can have significant effects on proline’s role in secondary structure.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Alanine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Glycine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Valine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Leucine.
What amino acid is pictured here?
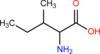
Isoleucine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Methionine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Proline.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Tryptophan.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Phenylalanine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Tyrosine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Serine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Threonine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Asparagine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Glutamine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Cysteine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Arginine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Lysine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Histidine.
What amino acid is pictured here?

Aspartic acid.
What is amino acid is pictured here?

Glutamic acid.
What are the three amino acids that have aromatic side chains?
Tryptophan (double ring system with a nitrogen atom), phenylalanine (benzyl side chain), and tyrosine (benzyl side chain with -OH).
Compared to phenylalanine, tyrosine is polar or nonpolar?
Phenylalanine is relatively nonpolar, while the -OH group makes tyrosine relatively polar.
What are the five amino acids that have polar, but not aromatic, side chains?
Serine and threonine (both have -OH groups making them highly polar and able to participate in hydrogen bonding), asparagine and glutamine (amide side chains, whose nitrogens do not gain or lose protons with changes in pH and do not become charged), and cysteine (thiol group, weaker group than OH which leaves cysteine prone to oxidation).
What are the two amino acids that have negative charges (acidic) on their side chains at physiological pH (7.4)?
Aspartic acid and glutamic acid. They both have -COO- groups, rather than amides.
What are the three amino acids that have positively charged (basic) side chains?
Lysine (has a terminal primary amino group), Arginine (three nitrogen atoms in its side chain, positive charge delocalized over all nitrogens), Histidine (aromatic ring with two nitrogens - imidazole ring)
Amino acids with long alkyl side chains are all strongly what and thus more likely to be found in the interior of the proteins?
Hydrophobic (i.e. alanine, isoleucine, leucine, valine, and phenylalanine).
All amino acids with charged side chains and amides are hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophilic (positively charged - histidine, arginine, lysine; negatively charged - glutamine, aspartate; amides - asparagine, glutamine)
What is are amphoteric species?
Something that can accept or donate a proton (how they react depends on the pH of their environement).
What happens to ionizable groups at low and high pH?
At low pH, ionizable groups tend to be protonated. At high pH, ionizable groups tend to be deprotonated.
What is the pKa of a group?
pKa is the pH at which, on average, half of the molecules of that species are deprotonated. [HA] = [A-]
What happens to a majority of a species if pH < pKa and if pH > pKa?
If pH < pKa, majority of species will be protonated.
If pH > pKa, majority of species will be deprotonated.
Because all amino acids have at least two groups that can be deprotonated, they all have at least two pKa values. They refer to which groups?
The first one refers to the carboxyl group and is usually around 2. For most amino acids, the second one refers to the amino group, which is usually between 9 and 10. (Note: Those with an ionizable side chain have three values.)
At very acidic pH values, amino acids then to what charged?
Positively charged. (i.e. at pH 1, we are below the pKa of the amino and carboxyl group, thus they will both be protonated)
At physiological pH, you will find the carboxyl group in its conjugate base form (-COO-; pH > pKa - deprotonation) and the amino group in its conjugated acid form (-NH3+; pH < pKa - protonation). We can call this what?
Zwitterion - a molecule with both a positive and negative charge. The two charges neutralize one another, and zwitterions exist in water as internal salts.
At very basic pH values, amino acids tend to be what charged?
Negatively charged.
When pH is close to the pKa value of a solute, the solution acts like what and what does the titration curve look like?
The solution acts like a buffer and the titration curve is relatively flat.
When every molecule is electrically neutral the pH is equal to what?
The isoelectric point. For neutral amino acids, it can be calculated by averaging the two pKa values for the carboxylic acid and amino groups.


