Chapter 1 Flashcards
Network admin needs to connect two routers directly via their FastEthernet ports. What cable should be used to connect each other?
Cross-Over Cable
If a router can not find a valid config file during the startup sequence, what will occur?
The router will prompt the user for a response to enter setup mode.
Passwords can be used to restrict access to all other parts of the Cisco IOS. Name three modes that can be protected.
VTY Interface, Console Interface, and Privileged EXEC mode.
Which two statements correctly describe the components of a router?
ROM contains diagnostics executed on hardware modules and Flash memory does not lose contents during a reboot.
What is the outcome of entering these commands? R1(config)# line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)# password check123 R1(config-line)# login
Sets the password to be used for connecting to the router using Telnet.
What is the correct flow of routines for a router startup?
Load Bootstrap, load IOS, apply config.
What three processes does a router execute when it receives a packet from one network that is destined for another network?
Decapsulates the Layer 3 packet by stripping off the Layer 2 frame header. Uses the destination IP Address in the IP header to look up the next-hop address in the routing table. Encapsulates the Layer 3 packet into the new Layer 2 frame and forwards it out the exit interface.
From what location can a router load the Cisco IOS during the boot process?
TFTP Server and Flash Memory.
A network admin has just entered new configs into Router1. What command should be executed to save config changes to NVRAM?
Router1# copy running-config startup-config
What is the default sequence for loading the config file?
NVRAM, TFTP, Console
What header addres info does a router change in the info it receives from an attached Ethernet interface before info is transmitted out another interface?
The Layer 2 source and destination address.
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator has configured the router with the interface IP addresses shown for the directly connected networks. Pings from the router to hosts on the connected networks or pings between router interfaces are not working. What is the most likely problem?

The interfaces must be enabled with the no shutdown command.
Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded from the routing table output in the exhibit? (2)

- The FastEthernet0/0 and Serial0/0/0 interfaces of this router were configured with an IP address and the no shutdown command.
- An IP packet received by this router with a destination address of 198.18.9.1 will be forwarded out of the Serial0/0/0 interface.
Refer to the exhibit. The frame shown in the exhibit was received by the router. The router interfaces are operational. How will the router process this frame? (2)

- The router will change the frame type to one supported by the WAN link before forwarding the frame.
- The frame was received on the Fa0/0 interface of the router and will be switched to the S0/0/0 interface.
Refer to the exhibit. After host 2 is connected to the switch on the LAN, host 2 is unable to communicate with host 1. What is the cause of this problem?

Host 1 and host 2 are on different networks.
Refer to the exhibit. All routers have a route in its routing table to each network that is shown in the exhibit. Default routes have not been issued on these routers. What can be concluded about how packets are forwarded in this network? (Two Answers.)
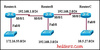
- If RouterA receives a packet that is destined for 192.168.3.146, it will be forwarded out interface S0/0/1.
- If RouterB receives a packet that is destined for 10.5.27.15, it will be forwarded out interface S0/0/1.
The serial connection shown in the graphic needs to be configured. Which configuration commands must be made on the Sydney router to establish connectivity with the Melbourne site? (Three Answers.)

- Sydney(config-if)# ip address 201.100.53.2 255.255.255.0
- Sydney(config-if)# no shutdown
- Sydney(config-if)# clock rate 56000
Refer to the exhibit. What can be concluded from the output of the running-configuration of a router?

The commands that are displayed determine the current operation of the router.




