Chap6 Fish population Flashcards
Represent the dynamics of a fish population governed by births and deaths ( Without human intervention) through CLD
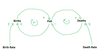
Determine the needed variables for the fish population. And Draw SFD!
- Fish (variable type: stock, unit: tons (t), initial value 100 t)
- Births (variable type: flow, unit: t/year)
- Deaths (variable type: flow, unit t/year)
- Birth Rate (variable type: auxiliary, unit: 1/year)
- Death Rate (variable type: auxiliary, unit: 1/year)

_What happens in each scenario ?
Scenario 1: Birth Rate Equals Death Rate_
Set both rates to 0.3/year.
Scenario 2: Birth Rate Smaller Than Death Rate
Set Birth Rate to 0.2/year and keep Death Rate at 0.3/year.
Scenario 3: Birth Rate Greater Than Death Rate
Set Birth Rate to 0.32/year and keep Death Rate at 0.3/year.
This is not realistic on the long run, because there is always ( population dependent density factors) like space and food, that constitute a carrying capacity limit. At some point there will be no food and fish should start dying. In addition assuming constant birth and death rates on the long run is not realistic.

No we assume we have an additional loop (Fish -> Relative Population Density -> Death Rate -> Deaths -> Fish) which controls (dependent on the population size) how powerful the negative feedback loop Fish -> Deaths -> Fish is in relation to the positive loop Fish -> Births -> Fish.
Draw the new diagram!
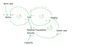
As usual draw SFD after defining all necessary variables with units and equations!
Variables
- Fish (variable type: stock, unit: tons (t), initial value 100 t)
- Births (variable type: flow, unit: t/year)
- Deaths (variable type: flow, unit t/year)
- Birth Rate (variable type: auxiliary, unit: 1/year)
- Death Rate (variable type: auxiliary, unit: 1/year)
- Capacity (variable type: auxiliary, unit: t)
- Relative Population Density (variable type: auxiliary, unit: dimensionless (= Dmnl))

What happens at following scenarios ?

Scenario 1: Base
The intial size of the fish population amounts to 100 t.
Scenario 2: Start at Capacity
Set the initial population size to 5000 t (which is, in our model, the ecosystem’s carrying capacity for such a fish population).

Scenario 3: Start with Overpopulation
Set the initial population size to 7000 t (assume 2000 t of fish have been swept into our marine ecosystem due to unusual currents caused by a severe storm).
Describe the net increment.
Net Increment (Births – Deaths)


