Ch.15, Part 1 - Cell Compartments Flashcards
- Mem-Enclosed Organelles - Protein Sorting (54 cards)
Where in the cell are steroid hormones synthesized, organic molecules (e.g. alcohol) detoxed, and Ca2+ stored for signaling?
SER
Describe the key functions of endosomes.
Endosomes:
- Series of compartments thru wh materials pass before endocytosed into lysosomes.
- Sort ingested molecules and recycle some of them back to pmem.
Peroxisomes break down lipids and toxic molecules thru ________.
Peroxisomes break down lipids and toxic molecules thru oxidation.
T/F: Synth of virtually all proteins begins on free ribosomes.
True
Synth of virtually all proteins begins on free ribosomes.
- Exception: a few mito/chloro proteins are synthd on ribos w/i organelle itself.
Proteins w a _________ are directed to certain organelles, otherwise remain in cytosol.
Proteins w a sorting signal are directed to certain organelles, otherwise remain in cytosol.
Endocytosis of water-soluble proteins occurs via diff mechanisms in diff organelles. Describe the pathway for proteins moving fr the cytosol into the nucleus.
Cytosol → nucleus: xprtd thru nuclear pores.
- Pores function as selective gates that actively transport specific macros but also allow free diffusion of smaller molecules
Endocytosis of water-soluble proteins occurs via diff mechanisms in diff organelles. Describe the pathway for proteins moving fr the cytosol into ER/mito/chloro.
Cytosol → ER/mito/chloro: xprtd across mem via protein translocators in mem.
- Unlike xprt thru nuclear pores, xprtd protein typ must unfold → snake across mem thru translocator.
- Bac: similar protein translocators in pmem → export proteins fr cytosol.

Unlike xprt thru nuclear pores, xprt fr cytosol to ER/mito/chloro typ reqs the protein to _____ and snake across mem thru _________.
Unlike xprt thru nuclear pores, xprt fr cytosol to ER/ mito/chloro typ reqs the protein to unfold and snake across mem thru translocators.
Endocytosis of water-soluble proteins occurs via diff mechanisms in diff organelles. Describe the pathway for proteins moving fr the ER to its target/other endomem compartments.
ER → target, also b/w endomem compartments: proteins ferried by transport vesicles, wh pinch off fr mem of one compartment → fuse w mem of second compartment.
- Transport vesicles deliver soluble cargo proteins, as well as proteins/lipids that are part of vesicle mem.

Sorting signals are a continuous stretch of ~ ____ AAs long that are _____ (often/always) cleaved off after sorting.
Sorting signals are a continuous stretch of ~ 15-60 AAs long that are often (not always) cleaved off after sorting.
What would happen if a sorting signal (signal seq) was deleted fr an ER protein?
Sorting signals can be added/removed/shuffled → change nature of protein.
- E.g. signal seq deleted fr ER protein → converted into a cytosolic protein.
T/F: wrt sorting signals, the specific AA seq matters more than the physical properties of the AAs w/i the signal seq.
False
Physical props (hydrophobicity) matter more than AA seq, i.e. can swap one hphobic AA for another and still retain proper sorting.
The nuclear envelope is formed fr two concentric bilayers. Describe the general struc/func of ea.
Nuclear envelope - formed fr two concentric bilayers:
-
Inner mem contains some proteins that act as binding sites for chromos, others provide anchorage for nuclear lamina.
- Nuclear lamina - fine meshwork of protein filaments; lines inner face of inner mem; struc support.
- Outer mem closely resembles and is continuous w ER.

The __________ a finely woven meshwork of protein filaments that lines _____ (inner/outer) face of the ______ (inner/outer) nuclear mem and provides structural support.
The nuclear lamina a finely woven meshwork of protein filaments that lines inner face of inner nuclear mem and provides structural support.

Nuclear pores are a complex of ~30 proteins characterized by extensive _______ regions wh fill the _______ (inside/outside/center) of the channel.
Nuclear pores are a complex of ~30 proteins characterized by extensive unstructured regions (intrinsically disordered seqs) wh fill the center of the channel.
- Unstruc regions consist of short, repeated AA seqs wh bind one/an when pore is empty and form loose gel thru wh small, water-soluble molecules can pass freely and nonselectively.

Nuclear pores are a complex of ~30 proteins characterized by extensive unstructured regions (intrinsically disordered seqs) wh fill the center of the channel. How does this soft, tangled meshwork of proteins influence the function of nuclear pores?
Unstructured regions (disordered seqs) form soft, tangled meshwork that fill center of channel → prevent passage of large molecules while allowing small, water-soluble molecules to pass freely and nonselectively.
- Unstruc regions consist of short, repeated AA seqs wh bind one/an when poor is empty and form loose gel thru wh small, water-soluble molecules can easy traverse.
- Larger molecules pass via import receptors, wh penetrate pore by interrupting interactions b/w repeated AA seqs of unstruc regions → open local passageway, bumping fr one repeat seq to next → delivers cargo into nucleus → empty receptor returns to cytosol via nuclear pore for reuse.

T/F: Nuclear pores allow small, water-soluble molecules to pass freely and nonselectively.
True
T/F: Nuclear pores allow small, water-soluble molecules to pass freely and nonselectively.
In order for large molecules/macromolecules to pass thru nuclear pores, they must display an appropriate __________.
In order for large molecules/macromolecules to pass thru nuclear pores, they must display an appropriate sorting signal (signal seq).
- Nuclear localization signal - signal seq that directs protein fr cytosol into nucleus; typ 1-2 short seqs w several positively charged lysines (lys; K) or arginines (arg; R).

Nuclear localization signals are signal seqs that direct protein fr ______ into ______; typ 1-2 short seqs w several ________ (pos/neg) charged lysines (Lys; K) or arginines (Arg; R).
Nuclear localization signals are signal seqs that direct protein fr cytosol into nucleus; typ 1-2 short seqs w several positively lysines (lys; K) or arginines (arg; R).

Cytosolic proteins containing nuclear localization signals are recognized by ____________, wh interact w __________that extend fr the rim of the pore.
Cytosolic proteins containing nuclear localization signals are recognized by nuclear import receptors, wh interact w cytosolic fibrils that extend fr the rim of the pore.
- Similar export receptors/mechanism.
- Larger molecules pass via import receptors, wh penetrate pore by interrupting interactions b/w repeated AA seqs of unstruc regions → open local passageway, bumping fr one repeat seq to next → delivers cargo into nucleus → empty receptor returns to cytosol via nuclear pore for reuse.

Describe how larger molecules traverse nuclear pores via import receptors.
Larger molecules pass via import receptors, wh penetrate pore by interrupting interactions b/w repeated AA seqs of unstruc regions → open local passageway, bumping fr one repeat seq to next → delivers cargo into nucleus → empty receptor returns to cytosol via nuclear pore for reuse.
- Recall: when pore empty, unstruc regions (repeat AA seqs) bind w ea/o → form loose gel thru wh small, water-soluble molecules pass freely/nonselectively.
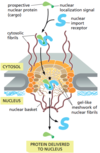
Import of nuclear proteins reqs energy via ___ hydrolysis, mediated by ____ - a monomeric GTPase.
Import of nuclear proteins reqs energy via GTP hydrolysis, mediated by Ran - a monomeric GTPase.

T/F: Nuclear pores xprt proteins in their fully folded conformation.
True
Nuclear pores xprt proteins in their fully folded conformation.
- Distinguishes nuclear xprt fr protein xprt into other organelles, e.g. mito/chloro - proteins must unfold to cross.
- Ribosomal components are xprtd as assembled particles.
Import of nuclear proteins reqs energy via GTP hydrolysis, mediated by Ran - a monomeric GTPase. Describe this nuclear xprt mechanism.
Nuclear xprt via GTP hydrolysis mechanism:
- Nuclear import receptor binds protein w nuclear localization signal in cytosol → enters nucleus thru pore.
- Ran-GTP binds import receptor → releases protein → import-Ran-GTP complex leaves nucleus thru pore.
- Accessory protein in cytosol triggers Ran to hydrolyze terminal P of GTP → Ran-GDP dissocs fr import receptor → import receptor ready to bind next protein.
- Similar cycle for nuclear export receptors.



















