Ch 11. Inflammatory Diseases Of the Retina Flashcards
Given that this is a young Japanese patient that presented with acute vision loss after a flu-like prodrome, with mayor vessel perivascular infiltration and disc edema what is the most likely diagnosis?

Frosted branch angiitis.
Name causes for frosted branch angitis
- idiopathic
- Secondary: including cytomegalovirus retinitis, Behçet’s disease, lupus erythematosus, Epstein–Barr virus retinitis, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, herpetic retinitis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positivity, Hodgkin’s disease, rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, staph and streptococcal endophthalmitis.
What is the name for the inflamatory reaction induced by initial ATB treatment of ocular syphilis?
Jarisch-Herxheimer
The following statement and image refer to,
“typically affects young healthy male or female patients (average age approximately 25 years), who develop rapid loss of vision in one or both eyes secondary to multiple postequatorial, circumscribed, flat, gray subretinal lesions involving the retinal pigment epithelium”

ACUTE POSTERIOR MULTIFOCAL PLACOID PIGMENT EPITHELIOPATHY
(APMPPE)
To what potentially fatal complication is APMPPE associated ?
Cerebral Vasculitis, with a 95% fatality rate if not promptly treated.
Laterality of APMPPE
Usually bilateral, the second eye is usually involved within a few days or weeks after the first.
T/F
APMPPE has a very poor visual prognosis, most patients end up with vision wost than 20/40.
False, it has a great prognosis, with most patients returning to 20/20.
APMPPE is dangerous not for its visual prognosis, but its association to cerebral vasculitis, which does have a high mortality rate.
Many patients can describe a paracentral scotoma when carefully examined.
How are APMPPE plaques imaged in the FA?
They are hypo-fluorescent in early stages (blockage) and stain during late stages
APMPPE and Serpiginous Choroiditis may present similar in early stages but have entirely different clinical courses. Name differences between them.

This 43-year-old patient’s illness has been characterized by a multifocal chronic/recurrent choroidal inflammation that began at the nerve and has spread centrifugally. What is the most likely dx?
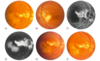
Serpiginous Choroiditis
What difference do the acute Serpiginous Choroiditis plaques have when compared to APMPPE ones?
They are both early-hypo, late hyper… fluorescent.
But SC ones stain from the periphery, so they present a halo appearance during “early” late stages.
<em>This is because APMPPE is not associated with choriocapillaris shut down, while SC affects primarily the inner half of the choroid. </em>
If a patient under treatment for serpiginous choroiditis is not responding to steroids, what other Dx must be ruled out (if not before starting Tx)
Tubercular Serpiginous Choroidopathy
What is the visual prognosis of acute idiopathic maculopathy?

Excelente.
This young patient presents a couple of weeks after having a flu-like illness, with unilateral paracentral scotomas, photopsia, vitritis, and this funduscopic image.
Name the most likely Dx.

MEWDS
An enlarged blind spot will most likely be present if this is the correct dx and must be looked for.
Is vitritis present in MCP?
In its original description, yes, this was actually one of the ways to tell the difference from POHS.
Nevertheless, it is now clear that it may not have cells at the time of clinical assessment.



