Cells & Tissues of Immune System Flashcards
All immune cells are derived from ____ as a fetus, but then ___ at 7 months.
But the innate immune system is derived from a ___ progenitor and consists of ____
And the adaptive immune system is derived from a ___ projgenitor and consists of
Fetal liver & spleen, but then pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow

Innate - myeloid progenitor; neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, mast cells, macrophages
Adaptive immune system - lymphoid progenitor; B & T cells
B cells mature in the ___
T cells mature in the ___
B cells mature in the bone marrow (where all immune cells originate)
T cells go mature in the thymus
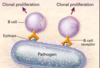
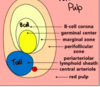
What happens in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and spleen?
Lymph nodes: B & T cells in lymph meet and get activated
Spleen: B & T cells in blood meet and get activated
Mucosal lymphoid organs - tonsils, adenoids, Peyer’s patches
Name the cell:
Produces antibodies
Cytotoxic and helper functions
Small lymphocyte
B cell
T Cell

Name the cell:
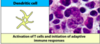
Activates T cells
Initiates adaptive immune responses
Name the cell:
Fully differentiated form of B cell that secretes antibodies

Name the cell:
Expels parasites from the body byer leasing histamine and other active agents

Name the cell:
Kills cells infected w certain viruses

Name the cell:
circulator precursor cell to a macrophage

Name the cell:
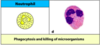
phagocytosis and killing microorganisms
Neutrophils make up the majority of leukocytes!
Name the cell:
Phagocytosis & killing microorganisms
Activation of T cells and initiation of immune response

What cell…
- Kills antibody coated parasites through release of granule contents?
- Controls immune responses to parasites?
- Is involved in platelet formation, wound repair?

Lymphocyte maturation (B cell in bone marrow, T cellin thymus) is antigen-independent.
What happens in lymphocyte maturation in BOTH T and B cells?
- Acquire antigen-specific cell surface receptors
-
Elimination of auto-reactive lymphocytes, especially T cells
- If they aren’t killed, then –> autoimmunity
T cell maturation
- Immature T cell interacts with cortical thymic hormones (thymosin, thymulin, thymopoietin)
- Acquires a T cell receptor (TCR) heterodimers (mostly TCR aB)
- CD3 is the signaling component of TCR
- Establish a phenotype
- At first cells have neither: CD4-, CD8-
- Then, they get both: CD4+, CD8+
- Then, one gets turned off: CD4 for helper, CD8 for cytotoxic
- Recognize the processed antigen presented by APCs on an MHC
B cell maturation
(not in lecture)
- Acquire B cell receptor: IgM
- (This receptor is the same antibody that the B cell is going to secrete when activated)
- Recognize and bind the native (unprocessed) antigen
- Clonal proliferation creates memory cells & plasma cells