Cells and Tissues of the Immune System Flashcards
What are primary lymphoid tissues?
Primary lymphoid tissues are where white blood cells originate and develop.
Bone marrow and thymus
What tissues comprise primary lymphoid tissues?
Bone marrow and thymus
What are secondary lymphoid tissues?
Secondary lymphoid tissues are where white blood cells migrate to interact and generate an effective, adaptive immune response
Lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, lymphoid tissues (MALT, GALT, BALT)
What tissues comprise secondary lymphoid tissues?
Lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, and lymphoid
Where do all WBCs originate?
Bone marrow
What does the common stem cell give rise to?
Lymphoid stem cells and myeloid stem cells
Which cells are derived from myeloid cells?
- Neutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils/mast cells
- Monocytes/macrophages
- Other antigen-presenting cells
Which cells are derived from lymphoid cells?
- B-Cells
- T-Cells
- Natural Killer Cells
Where do all myeloid-derived cells mature?
Bone marrow
What does the lymphatic system consist of?
- Lymph veseels
- Tissues and organs w/ high density of lymphocytes
- Lymph nodules
- Lymph nodes
- Thymus gland
- Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue
- Bone marrow
What kind of cell is this?

Neutrophil; Multi-lobed nucleus

What kind of cell is this?

Eosinophil;
Bi-lobed cells with bright pink cytoplasmic granules
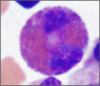
What kind of cell is this?
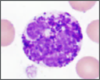
Basophil;
Deep blue, dark cytoplasmic granules

What is MALT called when it is in the gut?
Gut-associated lymphatic tissue (GALT)
What is MALT called when it is in the airway?
Bronchus-associated lymphatic tissue (BALT)
What kind of cell is this?

Mast Cell;
Deep blue dark cytoplasmic granules

What are antigens?
Substances, tissues, or infectious organisms foreign to the body
What kind of cell is this?
Where are you likely to find it?

Monocyte; kidney shaped nucleus, lilac cytoplasm
Found in peripheral blood

What are the functions of supporting cells?
Regulate immune response and play roles in presenting antigen to lymphocytes
What does the stroma of lymphatic nodules, nodes, and spleed consist of?
Reticular fibers (small diameter collagen fibers w/ high sugar content)
Produced by reticular cells
What does the stroma of the thymus consist of?
Branching interconnecting epithelioreticular cells
From third branchial pouches
Which cell types are surveillance cells?
- Macrophages
- Langerhans cells (epidermis)
- M cells (intestinal epithelium overlying lymph nodules)
- Dendritic cells (lymphatic tissues)
What kind of cell is this?
Where is it found?

Macrophage;
Reside in tissues

Describe the path that long-lived circulating lymphocytes move in
- Leave blood venules to enter lymphatic organs and tissues for immune surveillance
- Re-enter circulation to go to other lymphatic tissues
- Pass through walls of vasculature in high endothelial venules in lymphatic tissues and organs (postcapillary)










