cell chemistry 9/12 Flashcards
what are characteristics of lipids (fats, oils, sterols)?
§Non Polar compounds and non polar
§Hydrophobic
§Play crucial roles in most membrane and as energy storage molecules
§Composed of C, H, O but not in 1:2:1 ratio
general characteristics of carbs
§Polymers of sugar units bonded together by glycosidic bonds
§Play important roles in cell walls and as energy storage molecules
(mono,polysaccarides)
characteristics of proteins
§Most abundant macromolecules in cells
§Found throughout cell
§Have important structural and enzymatic roles
(polymers of amino acids)
nucleic acids general
- polymers of nucleotides
- RNA and DNA
- RNA bigger than DNA
characteristics of monomers (mono and disaccharides)
§Organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen at a ratio of 1:2:1; polar molecules; hydrophilic
§Most biologically important have 5 or 6 carbon atoms
§Pentoses (C5 sugars): structural backbones of nucleic acids
§Hexoses (C6 sugars): monomeric constituents of cell wall polymers and energy reserves
§Functions: energy storage; building blocks for polysaccharides and nucleotides
structure and function of glucose
energy source; cell walls
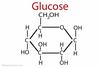
glucose and fructose are
structural isomers
what are derivatives or modified monosaccharides
When other chemical species replace one or more of the hydroxyl groups on the sugar, derivatives are formed (derivatives of simple carbs are common in cells)
what are the different names of carbs depending on how many monosaccharides they contain
§Disaccharides: carbohydrates containing two monosaccharides
§Trisaccharides: carbohydrates containing three monosaccharides
§Oligosaccharides: carbohydrates containing several monosaccharides
§Polysaccharides: carbohydrates containing many monomeric units (monosaccharides) connected by glycosidic bonds
what are glycosidic bonds
§covalent bonds linking adjacent sugars together
what are the possible geometric orientations of glycosidic bonds and what does this mean for macromolecules
§Two possible geometric orientations: alpha (a) and beta (b) (crosses plane of ring structure)
§Configuration of bond imparts different functional properties to macromolecules composed of the same building blocks (e.g., starch and cellulose)
what are the different types of polysaccharides and what are they made of
- energy storage
- starch - polysaccharide composed of glucose monomers joined to each other by alpha glycosidic bonds (tend to be hydrophobic)
- structural strength of cell walls
- Structural polysaccharide (cellulose, chitin,etc) – polysaccharide composed of glucose monomers joined to each other by beta glycosidic bonds (hydrophobic)
what type of macromolecules combine with polysaccharides to form complex polysaccharides
- Glycoproteins - polysaccharides + proteins – common in eukaryotes
- include eukaryotic cell-surface receptor molecules; typically reside on external surfaces of the membrane
- Glycolipids - polysaccharides + lipids – found in cell walls
- important in cell walls of gram-negative bacteria
what are triclycerides (simple fats) made up of and what is there function
- Composed of three fatty acids bonded to the 3 carbon alcohol, glycerol
- Has ester bonds (linkages) between glycerol and fatty acids
- Fatty acids consist of carboxyl group and hydrocarbon chain
- energy storage
what is the difference between saturated and unsaturated
§Saturated fatty acids – no double bonds between Cs; straight, linear molecule
§Unsaturated fatty acids – one or more double bonds between the carbons; bent or kinked molecule

