Cell adhesion Meolcuels and Junctional Complexes Flashcards
Simple non ciliated columnar epithelium is most likely to be found associated with which of hte following?
- urniary tract
- respiratory tract
- integument
- digestive tract
digetive tract
Junctional complexes are associated with which cellular domains
- Apical
- Basolateral
- Basal only
- Lateral only
Basolateral
Transtional epithelium is associated with which of the following system?
- Respiratory
- Lymphatic
- Cardiovascular
- Urniary
Urniary
Although not common,stratified cuboidal epithelium may be found in which of the following areas?
- Vaginal epithelium
- Part of the male urethra
- urniary bladder
- kidney tubuels
Male urethra
Lightly keratinizied stratified squamos epithelium is chareceristic of which of the following locations?
- Vaginal Epithelium
- Part of hte male urethra
- Urniary bladder
- kidney tubuels
Vaginal epithelium
Charecteristics of the basement membrane
- Basement membrane separates an epithelial layer from its connective tissue support
- Basement membrane is approxmimately 50-80nm thick
- Basement membrne consists of two components
–basal lamin-produced by the epithelium
–Reticular lamina produced by the connective tissue
-not a cellular membrane PAS+ can really see basement mebrane
Components of Basal Lamina
- Laminin -Fibronectin-
- Type IV collagen
– type IV collaen coes not form fibirls like type I collagen
– Type IV collagen is produced by epithelial cells ,unlike type I collagen which is secreted by fibroblasts
- Entactin(nidogen)
- Proteoglycans
Laminin:charecteristics
- This is the major component of the basal lamina; it consists of three chains:a,b,y
- Laminin has binding sites for integrins, type Iv collagen, entactin and proteoglycans(IE , heptran sulfate)
Fibronectin
-a protein made up of two polypeptide chains cross-linked by disulfide bonds
Forms of fibronectin
- Cellular-produced by fibroblasts;part of extracellular matrix
- Plasma-secreted into bloodstream by hepatocytes
Fibronecting binding sites for what molecules
- heparin
- integrins
- collagen
- Fibrin

- Laminin is hte major component of hte basal lamina
- consists of three disulfide linked polypeptide chains designated a, b,y chains
- Varients for each chain give rise to several laminin isoforms with different strucutre and fuction
- Have binding sites for cell surface receptors(integrins),type IV collagen, and other adhesioin proteins(ex. nidogen aka entactin)
- Laminin monomers self-associate to form a network that is part of the basal lamina

Fibronectin
- A glycoprotein formed by two identical chains joined by disulfide linkages close to the C-terminal
- two forms
- Plasma fibronectin-produced by hepatocytes and secreted into the bloodstream
- Cellular fibronectin-produced by fibroblasts ,forms part of the extracellular matrix
- Has binding sites for integrins, collagens , heparan sulfate and fibrin
Cell Adhesion Molecules(CAMs)
- Depending on the need for calcium in their interactions with other molecules , cell adhesion molecules are divided into two groups
- Calcium dependent
- Cadherins
- Selectins
- Calcium indepndent
- Integrins
- Immunoglobulin superfamily molecules
- Calcium dependent

Classical Cadherins
- Major components in calcium mediated adherens junctions
- TYpically form cis and trans homophilic dimers
- include:
- E-cadherins:found in epithelial tissues
- N-Cadherins:found in nerve cells
- P-cadherins: found in the placenta

Nonclassical cadherins
- Include desmocollins and desmogleins
- Found in desmosomes(macula adherens)
E-Cadherins
- The most common type of cadherins
- Form dimers via a HVA binding face(Histidine-valine-alanine sequence)
- Found at tip of extracellular end of cadherin molecule
- calcium ion binds to four extracellular domains and facilitate cis-homophilic dimers
- Loss of e-cadherins is associated with invasive behaviors of tumor cells
- Cadherin molecules pass through the cell membrane and will have an intracellular and extracellular component
- Need to link cell to basement membrane and see other integrins linking together the cytoskeleton with other proteins
Catenins
- Small proteins that link the cytoplasmi end of a cadherin with cytoplasmi action
- three forms:
- B and y/plakogolobin catenins:
- Attached to cytoplasmic end of a cadherin
- Beta may also serve as a transcription cofactor
- Beta is also attached to alpha catenin
- insdie the cell
- a catenin
- Binds directly to cytoplasmic actin
- B and y/plakogolobin catenins:
- Serve as a major interface between the cadherins that hold adjacent cells together and the actin cytoskeletons of those cells
Selectins
- Selectins bind to carbohydrates;therefore , they belong to the lectin group
- The binding site for carbohydrates is located at the carbohydrate-recognition domain(CRD) at the extracellular end of the selectin
- Calcium binding sites are also found near the CRD and calcium is required for the binding activity
- Selectins are invovled in the movement of leukocytes from blood to tissues(extravasation)
- Extravasation-moving out of the blood cells
Selectins and types

- Selectins have three extracellular domains
- A carbohydrate recognition domain(CRD) specific for particular sugar(galactose, mannose,N-acetylgucosamine, and others)
- A domain homologous to a repeat found in epidermal growth factor(EGF-like)
- Many consensus repeats found in complement regulatory proteins
- 3 major types of selectins:
- L-selectin- carried by lymphocytes and with binding affinity to sulfated carbohydrates
- E-selectin-expressed by activated endothelial cells
- P-selectin-expressed by platelets and activated endothelial cells
- Selectins, together with integrins and intercellular cell adhesion molecules(ICAMs) play a siginifcant role in inflammation and in the periodic migration of lymphocytes from the circulation into lymphoid organs(homing)
Integrins
- Glycoproteins that are mainly involved in cell extracellular matrix interactions
- bind to both the extracellular matrix and to the cytoskeleton
- Consist of two subunits:
- Each integrin consists of one alpha subunit(17 kinds) and one beta subunit(8 kinds)
- Extracellular domains of integrins bind to molecules in the extracellular matrix such as fibronectin and laminin
- In hemidesmosomes , integrins link the basal domains of cells to the extracellular matrix via the intracellular tonofilaments(intermediate filaments such as keratin)
- intermediate filaments are slightly larger in diamter then actin

What sequence in fibronectin and laminin do integrins interact with?
- Interact with RGD(Arg-Gly-Asp)
Laminin and fibronectin in the basement membrane interact with what?
- collagen
- heparan sulfate proteoglycans
- entactin(nidogen)
How do integrins differ from other cell adhesion proteins

- Consist of two subunits
- Have a dual function
- Bind to the extracellular matrix
- Bind to the internal cytoskeleton
- a subunit of an integrin has two chains linked by a disulfide linkage and a globular head with binding sites for divalent cations
- B subunit has two significant charecteristics
- Extracellular chain contains repeating cysteine-rich regions
- Intracellular portion interacts with actin filaments through three connecting proteins:
- Talin
- Vinculin
- a-actinin
Neutrophil Homing

- 1.Leukocytes(neutrophils) in circulation resist shear forces to slow down along the vascular endothelium
- Loose adhesion to the endothelium under conditions of slow flow causes the leukocytes to roll.
* Selectins present on the endothelial cell surface bind to carbohydrate ligands on the leukocyte surface
- Loose adhesion to the endothelium under conditions of slow flow causes the leukocytes to roll.
- Integrin receeptors for endothelial ICAM-1 and ICAM-1 ligands are rapidly activated on the leukocyte surface druing rolling
* Chemical mediators in the sites of inflammation stimulate the activation of integrins B1 and B2.
* Integrins strengthen leukocyte binding to endothelial cell surfaces
- Integrin receeptors for endothelial ICAM-1 and ICAM-1 ligands are rapidly activated on the leukocyte surface druing rolling
- Transendothelial migration is mediated by integrins interacting with ligands on endothelial cell surfaces. F-actin dynamics participate in this process

Immunoglobulin Superfamily
- Members of this family possess an extracellular segment with one or more folded domains charecterisitc of immunoglobings
- Members of the IG-superfamily
- N-CAM-are neural adhesion molecuels
- they mediate both homophilic and heterophilic interactions
- I-CAM-1 and I-CAM-2:
- I-CAM-1 facilitates transendothelial migration of leukocytes
- N-CAM-are neural adhesion molecuels

Adherens
- These are molecular complexes that anchor cells together and reinforce the physical integrity of tissues and the cells that make up the tissues
- Can be found on the basolateral surface of epithelial cells
- Most reponsible to holding together cells , particular epithelial cells
Occludens
- Molecular compelxes that establish an impermeable barrier between adjacent cells,especially epithelial cells that prevents paracellular transport and maintains concentration differences between the environments on either side of hte epithelial sheets
- prevent paracellular transport, prevent molecules from slipping by the cell surveillance and linking between cells
Gap Junctions
- These are composed of molecular pores that enable cells to rapidly exchagne ions and small molecules that help coordinates activities among the cells that make up the tissue
- Can help spread signal molecuels to cell to cell
Zonula
- This can be either of the adherens or occludens variety
- Zonula complexes travel all the way around the circumference of the cell and link all neighboring cells to the central cell. They are sometiems referred to as belt-like compelxes
- Associated with intracellular actin
Macula
- A spot or snap like junction
- They are of the adherens variety and are often referred to as desmosomes (associated with the lateral domains of epithelia cells) or hemidesmosomes(associated with the basal domain of epithelial cells)
- The are associated with intracellular intermediate filaments(tonofilaments)
*

What type of proteins fill Adherens
- These are anchoring junctions charecterized by intercellular spaces which are filled with cadherin proteins
- Desmogleins
- Desmoglein 1 and 2 are found in the epidermis
- autoantibodies to the desmoglein 1 result in pemphigus foliaceus
- Desmocollins
- Desmogleins
- Cadherin proteins are anchored to cytoplasmic plaques
- Desmoplakin
- Plakoglobin
- If you have autoantibodies producd against desmoglein 1
- Predominateed in the above status spinosum in straited epithelial cells
Adherens junctional compelxes
- Zonula adherenes are associated with actin microfilaments
- Macula adeheres are associated with intermediate filaments(tonofilaments)
- These associations are mediated by interactions with cadherins:
- Desmocollins
- Desmogleins
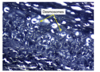
Desmosomes in stratified Squamos Epithelium
Hemidesmosomes
- Hemidesmosomes are anchoring junctions that anchor the basal domain of the epithelial cell to the basla lamina
- A hemidesmosome conssits of:
- Cytoplasmic palte associated with intermediate filaments such as keratin
- A membrane plaque linking the hemidesmosome to the basal lamina via anchroing filaments(laminin 5) and integrins(integrina6B4
- Note that at one time,hemidesmosomes were thought to be half demosomes, with the desmosome associated with the epithelial cell

Zonula Occludens
- Zonula occludens(tight junction) is a belt-like occluding junction
- Occluding junctions provide a barrier against the paracellular transport pathway whereby solutes and fluids are transported from one sdie of an epithelial barrier to the opposite side by passing between the cells
- Claudins and occludins are transmembrane proteins associated with unctional complex and are responsible for the occlusive properites of the tight junction;they attach intracelluarly to zonula occludens proteins ZO-2 and ZO-3
Transmembrane proteins include jucntional adhesion molecules(JAMs) and Nectin related to Zonula Occludens
- Both JAMs and nectin are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily. They are stabilized by disulfide bonds and form cis-homodimers that facilitae cell adhesion
- Nectin is associated with an intracellular molecule, afadin
- JAMs are associated intracellularly with both afadin and with ZO-1
- The zonula occludens proteins and afadin facilitate interaction with the intracellular actin filaments
Focal Adhesions
- Spots tah anchor the cell to the extracellular matrix via integrins
- Differ from desmosomes in that the intracellular attachment is not to tonofilaments such as keratin but to actin filaments via connecting proteins
- Focal adhesions may be very stable interactions invovled in tissue integrity or may turn over rapidly as cells move
- Extracellular portions of the integrins may be folded clsoe to the plasma membrane and unattached to the ECM
- Cytosolic signals may cause the integrin heads to unfold and attach to ECM components such as fibronectin or laminin
- can be ery stable or turn over very rapidly which allow cells to make or break junctions very easily
- can be extended or folded

Gap Junctions
- Gap junction is a communicating junction that allows cell to directly communicate
- Gap junctions are composed of connexons:
- Each connexon consists of 6 connexins ,forming a hexagonal strucutre with a hollow cneter
- Connexons facilitate movement of molecules up to 1.2nm in diameter
- Connexons are often clustured into patches
- Connexons going from cytoplasm to cytoplasmand faciliates flow of information from one cell to the other

When do Gap junctions close?
- Close when calcium ion concentrations are high
- Gap junctions are reponsible for chemical and electrical coupling
- Each connexon consists of 6 connexins, forming a hexagonal strucuture with a hollow center
- Related pathologies include:
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy
- Congenital cataracts

Basal lamina is associated with which type of collagen
Type IV
Which of the following types of cell adhesion molecule is associated with zonula occludens and desmosomes?
Cadherins
Desmocollings and Desmogleins belong to which of the following groups of Cell adhesion molecules(CAM)
Cadherins
Extracellular domains of which of the following bind to molecules in the extracelular matrix such as fibronectin and laminin?
Integrins
Which of the following are molecular complexes that anchor cells togehter and reinforce the physcial integrity of tissues and the cells that make up the tissues?
Zonula adherens
Which of the following are molecular complexes that primarly serve to prevent paracellular transport?
Zonula Occludens


