Catecholamines Flashcards
1
Q
What NT is this?

A
Dopamine
2
Q
What NT is this?
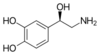
A
Norepinephrine
3
Q
What NT is this?

A
Epinephrine
4
Q
Fill in the blanks
A
5
Q
Reserpine
A
- inhibits VMAT
- depletes DA and NE
- treatment causes
- sedation:animals
- depression:humans
6
Q
Cocaine
A
- inhibits DAT
- leads to synaptic accumulation of DA
7
Q
Amphetamine
A
- Enters cell through DAT
- Releases DA from vessicles
- Reverses flow of DA through DAT
- Increases DA in the synapse
8
Q
Dopamine Receptors
D1 and D2
A
Both are G-protein coupled
D1 signals through Gsalpha to increase cAMP (excitatory)
D2 signals through Gialpha to decrease cAMP (inhibitory)
9
Q
State and describe the dopaminergic pathways
A
- Nigrostriatal System: projects from the substantia nigra and VTMA to striatum
- Tuberoinfundibular System: projects from the medial eminence to the pituitary
- Mesolimbic/Mesocortical system: projects from the VMTA to the limbic system, nucleus accumbens,
10
Q
6-OHDA (6-hydroxydopamine)
A
- neurotoxin
- BBB permeable
- used for sterotaxic surgeries
- Bilateral Lesion: sensory neglect, motivational deficits, motor impairment
- Unilateral lesion: nigrostriatal pathway results in postural assymmetry and turning
11
Q
A


