Case scenarios in dermatological neopathology Flashcards
What are the top 3 skin cancers?
Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma
What are the findings on a BCC biopsy?
Irregular borders between epidermis and dermis (basaloid nests); broken off cancer cells travel into dermis (retraction artefact). The key feature of basal cell carcinoma at low power magnification is of a basaloid epithelial tumour arising from the epidermis. The basaloid epithelium typically forms a palisade with a cleft forming from the adjacent tumour stroma. Centrally the nucleibecome crowded with scattered mitotic figures and necrotic bodies evident. A useful distinguishing feature from other basaloid cutaneous tumours is the presence of a mucinous stroma (figure 4). Some tumours may also show foci of regression, seen as areas of eosinophilic stroma with lack of basaloid nests.
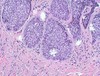
What are the histological subtypes of BCCs?
Nodular, Superficial, Micronodular, infiltrative
What are the findings on a SCC biopsy?
Keratinocytes deep in the dermis (keratin whirls). Typical SCC has nests of squamous epithelial cells arising from the epidermis and extending into the dermis (figure 1). The malignant cells are often large with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and a large, often vesicular, nucleus. Variable keratinisation (keratin pearls etc) is present (figure 2).
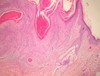
How does a melanoma lesion present?
Irregular edge, irregular colour, asymmetrical, multilobular, wrinkled skin
What are the histological subtypes of melanoma?
Superficial spreading, Nodular, lentigo maligna melanoma, acral lentignous melanoma
Define melanoma
A highly malignant tumour arising from melanocytes. Risk factors include extensive sun exposure, light skin, and a family history of melanoma. Metastasis is common and prognosis correlates with depth at first clinial viewing
Define BCC
A slow growing locally invasive malignant neoplasm of the skin that arises from basal epithelial cells. Most common type of skin cancer. Typically develops in sun exposed areas as a pearly, indurated, nodular, nontender lesion with a rolled border and central ulceration
Define SCC
Occurs as a result of malignant transformation of keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum of the epidermis. Although the classical presentation is a painless, non-healing, bleeding ulcer with everted edges, cSCC may present as plaques, nodules, or even warty lesions
What are the histological findings of melanoma on biopsy?
Histologically, melanomas are asymmetrical and poorly circumscribed lesions with architectural disturbance and usually marked cytological atypia. Specific features include consumption of the epidermis, pagetoid spread of melanocytes, nests of melanocytes with variable size and shape (which may be confluent and lack maturation), melanocytes within lymphovascular spaces, deep and atypical mitoses and increased apoptosis. Ulceration, if present, is a poor prognostic factor. Mitotic figures are common.
Melanoma cells can be categorized in two major types: epithelioid and spindle cells. Epithelioid cells are large and round with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, prominent vesicular nuclei and large nucleoli. They most commonly arise in superficial spreading and nodularmelanomas.

Melanoma

SCC

BCC
What is the Clark level?
I- In situ
II- Papillary dermis
III- Expansion of dermis
IV- Infiltration of reticular dermis
V- Anything in subcutaneous tissue


