Cardiovascular System Flashcards
Cardiac cycle
- Mechanical and electrical events that happen in 1 heart beat
- Diastole: relaxation - fill with blood and twice as long as systole
- Systole: contraction
Heart rate regulation
Intrinsic:
- Spontaneous rhythmicity: Special heart cells generate and spread electrical signals
- SA node: pacemaker of heart
- AV node: delay to fill ventricles
- AV bundle: continues the stimulus
- Purkinje fibers: spread impulse rapidly through ventricles
- Intrinsic HR - 100 bpm
Extrinsic:
- Autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic ) and hormonal control
- Parasympathetic system controls heart rate at rest
HR values
Rest: 60 to 100 bpm Exercise: Max 200 bpm Maximal heart rate: the max heart rate the heart can beat at. Impacted by age. 220-age= MAX HR

Loose electrode
- Characterized by scribbles without distinguishable waves

Atrial fibrillation
- Characterized by fluttering of P wave
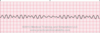
Ventricular fibrillation
- Characterized by small waves, no QRS

Sinus/Normal rhythm

Myocardial infarction
- Characterized by unfinished QRS

Cardiac arrest/death
- Characterized by no waves
Arrhythmias
Extrasystoles: extra beats
Premature atrial contraction (PAC): parts of the atria become prematurely electrically active and depolarization spontaneously prior to S-A node excitation
Premature ventricular contraction (PVC): premature excitation of ventricles. Ventricular fibrillation
Fick’s Equation
VO2 = Q (AO2-VO2)
AO2 = arterial oxygen
VO2 = venous O2
Importance: blood flow to an organ can be calculated and be diverted to active muscles
Blood Pressure Responses
- Resting cardiac output: 5L/min
- Steady-state exercise: increases systolic pressure in first few mins and then levels off
- Resistance exercise: increases blood pressure dramatically
- Rest: 120/80 mmHg
- Endurance: 175/80 mmHg
- Bicep curl: 240/160 mmHg
- Leg press: 280/180 mmHg
Stroke Volume
- Volume of blood pumped in one heartbeat
- Equation : EDV - ESV = SV
- Exercise increases stroke volume
- Training adaptation increases blood volume and reduces resistance to blood flow in peripheral tissues.
- Rest: 50-70 ml/beat
- Exercise: 110-130 ml/beat
- Elite athletes have higher amounts so that their heart can beat less often
Frank Starling Mechanism
- SV increases in response to increased volume of blood in the heart
- Increased volume of blood stretches ventricular walls causing a more forceful contraction
Cardiac Output
- Volume of blood pumped per minute
- total blood volume circulated about once every minute
- Equation: Q= HR x SV
- in L/min
- Resting - 4.2 - 5.6 L/min
- Increases with exercise
- Increases through endurance training due to increase in SV
- HR and SV are the factors that impact cardiac output

